- This project showcases a delivery robot system that utilizes the MPU6050 sensor for angle detection and control. By integrating the MPU6050 with the delivery robot, we enhance its ability to maintain a straight trajectory during transportation.
- This project uses STM32F103C8T6 MCU which connects some peripherals to help robot detect do some basic task of whole robot.
- Big problem: The earphone manufacturing factory is facing challenges, such as increasing demand, rising labor costs, and the need for transporting electronic parts between some sections. A shipping robot that can automate the shipping process would help to address these challenges.
- The robot must be able to navigate autonomously in earphone manufacturing factory,
- The robot must be able to identify and avoid workers
- The robot not only uses wireless communication, for example, bluetooth or wifi, but also has to connect to the mobile app
- It can pick up and deliver packages, specifically a headset box under 500g
- as tracking positon, it can detect coordinate
- Especially, The weight and costs are under 2.5 kg and under 2 million vnd
Easy clone this project and open in STM32Cube IDE
+Some peripheral
- HC-05 (Bluetooth)
- HCSR-04 (Ultrasonic sensor)
- MPU6050 (IMU module)
- L298N (Driver motor)
- LCD (Option)
- Voltage stabilizer circuit (Option)
(Cỉcuit map in folder Circuit)
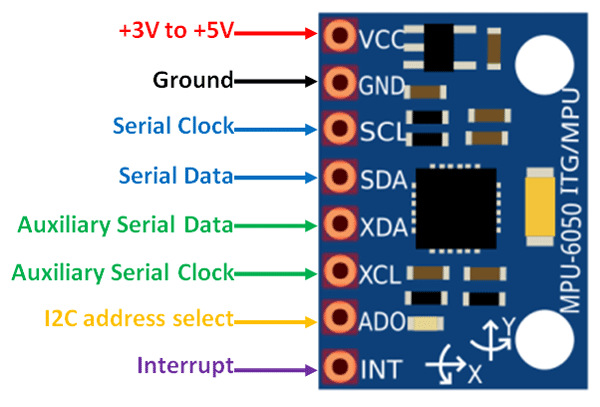
About MPU6050(IMU)
Gyroscope and Accelerator Axis
- Reference book: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1yAAfzYMUUJLWsbUDMVieYPOyikT2oKaV/view?usp=sharing
- The gyroscopes measures the angular velocity in degree per sec (dps).This angular velocity is given in 16 bits and with a full rate scale of -/+ 250 degrees and e LSB/deg/sec is 2^16:500=131.
- The accelerometers measure acceleration and therefore also the gravity of the earth. By determiningthe ratio of the different amount of gravity measured by the individual accelerometers the orientation with respect to the gravity can be calculated. the orientation with respect to the gravity can be calculated. This is done by equations 7.2 and 7.3 [16]. The variables ax, ay and az represent the acceleration measured by the individual accelerometers for the x-, y- and z-axis of the chip respectively. This results below in a roll angle that can go from -180 degrees to 180 degrees.
- The angles roll and pitch can now be calculated with the complementary filter equations.The aRoll and aPitch estimated with the accelerometers needs to be converted to degree since they are calculated in radians. α is the filter parameter and must be between 0 and 1. The lower the α the more the roll/pitch listens to the accelerometers. Because the gyroscopes are more reliable on the short term and the accelerometer and magnetometer more on the long term a high α is preferred.
- The yaw rotation cannot be calculated with only the use of the accelerometer. This is because the z-axis is defined in the direction of the gravity. To calculate a yaw rotation the magnetometers are used. The magnetometers measure the earth magnetic field, which is perpendicular to the gravity, and can therefore determine rotation in the horizontal plane. The yaw rotation is calculated by equations