-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Usage
- RedPitaya
- Cloned pyrpl repository on the open_fpga_fads branch
- Oscilloscope (for an unbiased view of what the RedPitaya is seeing and doing)
- Function generator (just for testing/evaluation purposes)
- Create a conda environment for pyrpl
conda create -y -n pyrpl-env python=3.7.* numpy scipy paramiko pandas nose pip pyqt qtpy pyqtgraph pyyaml quamash scp
conda activate pyrpl-env- Clone the pyrpl repository at the branch and install pyrpl
git clone https://github.com/wenzel-lab/pyrpl@open_fpga_fads
cd pyrpl
python setup.py developFollow the pyrpl guide for preparing the hardware.
Afterwards copy the pyrpl/fads_logger directory to your RedPitaya
cd pyrpl/fads_logger
scp * root@<RedPitaya Hostname>:/root/mybin/loggerConnect to the RedPitaya over ssh and build the logger application
ssh root@<RedPitaya Hostname>
cd /root/mybin/logger
makeRun pyrpl on your computer (not the RedPitaya). To do so, start a new terminal tab and activate the conda environment (make sure you are in the top pyrpl directory)
conda activate pyrpl-env
python -m pyrpl example_filenameand follow the instructions for a basic setup.
CAUTION: DO NOT RUN THE LOGGER WHILE YOU START PYRPL! Pyrpl will overwrite the bitstream of the FPGA and if the logger is logging during this period, the bitstream write will fail and the RedPitaya needs to be restarted.
- Add the
asgs,scopesand thefadssmodules to the gui. - Set the following defaults

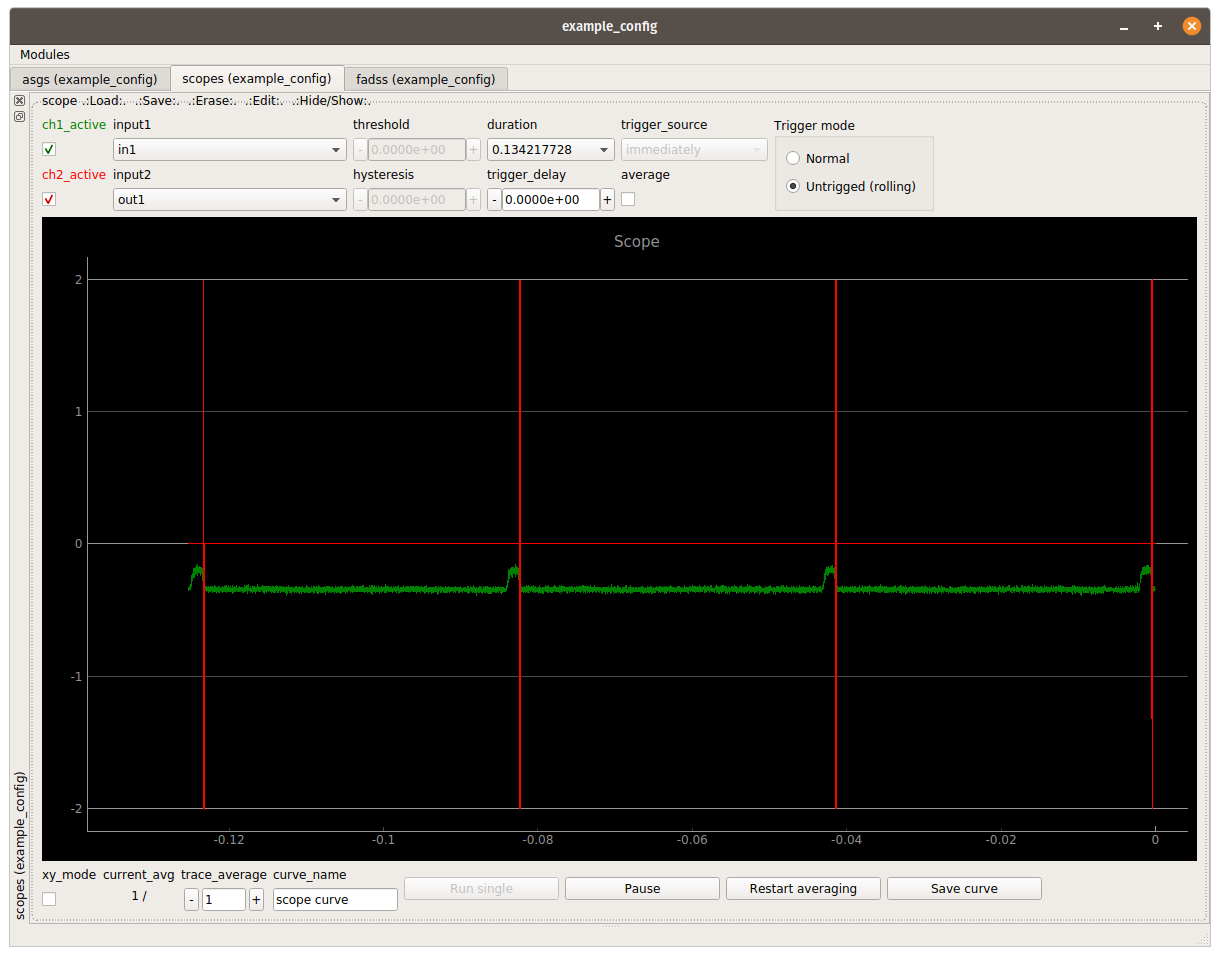
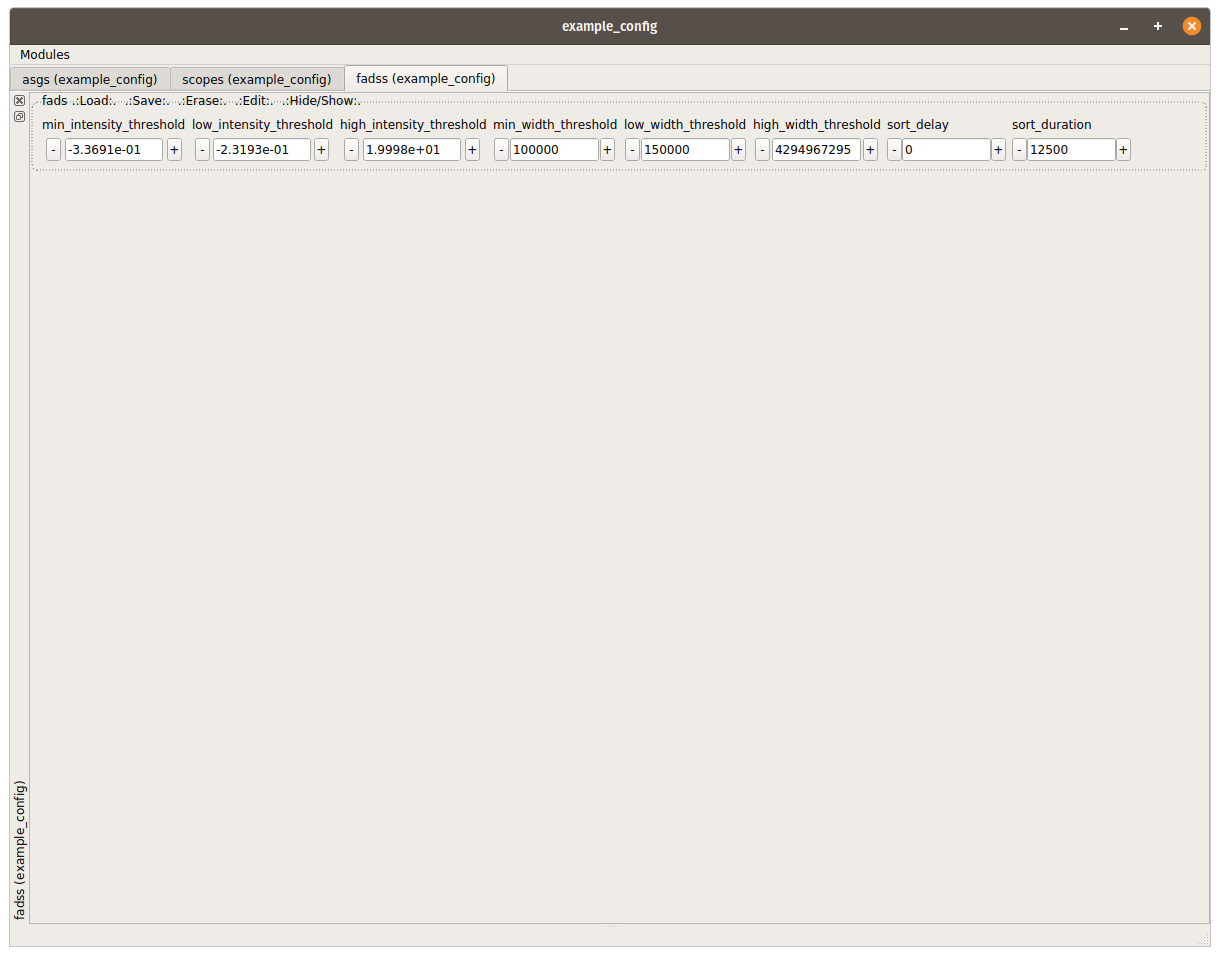
- Connect the photodetector to IN1 and the high voltage amplifier to OUT1
Run the following command in a ssh connection to the RedPitaya.
