- Quick Start
- Optional Service Account Setup
- Setting Up Hardware
- Installing Neon
- Using Neon
- Making Changes
- Removing and re-installing Neon
Neon AI is an open source voice assistant. Follow these instructions to start using Neon on your computer. If you are using a Raspberry Pi, you may use the prebuilt image available on our website.
The fastest method for getting started with Neon is to run the modules in Docker containers.
The docker directory contains everything you need to run Neon Core with default skills.
You will need docker and docker-compose available. Docker provides updated guides for installing
docker and docker-compose.
Neon Core is only tested on Ubuntu, but should be compatible with any linux distribution that uses
PulseAudio.
Note: By default, only the
rootuser has permissions to interact with Docker under Ubuntu. To allow the current user to modify Docker containers, you can add them to thedockergroup with:
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER && newgrp
You can clone the repository, or just copy the docker directory contents onto your local system; this document will
assume that the repository is cloned to: ~/NeonCore.
Note: The
dockerdirectory includes required hidden files. If you copy files, make sure to include any hidden files. In must Ubuntu distros, you can toggle hidden file visibility in the file explorer withCTRL+h.
Note: If you run
dockercommands withsudo, make sure to use the-Eflag to preserve runtime envvars.
Note: Some Docker implementations don't handle relative paths. If you encounter errors, try updating the paths in
.envto absolute paths. Also note that any environment variables will override the default values in.env. In BASH shells, you can list all current envvars withenv
You can start all core modules with:
# cd into the directory containing docker-compose.yml
cd ~/NeonCore/docker
docker-compose up -dStop all modules with:
# cd into the directory containing docker-compose.yml
cd ~/NeonCore/docker
docker-compose downThe Mycroft GUI is an optional component that can be run on Linux host systems. The GUI is available with instructions on GitHub
With the containers running, you can interact with Neon by voice (i.e. "hey Neon, what time is it?"), or using one of our CLI utilities, like mana or the neon_cli_client. You can view module logs via docker with:
docker logs -f neon-skills # skills module
docker logs -f neon-speech # voice module (STT and WW)
docker logs -f neon-audio # audio module (TTS)
docker logs -f neon-gui # gui module (Optional)
docker logs -f neon-messagebus # messagebus module (includes signal manager)By default, the skills container includes a set of default skills to provide base functionality.
You can pass a local skill directory into the skills container to develop skills and have them
reloaded in real-time for testing. Just set the environment variable NEON_SKILLS_DIR before starting
the skills module. Dependency installation is handled on container start automatically.
export NEON_SKILLS_DIR=~/PycharmProjects/SKILLS
cd ~/NeonCore/docker
docker-compose upTo run the skills module without any bundled skills, the image referenced in docker-compose.yml can be changed from:
neon-skills:
container_name: neon-skills
image: ghcr.io/neongeckocom/neon_skills-default_skills:devto:
neon-skills:
container_name: neon-skills
image: ghcr.io/neongeckocom/neon_skills:devThe xdg/config directory is mounted to each of the Neon containers as XDG_CONFIG_HOME.
xdg/config/neon/neon.yaml can be modified to change core configuration values.
xdg/config/neon/skills contains settings files for each loaded skill
The xdg/data directory is mounted to each of the Neon containers as XDG_DATA_HOME.
xdg/data/neon/filesystem contains skill filesystem files.
xdg/data/neon/resources contains user skill resource files.
The xdg/cache directory is mounted to each of the Neon containers as XDG_CACHE_HOME.
Any cache information should be recreated as needed if manually removed and includes things like
STT/TTS model files, TTS audio files, and other downloaded files.
Note: When Docker creates files on the host filesystem, they are owned by
root. In order to modify anything in thexdgdirectory, you may need to take ownership with:sudo chown -R $USER:$USER xdg
There are several online services that may be used with Neon. Speech-to-Text (STT) and Text-to-Speech (TTS) may be run locally, but remote implementations are often faster and more accurate. Following are some instructions for getting access to Google STT and Amazon Polly TTS. During setup, these credentials will be imported and validated.
Note: If you complete this setup on a Windows PC, make sure to edit any files using a text editor such as Notepad++ to ensure compatibility in Linux. Also check for correct file extensions after copying your files to your Linux PC, as Windows will hide known file extensions by default.
-
Go to:
-
Sign in or create a
Google account -
Go to your
Console -
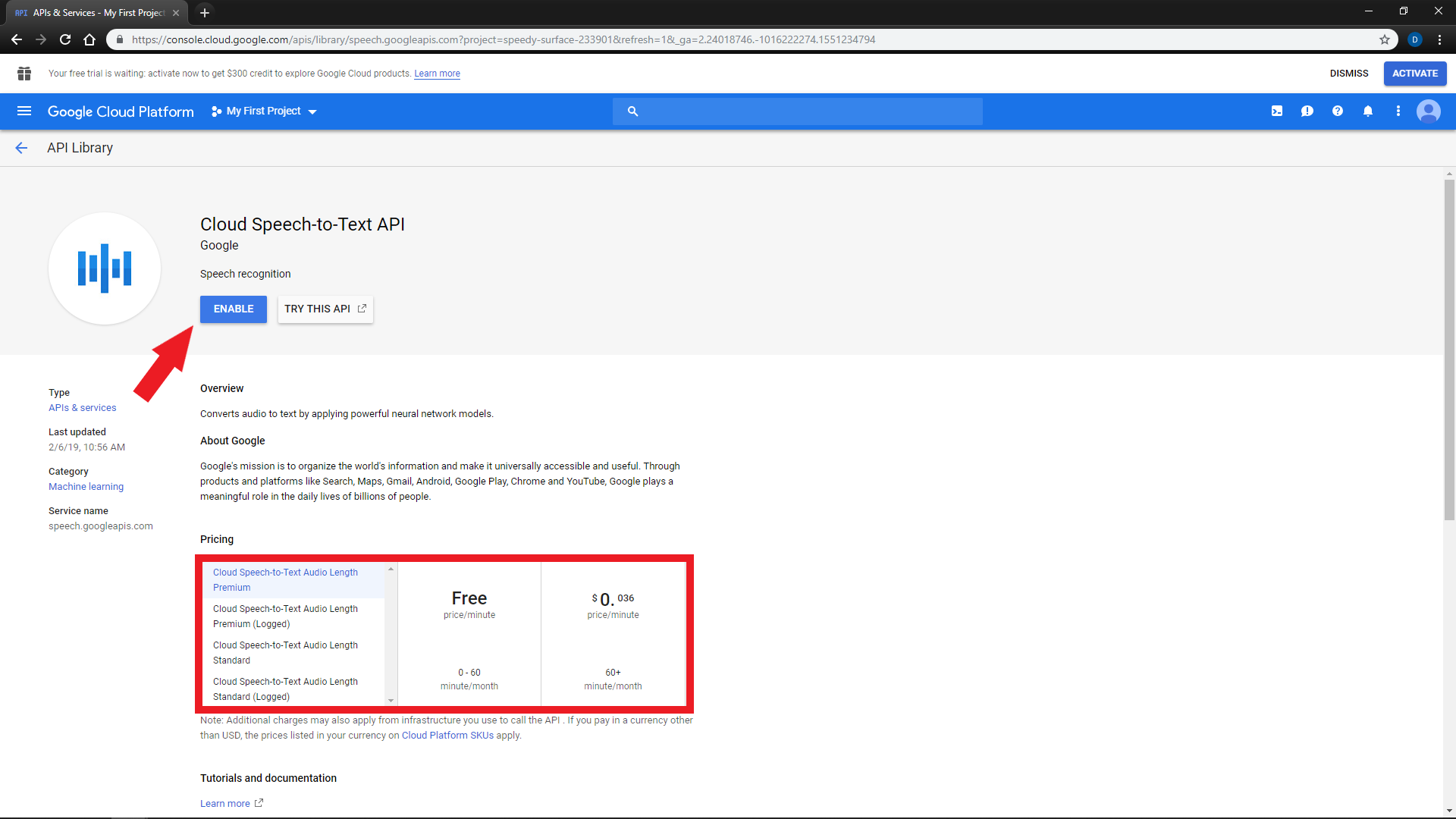
Search for and select
"Cloud Speech-to-Text"(Not to be confused with Text-to-Speech) -
Select the option you would like to use
-
You will be prompted to enable billing on your account at this point because this service is paid after a free monthly quota
Google will not automatically charge your card unless you give permission to do so.
