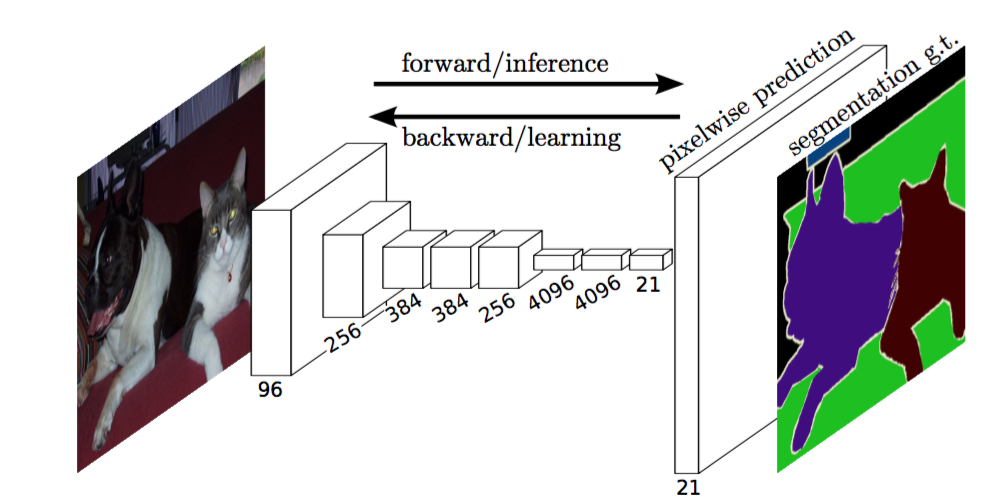
Implementation of various Deep Image Segmentation models in keras.
Link to the full blog post with tutorial : https://divamgupta.com/image-segmentation/2019/06/06/deep-learning-semantic-segmentation-keras.html
- Python Interface: https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1q_eCYEzKxixpCKH1YDsLnsvgxl92ORcv?usp=sharing
- CLI Interface: https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1Kpy4QGFZ2ZHm69mPfkmLSUes8kj6Bjyi?usp=sharing
- Attention based Language Translation in Keras
- Ladder Network in Keras model achives 98% test accuracy on MNIST with just 100 labeled examples
Following models are supported:
| model_name | Base Model | Segmentation Model |
|---|---|---|
| fcn_8 | Vanilla CNN | FCN8 |
| fcn_32 | Vanilla CNN | FCN8 |
| fcn_8_vgg | VGG 16 | FCN8 |
| fcn_32_vgg | VGG 16 | FCN32 |
| fcn_8_resnet50 | Resnet-50 | FCN32 |
| fcn_32_resnet50 | Resnet-50 | FCN32 |
| fcn_8_mobilenet | MobileNet | FCN32 |
| fcn_32_mobilenet | MobileNet | FCN32 |
| pspnet | Vanilla CNN | PSPNet |
| vgg_pspnet | VGG 16 | PSPNet |
| resnet50_pspnet | Resnet-50 | PSPNet |
| unet_mini | Vanilla Mini CNN | U-Net |
| unet | Vanilla CNN | U-Net |
| vgg_unet | VGG 16 | U-Net |
| resnet50_unet | Resnet-50 | U-Net |
| mobilenet_unet | MobileNet | U-Net |
| segnet | Vanilla CNN | Segnet |
| vgg_segnet | VGG 16 | Segnet |
| resnet50_segnet | Resnet-50 | Segnet |
| mobilenet_segnet | MobileNet | Segnet |
Example results for the pre-trained models provided :
| Input Image | Output Segmentation Image |
|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
- Keras ( recommended version : 2.4.3 )
- OpenCV for Python
- Tensorflow ( recommended version : 2.4.1 )
apt-get install -y libsm6 libxext6 libxrender-dev
pip install opencv-pythonInstall the module
Recommended way:
pip install --upgrade git+https://github.com/divamgupta/image-segmentation-keraspip install keras-segmentationgit clone https://github.com/divamgupta/image-segmentation-keras
cd image-segmentation-keras
python setup.py installfrom keras_segmentation.pretrained import pspnet_50_ADE_20K , pspnet_101_cityscapes, pspnet_101_voc12
model = pspnet_50_ADE_20K() # load the pretrained model trained on ADE20k dataset
model = pspnet_101_cityscapes() # load the pretrained model trained on Cityscapes dataset
model = pspnet_101_voc12() # load the pretrained model trained on Pascal VOC 2012 dataset
# load any of the 3 pretrained models
out = model.predict_segmentation(
inp="input_image.jpg",
out_fname="out.png"
)You need to make two folders
- Images Folder - For all the training images
- Annotations Folder - For the corresponding ground truth segmentation images
The filenames of the annotation images should be same as the filenames of the RGB images.
The size of the annotation image for the corresponding RGB image should be same.
For each pixel in the RGB image, the class label of that pixel in the annotation image would be the value of the blue pixel.
