The main purpose of network analysis is the understanding of inter-components correlations, thus, how a changeover of the state of a component can affect the behaviour of the whole system. Up to hundreds of components can compose a logical model, the analysis of such models even on optimised software can be very time consuming, due to the huge number of cases that need to be analysed, especially in large models
The goal of the automatic analysis via scripts is the process different workflows/pipelines in order to process an automatic of logical models.
All scripts can be run in your Linux/MacOS/Windows machine. You can download the scripts and the tool from Here All command lines and steps to follow to process the results are described in this documentation. The same steps can be used for any other models. *Disclaimer: we will keep updating the tutorial in the GitHub as the different tools used evolve.
- Software:
- Python Packages:
- csv
- sys
- itertools
- collections
- math
- numpy
- matplotlib
- Scripts:
In order to run any scripts you can use the command:
java -cp GINsim.jar:extensions/jython-standalone-2.7.0.jar org.ginsim.Launcher -s SCRIPT.py Models/Model.zginml Note:: Please note that you need to change the name of the files depending on the version of GINsim and Jython that you are using. We reccomand the defeault give version of GINsim and Jython that you can download from this repository.
Example: In order to run the script ApplyPerturbation.py with arguments the pertubation Gene_A fixed at value 0 on the model MyGinsimModel.zginml, the command to run should be:
java -cp GINsim.jar:extensions/jython-standalone-2.7.0.jar org.ginsim.Launcher -s ApplyPerturbation.py Models/MyGinsimModel.zginml pert:Gene_A%0For the sake of organisation, we deployed the scripts as several functions in order to firstly, provide flexible and extensible code; secondly to integrate those function to define elaborated functions, as the fellow:
- Basic Functions (Assets): the functions can be used to perform small tasks like data parsing, convertion, export... those function are stored as python files but cannot be called by the user.
- Main Functions (Workflows): the main scripts implement and combine the basic functions with the user arguments in order to perform a more complex analysis.
The basic function are distributed as the follow
Assets
└─── model.py # contains function related the model.
│ └─── model(gs) = import the model as JAVA object
└─── components.py # contains function related the components (extraction - filtring...)
| └─── get_list_of_components_and_max(model) # returns the list of components and their max level
| └─── get_component(list_of_components_and_max) # get the list of components from the list of components and their max level can be combined with the previous function
| └─── get_all_index_nodes(gs): # get the index of the components of a model
| └─── get_inner_comp_index(gs):#get the index of inner nodes of a model
| └─── get_inputs_index_nodes(gs):#get the index of input nodes of a model
| └─── get_nodes_by_index(gs, list_of_index):#get the name of a node by index (Requires one of previous fonctions)
└─── convert.py # Contains the functions related format parsing and conversion.
| └─── tuples_to_lists(tuple) # take as input a tuple variable and convert the tuple to a list
| └─── biolqm_concatenation(a,z) # convert a given list as input to the biolqm perturbation format, example : input = ["a",2] -> output = "a%2"
| └─── Join_List_to_Strings(list) # Convert a list of string to string: input = ["x","x"] -> output = "x,x"
| └─── Check_Duplications(list) # Check duplicated items and returns boolean value : True if an element exist in the list or False if not
| └─── list_to_bioLQM_list(list) # Convert a list of perturbation to bioLQM pattern of perturbations using previous functions
| └─── list_of_perturbations_to_strings(list) # Convert a 2 dimention list of perturbations to list of biolqm perturbation format
| └─── csv_to_biolqm(csvfile) # convert one perturbation from csv file to biolqm string
| └─── csv_to_biolqmlist(csvfile) # take as input the name of csv file and return a list of perturbation extracted from this file as biolqm format
└─── export.py # Contains the functions related external export.
| └─── export_flat_list_to_csv(list,filename) # export one dim. list to csv file
| └─── export_list_of_lists_to_csv(list,filename) # export list of lists to a csv file
| └─── export_model(model,name) # export a model as sbml format.
└─── export.py # Contains the functions related external export.
| └─── Get_List_of_Stable_states(gs,model(gs) # the output is a list of values, each value represent the value of a specific component
| └─── Get_Stable_states_from_list(gs,model) # Get a list of satble states from a given list models.
| └─── filtre_states(list_of_stable_states, pattern) #make restriction on the list of stable states
└─── Perturbation.py # Contains the functions related to components perturbations.
| └─── Apply_Perturbation_to_model(model,perturbation) #Apply a given perturbation to a model
| └─── Apply_List_of_Perturbation_to_model(model,list_of_perturbations) #Apply a given list of perturbations to a model
| └─── input_combinations(list_of_nodes_name_and_max): # generate list of perturbations from nodes #size by default equal to one !