-
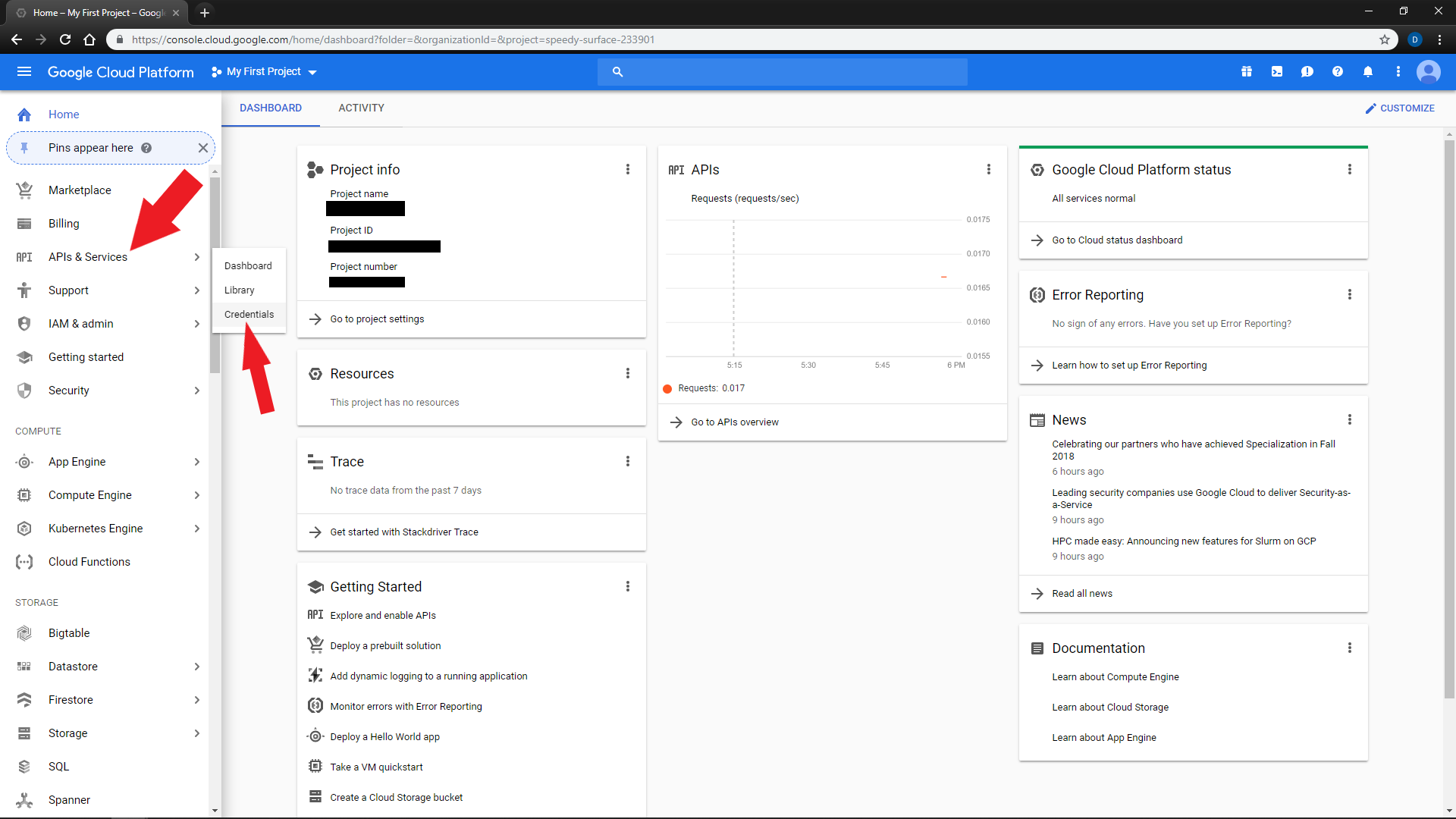
In the left
Navigation Menu, selectAPIs & Services,Credentials -
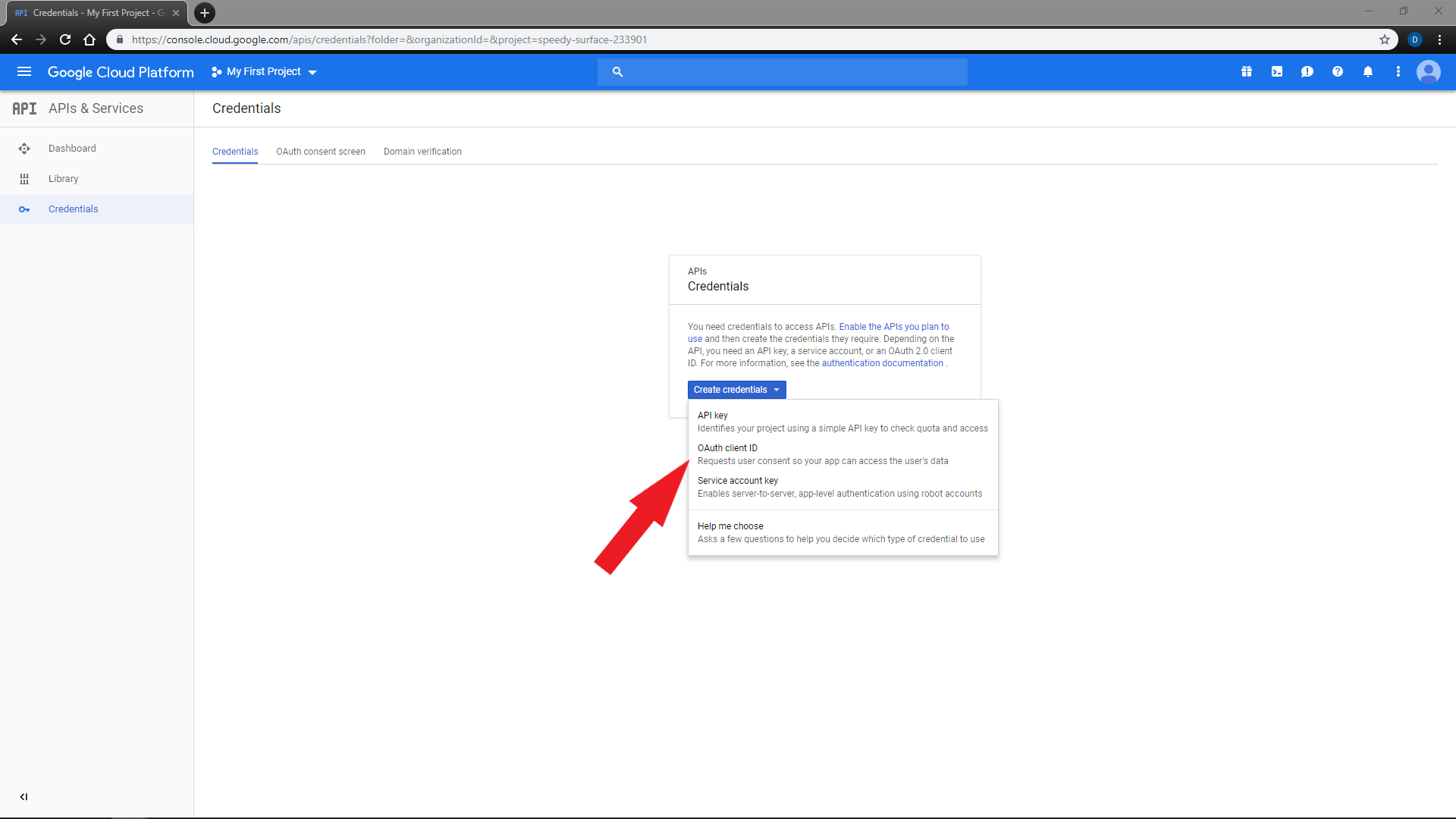
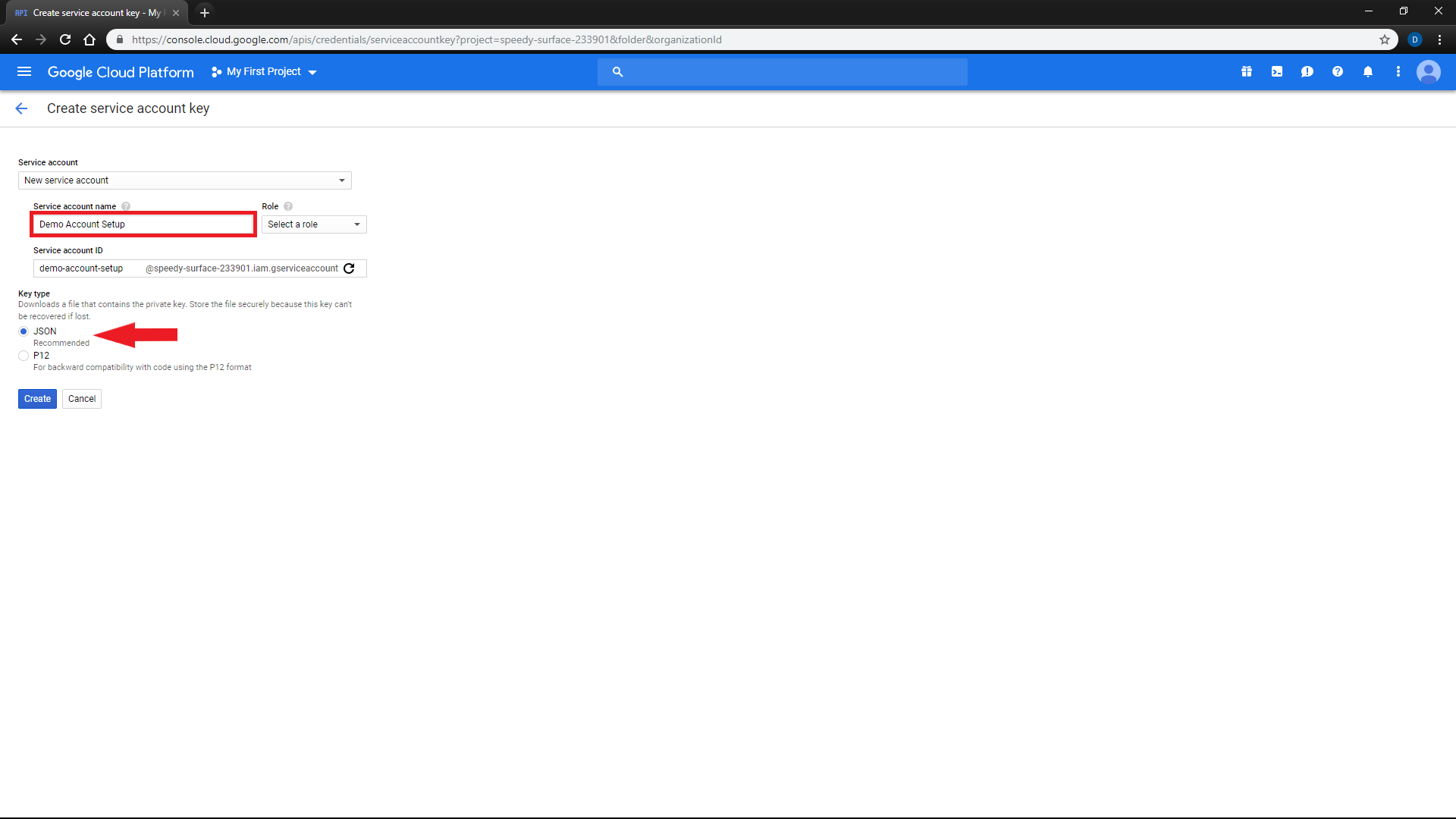
Click
Create credendials,Service Account Key -
Choose any service account name for your reference. You may leave the
Rolefield empty -
Make sure key type is
JSONand click onContinue -
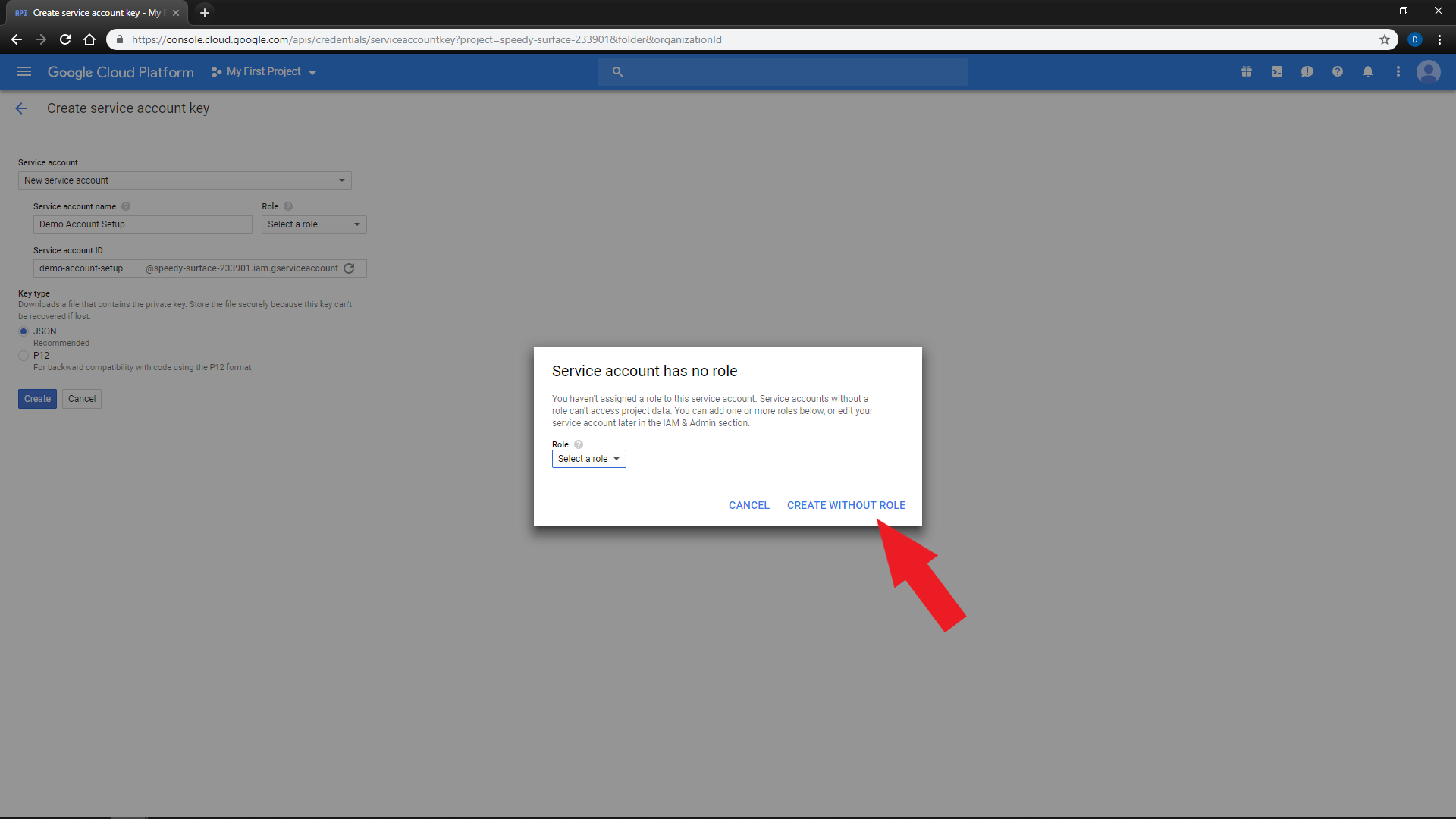
If you did not assign a role, you would be prompted. You may continue by clicking
'CREATE WITHOUT ROLE' -
You will see a prompt and your service key will automatically download
-
Rename the downloaded file to
google.jsonand move it into the same directory as neonSetup.shNote: The premium models are only available in US English and provide some enhancements to phone and video audio