Example code to generate annotation images :
import cv2
import numpy as np
ann_img = np.zeros((30,30,3)).astype('uint8')
ann_img[ 3 , 4 ] = 1 # this would set the label of pixel 3,4 as 1
cv2.imwrite( "ann_1.png" ,ann_img )Only use bmp or png format for the annotation images.
Download and extract the following:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B0d9ZiqAgFkiOHR1NTJhWVJMNEU/view?usp=sharing
You will get a folder named dataset1/
You can import keras_segmentation in your python script and use the API
from keras_segmentation.models.unet import vgg_unet
model = vgg_unet(n_classes=51 , input_height=416, input_width=608 )
model.train(
train_images = "dataset1/images_prepped_train/",
train_annotations = "dataset1/annotations_prepped_train/",
checkpoints_path = "/tmp/vgg_unet_1" , epochs=5
)
out = model.predict_segmentation(
inp="dataset1/images_prepped_test/0016E5_07965.png",
out_fname="/tmp/out.png"
)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.imshow(out)
# evaluating the model
print(model.evaluate_segmentation( inp_images_dir="dataset1/images_prepped_test/" , annotations_dir="dataset1/annotations_prepped_test/" ) )You can also use the tool just using command line
You can also visualize your prepared annotations for verification of the prepared data.
python -m keras_segmentation verify_dataset \
--images_path="dataset1/images_prepped_train/" \
--segs_path="dataset1/annotations_prepped_train/" \
--n_classes=50python -m keras_segmentation visualize_dataset \
--images_path="dataset1/images_prepped_train/" \
--segs_path="dataset1/annotations_prepped_train/" \
--n_classes=50To train the model run the following command:
python -m keras_segmentation train \
--checkpoints_path="path_to_checkpoints" \
--train_images="dataset1/images_prepped_train/" \
--train_annotations="dataset1/annotations_prepped_train/" \
--val_images="dataset1/images_prepped_test/" \
--val_annotations="dataset1/annotations_prepped_test/" \
--n_classes=50 \
--input_height=320 \
--input_width=640 \
--model_name="vgg_unet"Choose model_name from the table above
To get the predictions of a trained model
python -m keras_segmentation predict \
--checkpoints_path="path_to_checkpoints" \
--input_path="dataset1/images_prepped_test/" \
--output_path="path_to_predictions"
To get predictions of a video
python -m keras_segmentation predict_video \
--checkpoints_path="path_to_checkpoints" \
--input="path_to_video" \
--output_file="path_for_save_inferenced_video" \
--displayIf you want to make predictions on your webcam, don't use --input, or pass your device number: --input 0
--display opens a window with the predicted video. Remove this argument when using a headless system.
To get the IoU scores
python -m keras_segmentation evaluate_model \
--checkpoints_path="path_to_checkpoints" \
--images_path="dataset1/images_prepped_test/" \
--segs_path="dataset1/annotations_prepped_test/"The following example shows how to fine-tune a model with 10 classes .
from keras_segmentation.models.model_utils import transfer_weights
from keras_segmentation.pretrained import pspnet_50_ADE_20K
from keras_segmentation.models.pspnet import pspnet_50
pretrained_model = pspnet_50_ADE_20K()
new_model = pspnet_50( n_classes=51 )
transfer_weights( pretrained_model , new_model ) # transfer weights from pre-trained model to your model
new_model.train(
train_images = "dataset1/images_prepped_train/",
train_annotations = "dataset1/annotations_prepped_train/",
checkpoints_path = "/tmp/vgg_unet_1" , epochs=5
)
The following example shows transfer the knowledge from a larger ( and more accurate ) model to a smaller model. In most cases the smaller model trained via knowledge distilation is more accurate compared to the same model trained using vanilla supervised learning.
from keras_segmentation.predict import model_from_checkpoint_path
from keras_segmentation.models.unet import unet_mini
from keras_segmentation.model_compression import perform_distilation
model_large = model_from_checkpoint_path( "/checkpoints/path/of/trained/model" )
model_small = unet_mini( n_classes=51, input_height=300, input_width=400 )
perform_distilation ( data_path="/path/to/large_image_set/" , checkpoints_path="path/to/save/checkpoints" ,
teacher_model=model_large , student_model=model_small , distilation_loss='kl' , feats_distilation_loss='pa' )The following example shows how to define a custom augmentation function for training.
from keras_segmentation.models.unet import vgg_unet
from imgaug import augmenters as iaa
def custom_augmentation():
return iaa.Sequential(
[
# apply the following augmenters to most images
iaa.Fliplr(0.5), # horizontally flip 50% of all images
iaa.Flipud(0.5), # horizontally flip 50% of all images
])
model = vgg_unet(n_classes=51 , input_height=416, input_width=608)
model.train(
train_images = "dataset1/images_prepped_train/",
train_annotations = "dataset1/annotations_prepped_train/",
checkpoints_path = "/tmp/vgg_unet_1" , epochs=5,
do_augment=True, # enable augmentation
custom_augmentation=custom_augmentation # sets the augmention function to use
)The following example shows how to set the number of input channels.