| └─── input_combinations_sizeN(list_of_nodes_name_and_max, N): # generate list of perturbations from nodes of size N
└─── filtre_pattern
| └─── filltr_patterns(patterns,filltrs): # apply the or filtre
| └─── filltr_patterns_and(patterns,filltrs): # apply the or filtre
| └─── filltr_patterns_not(patterns,filltrs)# apply the none filtre
| └─── check_size_equal(list_of_patterns) # check if the list of patterns have the same size
└─── filtre_perturbations
| └─── set_max_val # keep just the perturbation with value smaller than the max
| └─── set_min_val # keep just the perturbation with value greater than the min
| └─── get_perturbations_with_val_in_range # keep just the perturbation in a given range of values
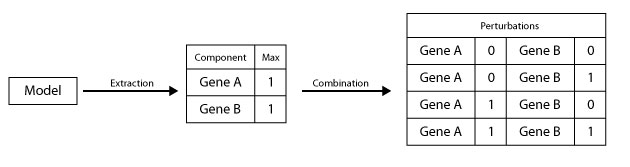
└────────────────────────────────────────────────This script allows the generation of all possible perturbations from a given model by:
- Extracting the name and the maximum value of a each node from the model.
- Computing all the possible states of each node.
- Combining the difirent satates of nodes (if the size of perturbation > 1 )
- Removing duplicated elements.
* A perturbation refer to fixing the value of a compunent at a given value
* The size of perturbation refer to how many components are modified at the same time
In order to run this script the user should specify: ..* The model ..* The Size of perturbation (Specific value or Range) ..* The file name and the path for exporting the resulting list of perturbations (Optional)
In this example let supose that we want to get the list of all possbile single perturbations (size = 1) of the model genesModels.zginml which is stored in the repository ~/models/, using the command: let's asume that the model contains three boolean components (Gene_A, Gene_B and Gene_C).
java -cp GINsim.jar:extensions/jython-standalone-2.7.0.jar org.ginsim.Launcher -s Workflow/GeneratePerturbations.py Models/genesModels.zginml size:1Finaly the list of perturbations is exported to the file List_of_Perturbations.csv as follow :
| Gene_A,0 |
| Gene_A,1 |
| Gene_B,0 |
| Gene_B,1 |
| Gene_C,0 |
| Gene_C,1 |
Working with the same previous model, we want to get all the possible perturbation of size 2 and 3. We can use the command
java -cp GINsim.jar:extensions/jython-standalone-2.7.0.jar org.ginsim.Launcher -s Workflow/GeneratePerturbations.py Models/genesModels.zginml size:2-3We get the list of perturbations exported to the file List_of_Perturbations.csv as follow :
| Gene_A,0, | Gene_B,0 |
| Gene_A,0, | Gene_B,1 |
| Gene_A,0, | Gene_C,0 |
| Gene_A,0, | Gene_C,1 |
| Gene_A,1 | Gene_B,0 |
| Gene_A,1 | Gene_B,1 |
| Gene_A,1 | Gene_C,0 |
| Gene_A,1 | Gene_C,1 |
| Gene_B,0 | Gene_A,0 |
| Gene_B,0 | Gene_A,1 |
| Gene_B,0 | Gene_C,0 |
| Gene_B,0 | Gene_C,1 |
| ... | ... |
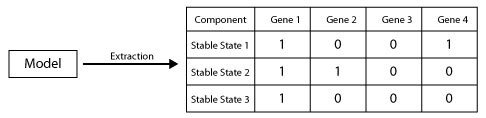
Biological phenotype are represented with stable states. based on a given model, this script generates the list of stable states of this model. Stable states can have two type of representation
- List of values where each value represent the level of exporetion of a component (the value -1 means that the components can take any value)
- A pattern (string) where each character represent the level of exporetion of a component (the character * means that the components can take any value)
java -cp GINsim.jar:extensions/jython-standalone-2.7.0.jar org.ginsim.Launcher -s Workflow/GenerateStableStates.py Models/genesModels.zginml export:list.csvUsing the model genesModels.zginml the command above allows to generating all possible statable states then exporting them as csv file
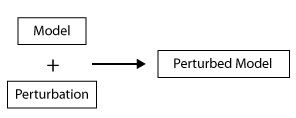
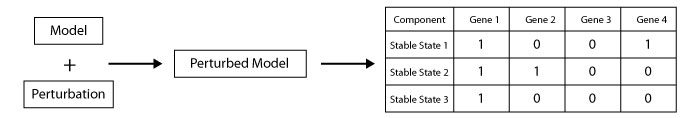
A perturbation basicly is fixing the a component into a given value. this script generate new model by applying a given perturbation to model.
java -cp GINsim.jar:extensions/jython-standalone-2.7.0.jar org.ginsim.Launcher -s Workflow/ApplyPerturbations.py Models/genesModels.zginml perturbation:GeneA%1Similar to the previous script, this one applies a given perturbation on an interaction in order to fix the interaction between two components of a given value
java -cp GINsim.jar:extensions/jython-standalone-2.7.0.jar org.ginsim.Launcher -s Workflows/ApplyInteractionPerturbation.py Model.zginml inter:listofpert.csvWith the file listofpert.csv containing the list of perturbations to apply.