which do not apply to this project. The options with Data Logging allows Google to use your audio and transcriptions to train their model. You may select the option without logging to opt out (note that the option with logging is discounted).
At this point, Neon can be partially tested without Amazon translations and Wolfram information skills. You may run
setup without continuing, but Amazon and Wolfram|Alpha services are highly recommended.
-
Go to:
-
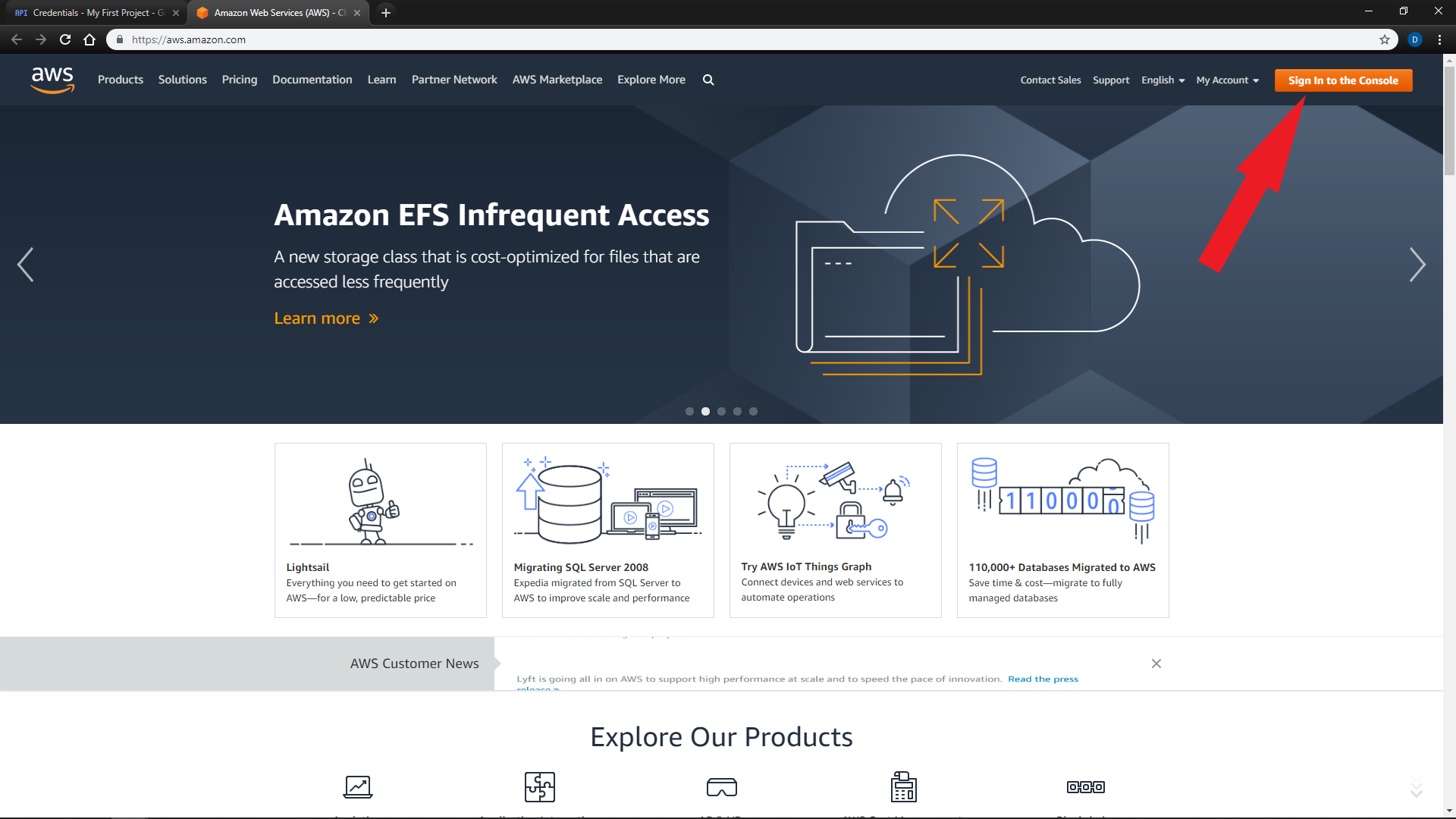
Click
"Sign into the Console"at the top right of the screen -
Sign in or register for an account
-
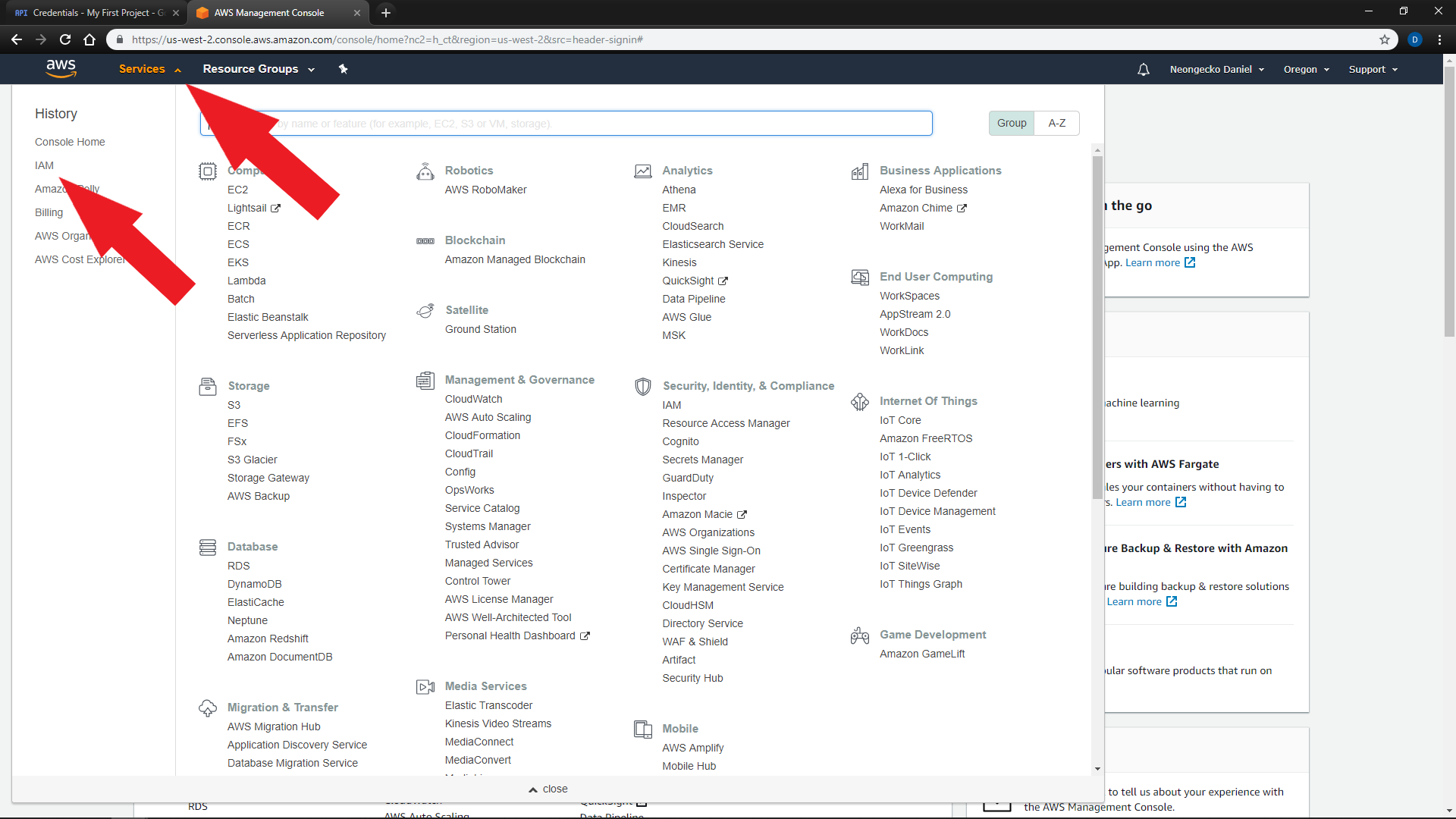
Go to the
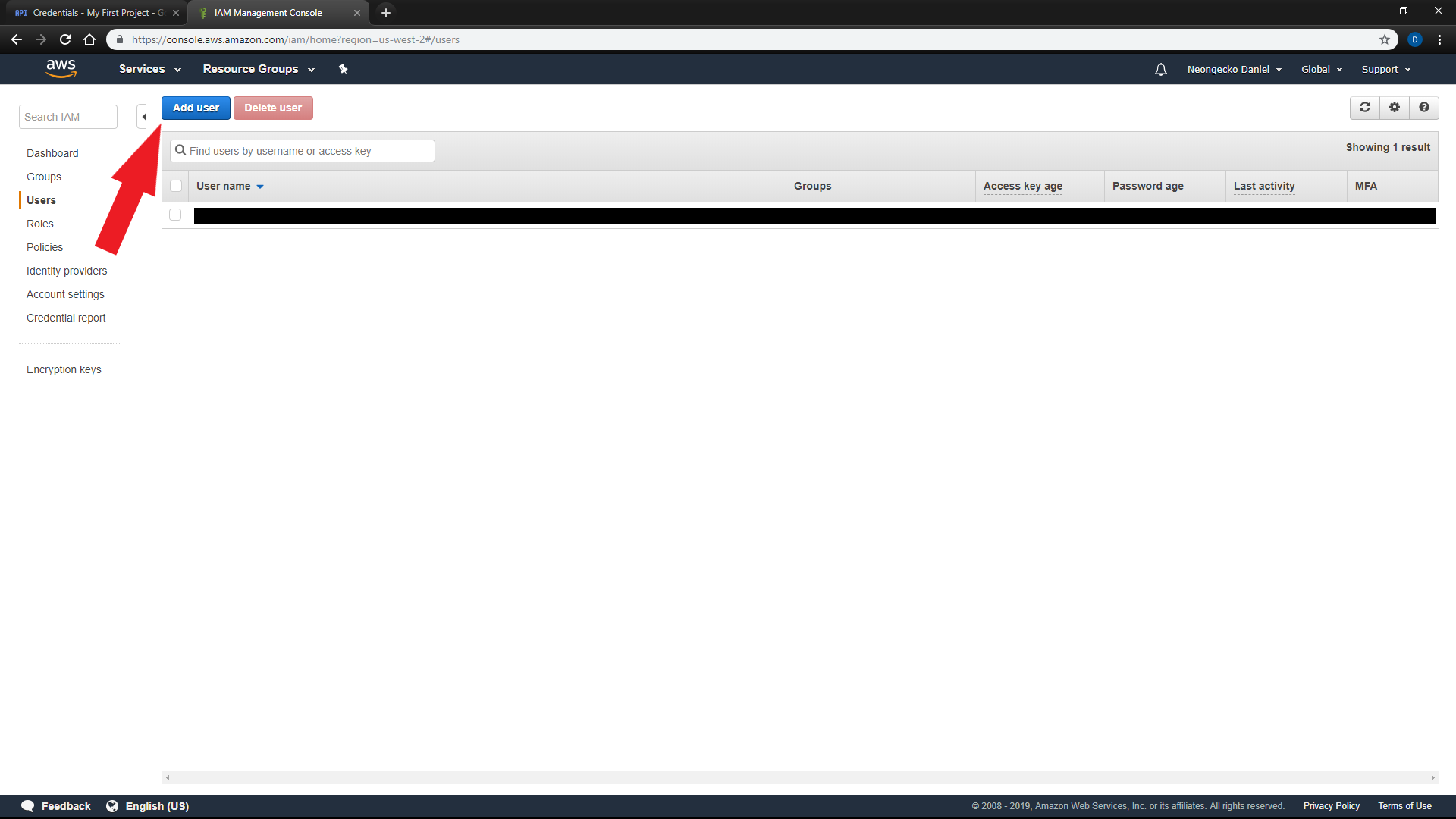
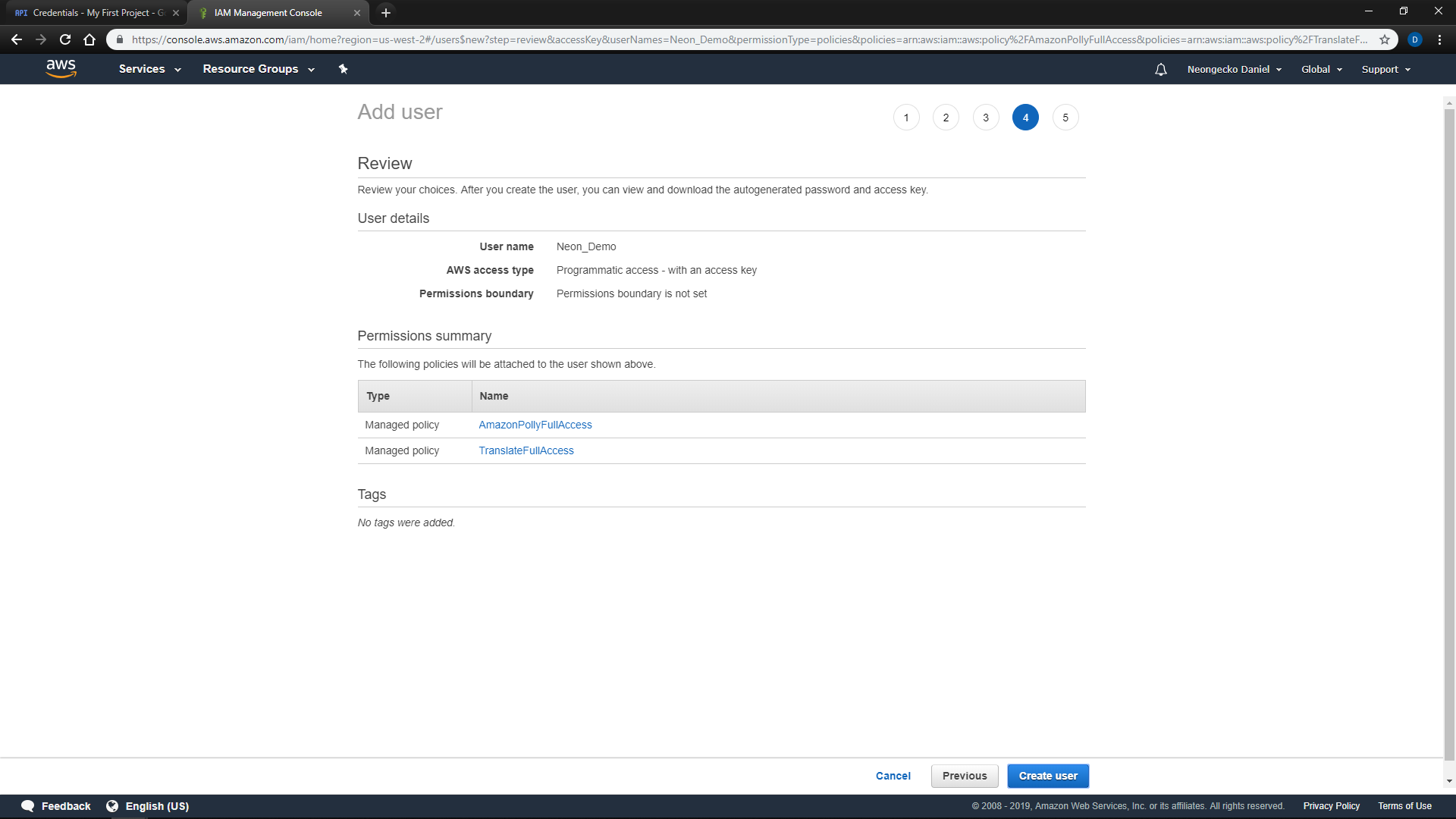
Services Menuat the top left of the screen and clickIAM -
Select
