With Agent delegation methods, implemented in matlab
Rapidly exploring Random Trees are algorithms used to explore spaces and find paths. Formalized by LaValle [1] in '98, they are very common in path planning for robotics.
Core RRT properties and methods are implemented directly inside the RRT class. The method to select which vertex to grow and the method to choose in which direction to grow it live here, and are key to generate different RRT flavors, like RRT-path [2].
The mobile robot is modeled by a class, and it provides the inverse kinematic method, the control shuffle method and the usual state manipulation methodds (state update, random state generation, etc.). This allows to abstract the algorithm from the robot model, and treat a whole formation of robots as a single agent.
The world is modeled as a class, and it provides obstacle map loading, C_free checking and starting points and goal management.
Graph methods are provided by the digraph class.
As an example a UAV class is implemented and used as an agent. But smooth trajectories were imposed in the inverse kinematic model, imposing a saturation in the turning angle. Control shuffle was done using only 3-angle steering.
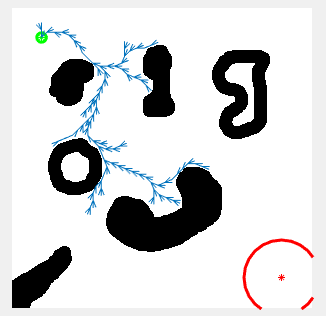
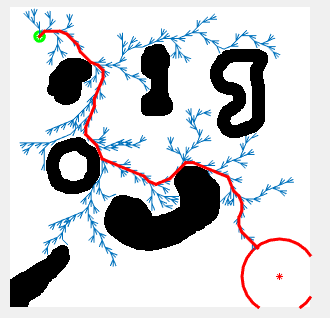
Path
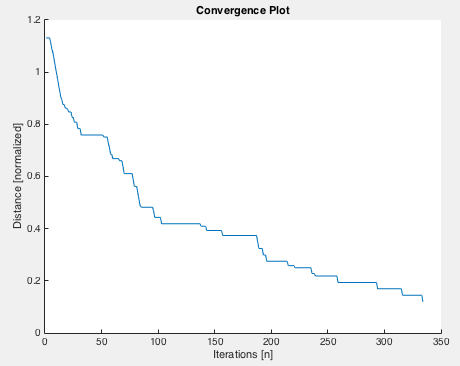
Convergence
I attended the course "Path planning for mobile robots in inspection, surveillance, and exploration missions" by M. Saska at ECI2015 [3] and wanted to see the method working.
[1]. S. M. LaValle, “Rapidly-Exploring Random Trees A New Tool for Path Planning,” 1998.
[2]. V. Vonasek, J. Faigl, T. Krajník, and L. Přeučil, “RRT-path – A Guided Rapidly Exploring Random Tree,” in Robot Motion and Control 2009, vol. 396, no. 28, London: Springer London, 2009, pp. 307–316.
[3]. "Path planning for mobile robots in inspection, surveillance, and exploration missions", Prof. Martin Saska. Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Czech Technical University, Czech Republic, http://www.dc.uba.ar/events/eci/2015/cursos/saska