from keras_segmentation.models.unet import vgg_unet
model = vgg_unet(n_classes=51 , input_height=416, input_width=608,
channels=1 # Sets the number of input channels
)
model.train(
train_images = "dataset1/images_prepped_train/",
train_annotations = "dataset1/annotations_prepped_train/",
checkpoints_path = "/tmp/vgg_unet_1" , epochs=5,
read_image_type=0 # Sets how opencv will read the images
# cv2.IMREAD_COLOR = 1 (rgb),
# cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE = 0,
# cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED = -1 (4 channels like RGBA)
)The following example shows how to set a custom image preprocessing function.
from keras_segmentation.models.unet import vgg_unet
def image_preprocessing(image):
return image + 1
model = vgg_unet(n_classes=51 , input_height=416, input_width=608)
model.train(
train_images = "dataset1/images_prepped_train/",
train_annotations = "dataset1/annotations_prepped_train/",
checkpoints_path = "/tmp/vgg_unet_1" , epochs=5,
preprocessing=image_preprocessing # Sets the preprocessing function
)The following example shows how to set custom callbacks for the model training.
from keras_segmentation.models.unet import vgg_unet
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import ModelCheckpoint, EarlyStopping
model = vgg_unet(n_classes=51 , input_height=416, input_width=608 )
# When using custom callbacks, the default checkpoint saver is removed
callbacks = [
ModelCheckpoint(
filepath="checkpoints/" + model.name + ".{epoch:05d}",
save_weights_only=True,
verbose=True
),
EarlyStopping()
]
model.train(
train_images = "dataset1/images_prepped_train/",
train_annotations = "dataset1/annotations_prepped_train/",
checkpoints_path = "/tmp/vgg_unet_1" , epochs=5,
callbacks=callbacks
)The following example shows how to add additional image inputs for models.
from keras_segmentation.models.unet import vgg_unet
model = vgg_unet(n_classes=51 , input_height=416, input_width=608)
model.train(
train_images = "dataset1/images_prepped_train/",
train_annotations = "dataset1/annotations_prepped_train/",
checkpoints_path = "/tmp/vgg_unet_1" , epochs=5,
other_inputs_paths=[
"/path/to/other/directory"
],
# Ability to add preprocessing
preprocessing=[lambda x: x+1, lambda x: x+2, lambda x: x+3], # Different prepocessing for each input
# OR
preprocessing=lambda x: x+1, # Same preprocessing for each input
)Here are a few projects which are using our library :
- https://github.com/SteliosTsop/QF-image-segmentation-keras paper
- https://github.com/willembressers/bouquet_quality
- https://github.com/jqueguiner/image-segmentation
- https://github.com/pan0rama/CS230-Microcrystal-Facet-Segmentation
- https://github.com/theerawatramchuen/Keras_Segmentation
- https://github.com/neheller/labels18
- https://github.com/Divyam10/Face-Matting-using-Unet
- https://github.com/shsh-a/segmentation-over-web
- https://github.com/chenwe73/deep_active_learning_segmentation
- https://github.com/vigneshrajap/vision-based-navigation-agri-fields
- https://github.com/ronalddas/Pneumonia-Detection
- https://github.com/Aiwiscal/ECG_UNet
- https://github.com/TianzhongSong/Unet-for-Person-Segmentation
- https://github.com/Guyanqi/GMDNN
- https://github.com/kozemzak/prostate-lesion-segmentation
- https://github.com/lixiaoyu12138/fcn-date
- https://github.com/sagarbhokre/LyftChallenge
- https://github.com/TianzhongSong/Person-Segmentation-Keras
- https://github.com/divyanshpuri02/COCO_2018-Stuff-Segmentation-Challenge
- https://github.com/XiangbingJi/Stanford-cs230-final-project
- https://github.com/lsh1994/keras-segmentation
- https://github.com/SpirinEgor/mobile_semantic_segmentation
- https://github.com/LeadingIndiaAI/COCO-DATASET-STUFF-SEGMENTATION-CHALLENGE
- https://github.com/lidongyue12138/Image-Segmentation-by-Keras
- https://github.com/laoj2/segnet_crfasrnn
- https://github.com/rancheng/AirSimProjects
- https://github.com/RadiumScriptTang/cartoon_segmentation
- https://github.com/dquail/NerveSegmentation
- https://github.com/Bhomik/SemanticHumanMatting
- https://github.com/Symefa/FP-Biomedik-Breast-Cancer
- https://github.com/Alpha-Monocerotis/PDF_FigureTable_Extraction
- https://github.com/rusito-23/mobile_unet_segmentation
- https://github.com/Philliec459/ThinSection-image-segmentation-keras
If you use our code in a publicly available project, please add the link here ( by posting an issue or creating a PR )