Usersfrom the left side menu and clickAdd user -
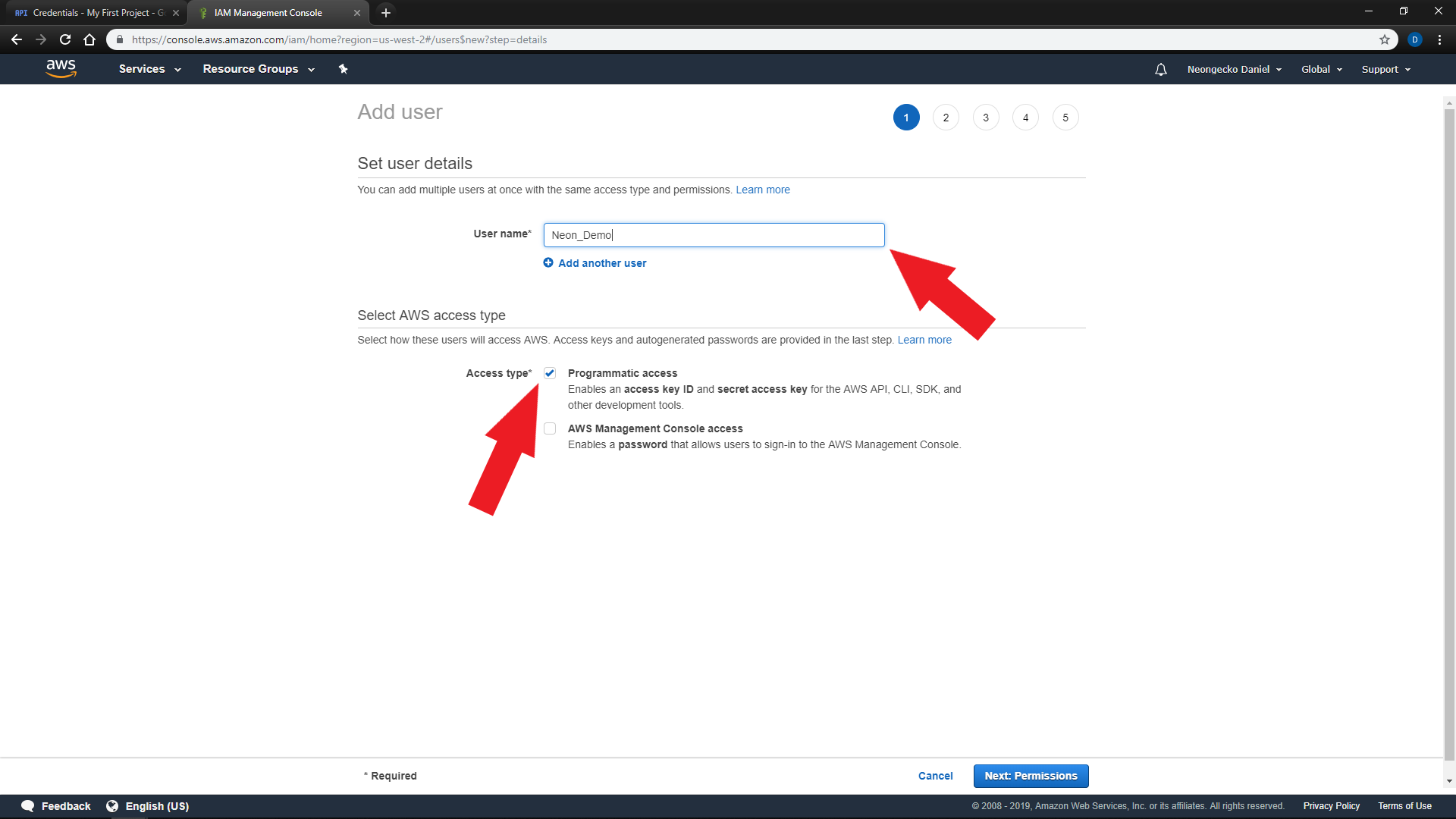
Enter a
User nameand check the box forProgrammatic access -
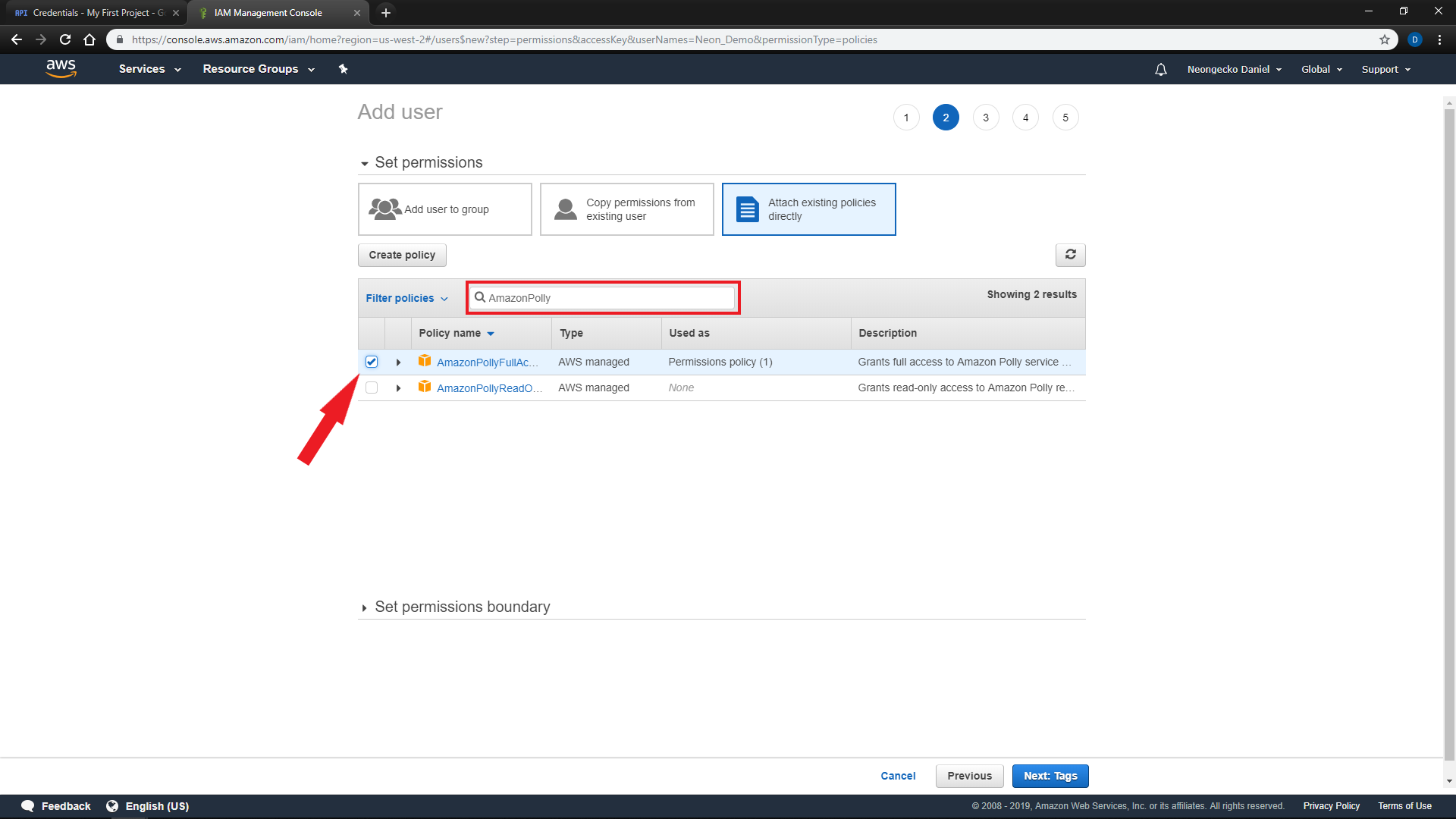
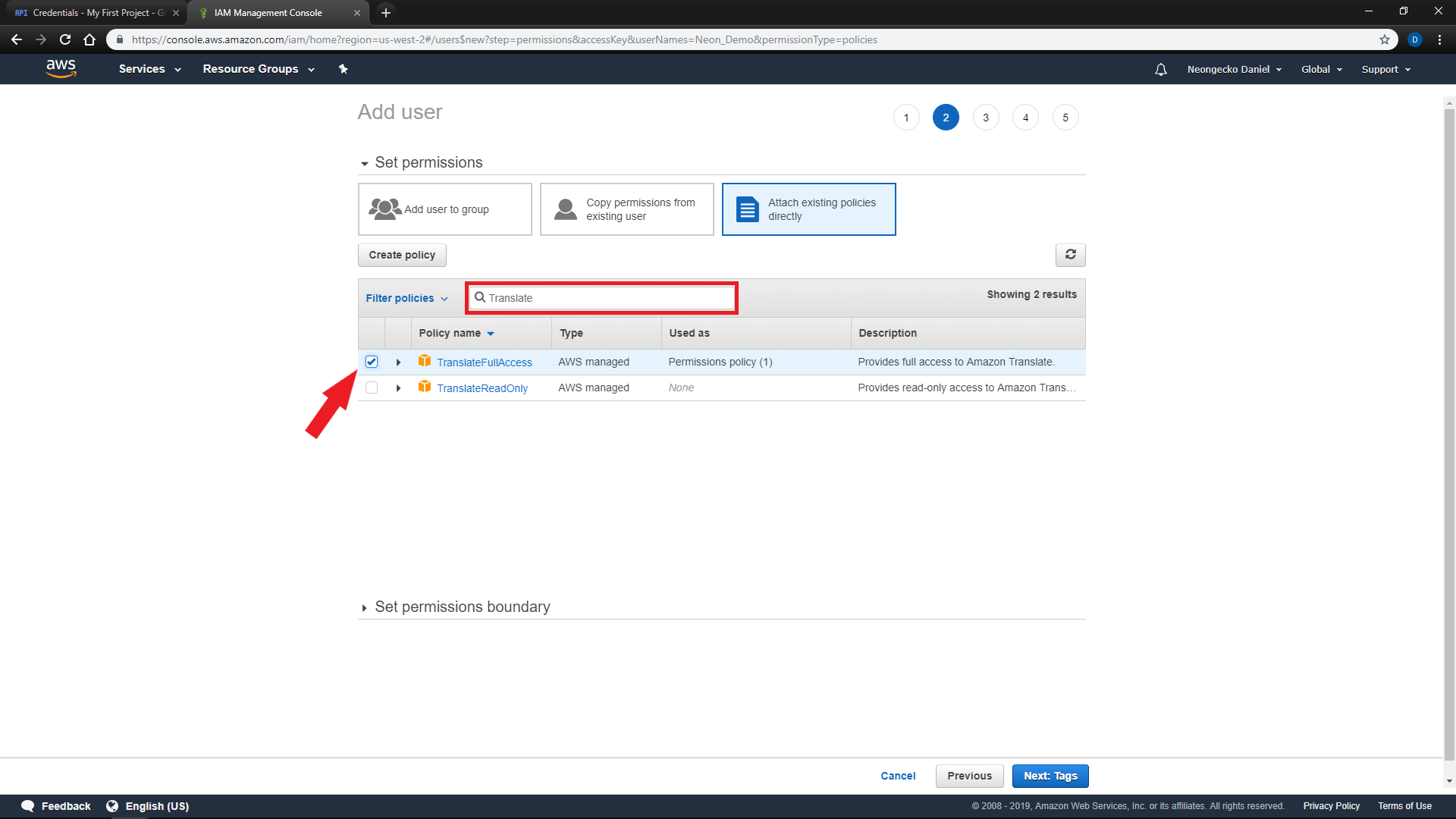
On the next page, Select
'Attach existing policies directly'and search for'AmazonPollyFullAccess'and'TranslateFullAccess' -
You may add tags on the next page if desired
-
Review your selections on the next page and
Create user -
On the next page you can see your
Access key IDandSecret access key -
Click the
Download .csv filebutton to save your credentials to your computer -
Copy or move the downloaded
accessKeys.csvto the same directory as neonSetup.shNote: You will not be able to view your secret access key after it is generated, so if you need a secret access key, you will have to generate a new Access key.
