This repository was created during my preparation to become a Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA) but has grown in functionality over time. The goal of this Playbook is to provide a slim solution for the provisioning of a Kubernetes cluster locally and for productive purposes with some additional components.
Disclaimer: This repository is primarily for personal use and covers mainly my personal use-case. Before using this repository you should make sure that all passwords are exchanged with secure ones and you should be aware of what the Ansible tasks do.
So far these features are implemented:
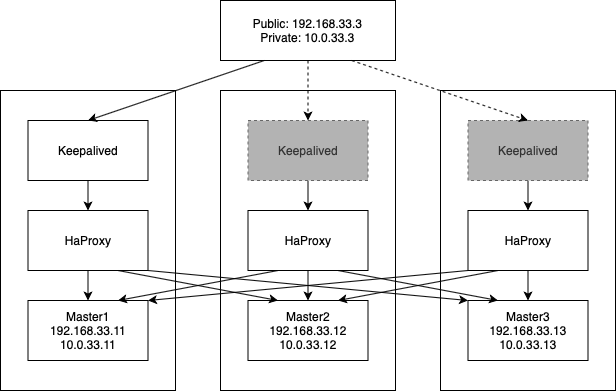
- HighAvailable Architecture
- Keepalived for VIP handling
- HAProxy for load balancing
- Traefik router
- Influxdb, Telegraph, Chronograph
There are 2 VIP's to ensure HA coverage:
- 192.168.33.3 (Public IP address to be used for applications)
- 10.0.33.3 (Private IP address used for the Kubernetes API and internal services)
Both VIP's are assigned to the hosts via Keepalived which distributes the traffic via HaProxy to all hosts.
The following steps only describe the installation for a local environment.
The following items are required to set up on a local environment:
- Virtualbox (tested in 6.1.12)
- Vagrant (tested in 2.2.7)
- Ansible (tested in 2.7.12)
You also need to install the vbguest plugin:
vagrant plugin install vagrant-vbguest
You should also make sure that your environment provides enough resources or adjust the Vagrantfile if necessary.
The Vagrantfile consists of 2 parts: base-box and nodes.
The base image must be built previously to increase the speed of the VM's rollout. To do this you have to execute the following to start the VM:
vagrant up base
Then the following commands must be executed to convert the VM into a box:
vagrant package base --output k8s.box && \
vagrant box add k8s-base k8s.box -f && \
vagrant destroy base -f
Afterwards the node VMs can be started with just one command:
vagrant up
This may take some time as several virtual machines are started
To access internal applications (like Traefik dashboard) on the Kubernetes cluster you also need the following entry in your hosts file:
10.0.33.3 chronograf.local traefik.local
Now you can reach both internal applications:
The internal applications are only forwarded to the outside if it is a vagrant environment, otherwise you should tunnel the corresponding port via SSH to your local machine, for example like this:
sudo ssh -L 80:localhost:30088 [email protected]
For all external application you have to use the public ip:
192.168.33.3 example.local
To create and reach a simple web application you can follow this guide, which is based on this documentation: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/connect-applications-service/
The following steps must be performed by one of the masters, to access them you can use the following command:
vagrant ssh master1
Now you can start with the example app.
Create a deployment:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/website/master/content/en/examples/service/networking/run-my-nginx.yaml
Create a service:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/website/master/content/en/examples/service/networking/nginx-svc.yaml
Now you can check if everything is working as it should:
kubectl get all -l run=my-nginx
You can also check if the service is providing the right application:
curl $(kubectl get service/my-nginx -o jsonpath='{.spec.clusterIP}')
After you have checked if everything is working properly you can create the traefik route to access the applications from outside the cluster:
apiVersion: traefik.containo.us/v1alpha1
kind: IngressRoute
metadata:
name: nginx-example
spec:
entryPoints:
- web
routes:
- match: Host(`example.local`)
kind: Rule
services:
- name: my-nginx
port: 80
Now you must apply the file as follows:
kubectl apply -f <file>
Now you should be able the application from your local machine via http://example.local.
- Use helm module
- Optimize influxdb role
- Kubernetes dashboard
- Habor registry
- Grafana