./fads_logger > /PATH/TO/LOGFILEand replace the path with one of your liking. You need to be in the logger directory (default /root/mybin/logger) for this to work.
CAUTION: This will overwrite the file if it already exists.
You can also use tee to simultaneously display the logger output while still writing the file:
./fads_logger | tee /PATH/TO/LOGFILECAUTION: This will overwrite the file if it already exists.
CAUTION: Keep the caveats in mind
CAUTION: DO NOT RUN THE LOGGER WHILE YOU START PYRPL! Pyrpl will overwrite the bitstream of the FPGA and if the logger is logging during this period, the bitstream write will fail and the RedPitaya needs to be restarted.
Currently, the logfile contains the following columns:
- Droplet ID (Basic autoincrementing counter of everything that reached
min_intensity_threshold) - Droplet intensity maximum (Raw value from the ADC before conversion)
- Droplet intensity maximum (Scaled to the HV +-20V range of the RedPitaya but NOT calibrated)
- Droplet width in FPGA clock cycles (125 MHz clock)
- Droplet width in milliseconds
- Encoded droplet classification
- Time in µs after last pyrpl start or reset
270 -54 -0.131836 190149 1.521192 17
271 -55 -0.134277 189880 1.519040 17
272 -50 -0.122070 189561 1.516488 17
273 -51 -0.124512 190321 1.522568 1
274 -56 -0.136719 190426 1.523408 17
275 -52 -0.126953 188813 1.510504 17
276 -55 -0.134277 190356 1.522848 17
277 -55 -0.134277 190898 1.527184 17
278 -52 -0.126953 192923 1.543384 17
279 -53 -0.129395 189686 1.517488 17
280 -53 -0.129395 190988 1.527904 1
The classification is made up of a 8 bit wide word. Each bit represents a flag for a specific classification:
| Bit | Decimal | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 7 | 128 | Positive Droplet |
| 6 | 64 | Currently unused |
| 5 | 32 | High Width |
| 4 | 16 | Positive Width |
| 3 | 8 | Low Width |
| 2 | 4 | High Intensity |
| 1 | 2 | Positive Intensity |
| 0 | 1 | Low Intensity |
The decimal values are summed up for set flags and the sum is displayed as the encoded classifcation.
Example:
Classification: 146
Bits 76543210
||||||||
146 (in base 10) = 10010010 (in base 2 or binary)
| | ∟ Positive Intensity
| ∟ Positive Width
∟ Positive Droplet
Classification: 17
Bits 76543210
||||||||
17 (in base 10) = 00010001 (in base 2 or binary)
| ∟ Low Intensity
∟ Positive Width
-
Take care of potential impedance mismatches between Photodetector and the High-Z RedPitaya scope
-
Thresholds can be tweaked using the scope screen and when daisy-chaining a Oscilloscope
- It is recommended to set the low and high thresholds to their maximum values (-2, 2 for intensity and 0 and 2^32 for width) first
- Afterwards the min thresholds can be tweaked
- Then the low and high thresholds
- Finally the sort delay and sort duration
-
The LEDs on the Red Pitaya encode the state of the state machine and thus, give an insight into what is happening
-
To Reset the FADS you can set the address 0x40600020 to 1 and afterwards back to 0 on the RedPitaya
- the
monitorcommand needs to be run on the RedPitaya
- the
monitor 0x40600020 0x1
monitor 0x40600020 0x0