The Users menu lets you create new users and new access keys per user as you wish, as well as modify permissions.
Before continuing, make sure you have your hardware setup ready for installation. You will need the following:
-
A computer running up-to-date Ubuntu 20.04
You can find our video tutorial for installing Ubuntu in a virtual machine here, or you can find written instructions here
Note: If you prefer to use Windows for your development environment, you can install the Windows Subsystem for Linux. You can find our video tutorial here. Audio and gui functionality will be limited in this case; you will only be able to interact with Neon via command line.
-
Speakers and a microphone recognized by Ubuntu
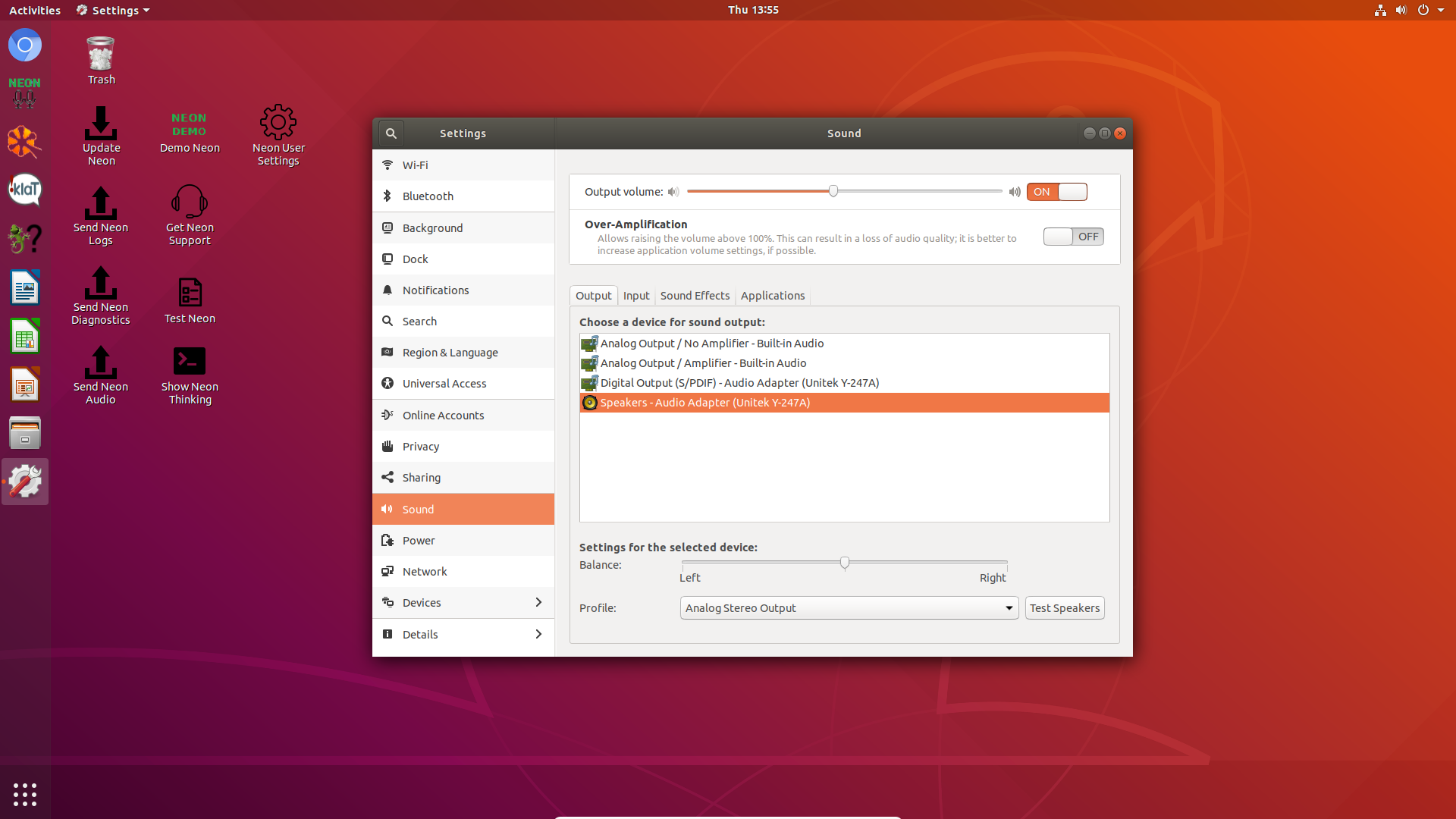
You can verify Ubuntu sees your devices by accessing
Settingsand thenSound- If you are unsure of which device to select, you can click
Test Speakersto play a test tone through the selected Output device - You can test your microphone under the
Inputtab, the Input level should move when you speak into the microphoneIf you do not see any microphone activity, make sure the correct device is selected and the Input volume is set above 50%
- If you are unsure of which device to select, you can click
-
Webcam (optional)
Some functionality requires a webcam (ex. USB Cam Skill). Most webcams also include a microphone that can be used for Neon.
-
An active internet connection
Note: A connection of at least 10Mbps is recommended. On slower connections, installation may take several hours.