This scripts allow to the users to apply a perturbation on a model then get the list of stable states of the perturbed model.
java -cp GINsim.jar:extensions/jython-standalone-2.7.0.jar org.ginsim.Launcher -s Workflows/GetStableStatesAfterPerturbations.py Model.zginml pert:CellCycleArrest,0-CellCycleArrest,1 export:ListOfStableStates.csvpert: the perturbation to apply.
export: the name of the csv file to export.
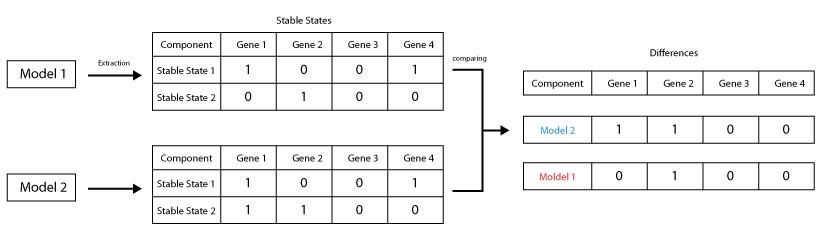
This scripts allows the comparaison the stable states of two given models and returns the diffrent stable states
java -cp GINsim.jar:extensions/jython-standalone-2.7.0.jar org.ginsim.Launcher \
-s Workflows/CompareStableStates.py Model1.zginml model:Model2.zginmlIn order to run this scripts the user should specify a pattern for the inputs, a pattern of restriction and the type of restriction to apply.
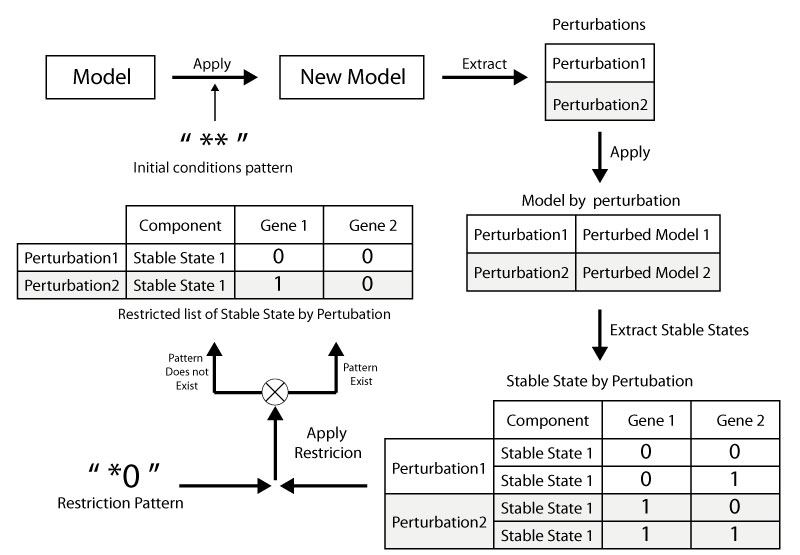
The type can be:
- not
- or
java -cp GINsim.jar:extensions/jython-standalone-2.7.0.jar org.ginsim.Launcher \
-s Workflows/SubStableStates.py Model1.zginml fix:00000000 type:not pattern:***1111*10101***01111java -cp GINsim.jar:extensions/jython-standalone-2.7.0.jar org.ginsim.Launcher \
-s Workflows/SubStableStates.py Model1.zginml fix:00000000 type:or pattern:***1111*10101***01111This script can be used to apply filtres in order to affine a list of perturbations of a model.
java -cp GINsim.jar:extensions/jython-standalone-2.7.0.jar org.ginsim.Launcher \
-s Workflows/getRestrictedPerturbations.py Model1.zginml size:1-2 rest:max:1the type of restrications can be:
- max
- min
- range
This script can be used to apply filtres in order to affine the resulting list of stable states of a model.
java -cp GINsim.jar:extensions/jython-standalone-2.7.0.jar org.ginsim.Launcher \
-s Workflows/getRestrictedPerturbations.py Model1.zginml pattern:*******001