-
At least
10GBof available disk space (15 GBif installing Mimic)Neon AI occupies less than 1GB itself. With dependencies, the installation takes about 5GB on an up-to-date Ubuntu 20.04 system. Mimic local speech-to-text requires about 3.5 GB. Additional space is used while installing packages during installation and updates. Several gigabytes is recommended in order to keep local transcriptions and audio files.
-
A system with at least 2GB RAM and 2 or more processing threads is required, with 4GB RAM and 4 threads recommended
Some features such as the vision service may not work on systems only meeting the minimum requirements. Responses and speech processing will take longer on lower performance systems.
This guide includes instructions for installing in both a Development environment and a User environment. User
environment is similar to what is found on our Raspberry Pi Image; packages will be
installed from distributions and installed code should not be modified.
A developer environment will clone NeonCore from source and include more debugging utilities.
Developer installations are also designed to run alongside other instances of Neon/OVOS/Mycroft.
A development environment is designed to be a testable installation of NeonAI that can be connected to an IDE
(ex. Pycharm) for modifications and skill development. This guide assumes installation in a development environment from
an unmodified fork of NeonAI. After installation, any changes and additions can be pushed to git or hosted on a private
server.
A user environment is designed to be an installation on a device that will be used normally as a voice assistant. You
may want to test how your changes affect performance on less powerful hardware or test how changes may be deployed as
updates.
If you are developing in a virtual machine, installation on physical hardware in a user environment is useful for
testing audio and video I/O which can be difficult in many virtualized environments.
All the following options, such as autorun and automatic updates can be easily modified later using your voice, profile settings, or configuration files.
Neon "core" is a collection of modules that may be installed and modified individually. These instructions will
outline a basic setup where the neon_audio, neon_enclosure, neon_speech, and any other modules are installed to their
latest stable versions. These modules may be installed as editable for further development; instructions for this can be
found here
- Install required system packages
sudo apt install python3-dev python3-venv python3-pip swig libssl-dev libfann-dev portaudio19-dev git mpg123 ffmpegNote: The following commands can be used to install mimic for local TTS
sudo apt install -y curl
curl https://forslund.github.io/mycroft-desktop-repo/mycroft-desktop.gpg.key | sudo apt-key add - 2> /dev/null && echo "deb http://forslund.github.io/mycroft-desktop-repo bionic main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mycroft-desktop.list
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt install mimic- Clone NeonCore from your forked repository into a local directory.
git clone https://github.com/NeonGeckoCom/NeonCore ~/NeonAI
cd ~/NeonAI- Create a virtual environment and activate it.
python3 -m venv ./.venv
. .venv/bin/activate
pip install wheel # this speeds up subsequent - If you have access to private Neon repositories, export your Github Personal Access Token as an environment variable
export GITHUB_TOKEN=<insert_token_here>- Install any desired requirements
pip install .[client,dev,remote]Note:
dev,client, andremoteare recommended for general development installations.localmay be substituted forremote
- Install the mycroft-gui package (optional)
git clone https://github.com/mycroftai/mycroft-gui
bash mycroft-gui/dev_setup.sh
rm -rf mycroft-gui
sudo apt-get install libqt5multimedia5-plugins qml-module-qtmultimediaNote: dev_setup.sh is an interactive script; do not copy/paste the full block above into your terminal.
- Create and update configuration
neon-config-importOpen ngi_local_conf.yml in your text editor of choice and make any desired changes.
If you selected local options above, you should change the following STT/TTS module lines:
tts:
module: neon_tts_mimic
stt:
module: deepspeech_stream_localYou may also choose to place logs, skills, configuration files, diagnostic files, etc. in the same directory as your cloned core
(default location is ~/.local/share/neon). This isolates logs and skills if you have multiple cores installed.
dirVars:
logsDir: ~/NeonCore/logs
diagsDir: ~/NeonCore/Diagnostics
skillsDir: ~/NeonCore/skills
confDir: ~/NeonCore/configNote: You may also have a configuration file you wish to copy here to overwrite the default one.
- Install default skills (optional)
neon-install-default-skillsInstallation of default skills will usually occur every time neon is started, but you may want to do this manually and
disable automatic skill installation to avoid conflicts with local development. The list of default skills may be changed
in ngi_local_conf.yml
skills:
default_skills: <url to list of skills or list of skill URL's>Note: The default_skills list may include URLs with branch specs, skill names, or a link to a text file containing either of these lists.
- Neon is now ready to run. You may start Neon with
neon-startfrom a terminal; to start Neon in the background, run:
coproc neon-start >/dev/null 2>&1 &Note: Starting Neon can take some time when skills are set to automatically install/update. You can speed this up by disabling automatic skill installation/updates in
ngi_local_conf.yml.
skills:
auto_update: falseInstalling in a User Environment differs from a developer environment; you will not be able to modify Neon Core if you use this installation method.
-
Download
setup.shfrom the NeonCore repository.Note: You can download this file by right-clicking
Rawand selectingSave link as... -
Take your
setup.shfile and place it in your home directory -
Open a terminal in your home directory (
ctrl+alt+t) -
Type in
bash setup.sh ${GITHUB_TOKEN}and pressEnter(where${GITHUB_TOKEN}is your Github token)Note: You can find instructions on how to generate a GitHub Personal Access Token here
-
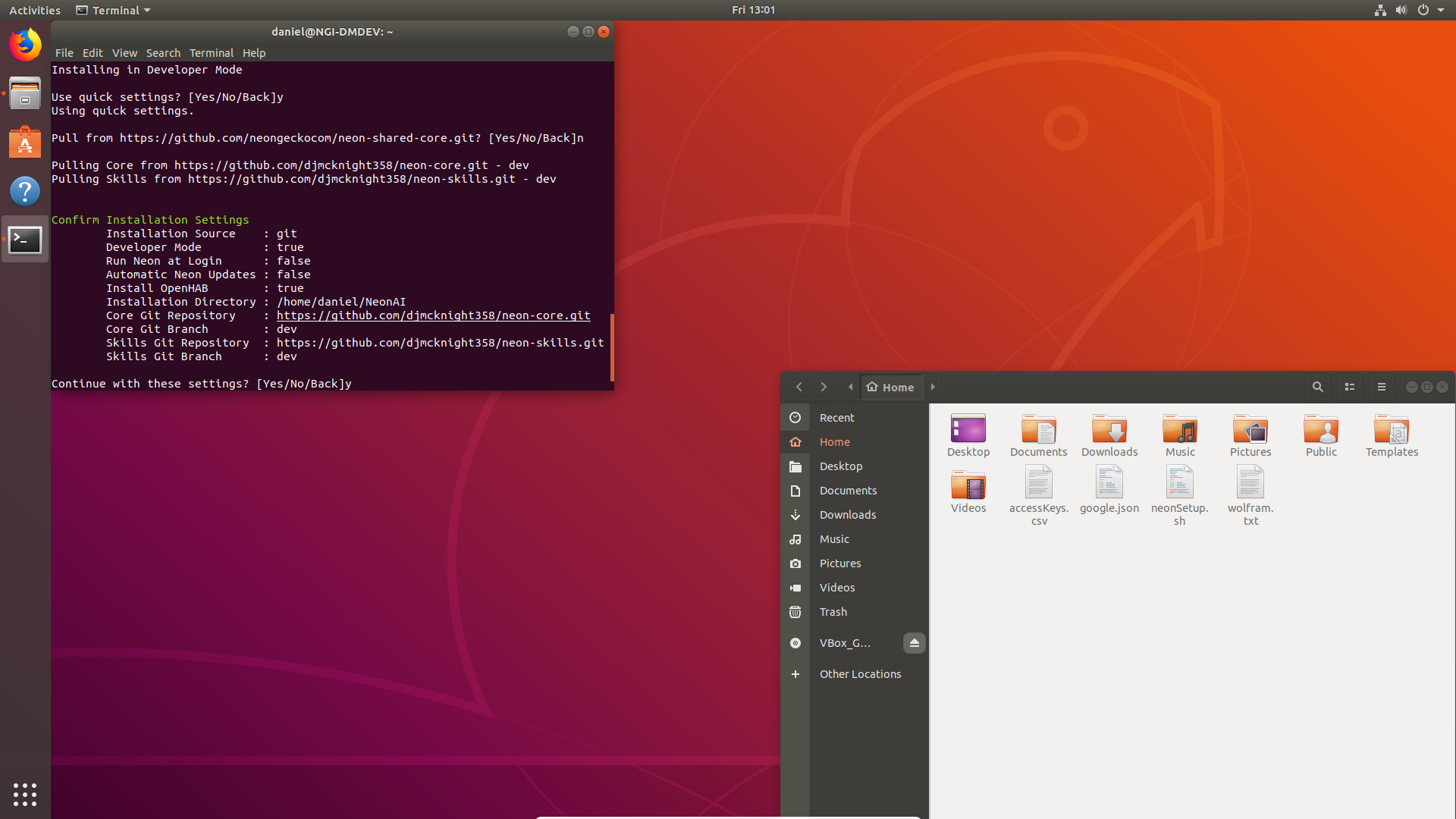
Type
nto Install in User Mode (Not Developer Mode) -
Type
nto Input Custom settingsNote: You may use quick settings and skip the following prompts
-
Type
nto install in User mode (yfor full Developer mode) -
Autorunis recommended (y) on for User Environments -
Automatic updatesare recommended (y) on for User Environments -
Local STTis NOT recommended (n) IF you have google and aws keys, as remote processing is faster and more accurate -
Install GUIis recommended (y) so long as your device has a display -
Find out more about OpenHAB here
-
Serveris NOT recommended (n) unless you know otherwise -
You will be prompted to confirm your settings, press
yto continue,nto start over, orbto go back and correct a previous setting -
When setup is complete, you will be able to start Neon via
start_neon.shand stop Neon via:stop_neon.sh
After you have completed Installing Neon, you will have a fully functional system ready to test.
If you followed the Developer instructions and attached Neon to an IDE
(such as PyCharm), your IDE likely configured a virtual environment in NeonCore/venv.
If you followed the User instructions, a virtual environment was
created at ~/NeonAI/.venv.
To interact with Neon from a terminal, you need to activate the correct virtual environment by running:
. ~/NeonAI/.venv/bin/activate (or the appropriate path if you installed to a different directory).
Note: If you are using an IDE like PyCharm, the built-in terminal will often activate the virtual environment automatically.
You will know that your virtual environment is active by the (.venv) printed in your terminal. You may exit the .venv
shell by running deactivate.
From your shell with the virtual environment activated, you can see a list of available terminal commands by typing neon
and tapping TAB twice. Depending on which packages were installed with Neon, you might see neon_cli_client which
will launch the CLI for debugging.
From your shell with the virtual environment activated, neon_skills_tests will launch automated testing. You will be
prompted to select a test set to run (no entry will run all). Neon will proceed to execute and respond to a number of
requests, corresponding to all default installed skills. After all tests have run, a summary will be printed to the terminal
followed by any logged errors.
Note: More complete logs and information can be found in the Diagnostics directory >By default, this is at
~\NeonAI\Diagnostics\testingfor Development Machines and~\Documents\NeonGecko\Diagnostics\testingfor User Machines.
If you encounter any of the following issues while using Neon, please try these troubleshooting steps
-
My computer is slow to respond
Check for high memory usage in
System Monitor. If your Memory and Swap both show 100% utilization underResources, try exiting PyCharm and Neon AI. If there is still abnormal memory usage, open a Terminal and type in:sudo systemctl stop openhab2.service
If you can determine the offending program, see if restarting the program or your computer resolves your issues. If not, you may find common solutions online.
-
Neon AI is not transcribing anything I say
Check that your microphone is working and active by going to
SoundtheSettingsMenu. Go to theInputtab and make sure the correct microphone is selected. Make sure theInput Levelis up and turned on and look for activity on theInput Levelbar when you tap the mic. If you change devices here, restart Neon AI. -
Some audio is very quiet, while other audio is louder
Check that the audio level for the affected application is turned up by going to
SoundtheSettingsMenu. Go to theApplicationstab.For quiet responses from Neon, ask Neon something with a longer response (ex. "Tell me a joke"). When an application named
neon-voiceappears, make sure it is not muted and that the volume is set to the maximum. Do the same for any other applications that are too quiet; start playing something and check the Application's volume. -
AVMusic will not pause or resume
If AVMusic playback is changed by something other than Neon, the skill can lose track of whether something is playing or paused. If something is paused and Neon will not resume, you may say "pause" to resume playback. "Stop" should work in any case.
-
Errors in the log when installing or updating Neon
Installation of dlib can fail if system memory is completely full; you can open System Monitor during installation or updates to monitor memory usage. A minimum 2GB RAM is required, 4GB+ recommended. Errors may also occur if system storage becomes full. You may monitor storage availability in System Monitor as well; keep in mind that cached files will be removed when installation fails, so your file system will show some available space before and after the error occurs.
-
Any other issues
If you encounter any other issues while using Neon, they can often be solved by restarting Neon or your computer. If this does not resolve you issue, please contact support at [email protected].
After completing setup and testing, you are ready to begin making changes and creating skills. An example workflow for making a change would be:
- Create or modify a skill
- Test changes in the Developer Environment (Look for errors in logs, unexpected behaviour, etc.)
- Run
Test Neonto check that all skills and TTS/STT behave as expected - Commit and Push changes to git (for collaborative development, it is often best to create a new branch for any changes)
- Install your updated skill in a User Environment (check for any missing dependencies, invalid file paths, etc.)
- Run complete tests using
Test Neon - Check logs for any errors
There are two aspects of the Neon AI system: core and skills.
The core is composed of several modules, but generally includes:
speechfor handling user inputs and performing speech-to-text (STT)skillsfor processing user input to find intent and provide a responseaudiofor speaking the response generated in skillsbusfor handling all communications between modulesenclosurefor handling any hardware interactions like speakers, microphone, lights, and buttons
Other modules may also be running for gui functionality, etc and may be added to provide new functionality.
skills provide the functionality of handling user inputs and generating responses or performing actions.
Check out our three part youtube series on how to create a skill: https://youtu.be/fxg25MaxIcE https://youtu.be/DVSroqv6E6k https://youtu.be/R_3Q-P3pk8o
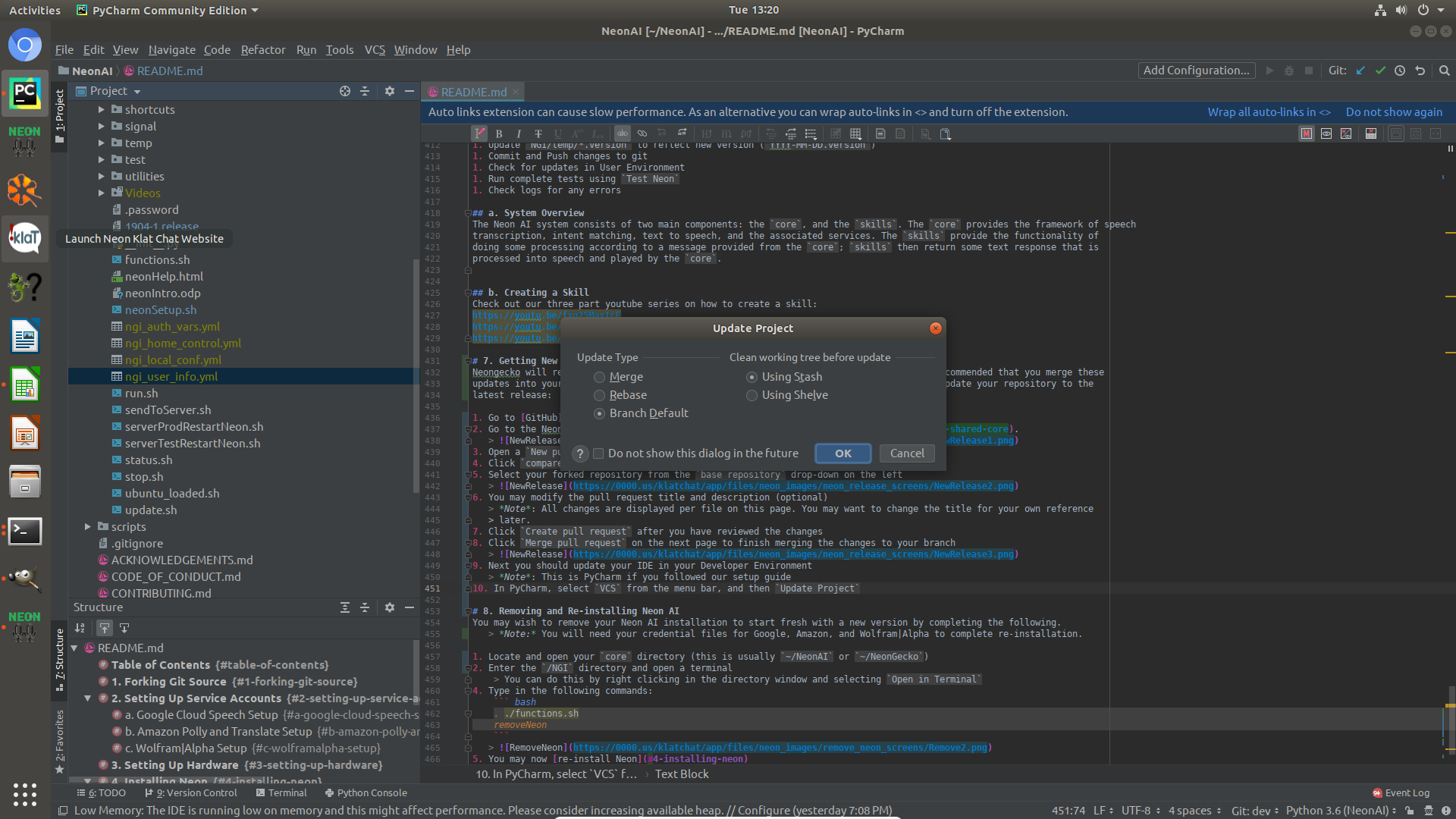
- Next you should update your IDE in your Developer Environment
Note: This is PyCharm if you followed our setup guide.
- In PyCharm, select
VCSfrom the menu bar, and thenUpdate Project - You will be prompted to
Update Project, you may leave the default settings and clickOK
You may wish to remove your Neon AI installation to start fresh with a new version. Below is a list of locaitons where Neon may have saved files:
~/Documents/NeonGecko~/Pictures/NeonGecko~/Videos/NeonGecko~/Music/NeonGecko~/.local/share/neon~/.cache/neon~/NeonAI~/.neon/opt/neon/tmp/neon
You may now re-install Neon
Note: You may need your credential files to complete re-installation.
Skills Service
docker run -d \
--name=neon_skills \
--network=host \
-v ~/.config/pulse/cookie:/tmp/pulse_cookie:ro \
-v ${XDG_RUNTIME_DIR}/pulse:${XDG_RUNTIME_DIR}/pulse:ro \
--device=/dev/snd:/dev/snd \
-e PULSE_SERVER=unix:${XDG_RUNTIME_DIR}/pulse/native \
-e PULSE_COOKIE=/tmp/pulse_cookie \
neon_skills