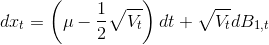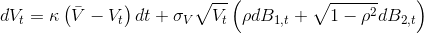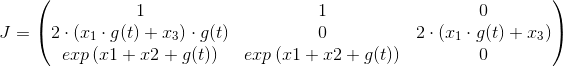Cocos is a package for numeric and scientific computing on GPUs for Python with a NumPy-like API. It supports both CUDA and OpenCL on Windows, Mac OS, and Linux. Internally, it relies on the ArrayFire C/C++ library. Cocos offers a multi-GPU map-reduce framework. In addition to its numeric functionality, it allows parallel computation of SymPy expressions on the GPU.
- Fast vectorized computation on GPUs with a NumPy-like API.
- Multi GPU support via map-reduce.
- High-performance random number generators for beta, chi-square, exponential, gamma, logistic, lognormal, normal, uniform, and Wald distributions. Antithetic random numbers for uniform and normal distributions.
- Provides a GPU equivalent to SymPy's lambdify, which enables numeric evaluation of symbolic SymPy (multi-dimensional array) expressions on the GPU for vectors of input parameters in parallel.
- Adaptation of SciPy's gaussian_kde to the GPU
- Installation
- Getting Started
- Multi-GPU Computing
- Memory Limitations on the GPU Device
- Examples
5.1. Estimating Pi via Monte Carlo
5.2. Option Pricing in a Stochastic Volatility Model via Monte Carlo
5.3. Numeric evaluation of SymPy array expressions on the GPU
5.4. Kernel Density Estimation - Benchmark
- Functionality
- Limitations and Differences with NumPy
- A Note on Hardware Configurations for Multi-GPU Computing
- License
NVidia CUDA must be installed on the system.
- Follow the instructions here:
https://github.com/arrayfire/arrayfire/wiki/Install-ArrayFire-From-Linux-Package-Managers, concretelysudo apt-key adv --fetch-key https://repo.arrayfire.com/GPG-PUB-KEY-ARRAYFIRE-2020.PUB- Register the ArrayFire repo as a software source for apt-get via
echo "deb [arch=amd64] https://repo.arrayfire.com/ubuntu focal main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/arrayfire.list
(if your distribution is based on a different version of Ubuntu, you must replace focal with the code name obtained vialsb_release -c) - Update software sources and install ArrayFire via
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install arrayfire
Docker must be installed on your system. See here for instructions: https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/ubuntu/.
- Set up the nvidia-docker plugin as follows:
- Add nvidia's cryptographic key to apt-get via
curl -s -L https://nvidia.github.io/nvidia-container-runtime/gpgkey | sudo apt-key add - - Add nvidia's repo to the software sources apt-get is able to access
curl -s -L https://nvidia.github.io/nvidia-container-runtime/ubuntu20.04/nvidia-container-runtime.list | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nvidia-container-runtime.list - Update the software sources and install the nvidia container runtime via
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install nvidia-container-runtime - Stop the Docker daemon via
sudo systemctl stop docker - Restart the Docker daemon via
sudo systemctl start docker
- Add nvidia's cryptographic key to apt-get via
- Build the Docker image from the Dockerfile via
sudo docker build --tag cocos .(this only needs to be done the first time) - Run a Docker container based on the image created in the previous step via
sudo docker run -it --gpus all cocos - To test the installation:
- Navigate to the Monte-Carlo example via
cd examples/monte_carlo_pi - Run Monte-Carlo example via
python3 -m monte_carlo_pi
- Navigate to the Monte-Carlo example via
ArrayFire's functionality is contained in dynamic libries, dynamic link libraries (.dll) on Windows and shared objects (.so) on Unix.
This step is to ensure that these library files can be located on your system.
On Windows, this can be done by adding %AF_PATH%\lib to the path environment variable.
On Linux and Mac, one can either install (or copy) the ArrayFire libraries and their dependencies
to /usr/local/lib or modify the environment variable LD_LIBRARY_PATH (Linux) or
DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH (MacOS) to include the ArrayFire library directory.
pip install cocos
or
pip3 install cocos
if not using Anaconda.
To get the latest version, clone the repository from github, open a terminal/command prompt, navigate to the root folder and install via
pip install .
or
pip3 install .
if not using Anaconda.
Print available devices
import cocos.device as cd cd.info()
Select a device
cd.ComputeDeviceManager.set_compute_device(0)
# begin by importing the numerics package import cocos.numerics as cn # create two arrays from lists a = cn.array([[1.0, 2.0], [3.0, 4.0]]) b = cn.array([[5.0], [6.0]]) # print their contents print(a) print(b) # matrix product of b and a c = a @ b print(c) # create an array of normally distributed random numbers d = cn.random.randn(2, 2) print(d)
Cocos provides map-reduce as well as the related map-combine as multi-GPU
programming models. The computations are separated into 'batches' and then distributed
across GPU devices in a pool. Cocos implements multi-GPU support via process-based parallelism.
To run the function my_gpu_function over separate batches of input data on multiple
GPUs in parallel, first create a ComputeDevicePool:
compute_device_pool = cocos.multi_processing.device_pool.ComputeDevicePool()
To construct the batches, separate the arguments of the function into
- a list of args lists and (one list per batch)
- a list of kwargs dictionaries (one dictionary per batch)
args_list = [args_list_1, arg_list_2, ..., arg_list_n] kwargs_list = [kwargs_dict_1, kwargs_dict_2, ..., kwargs_dict_n]
Run the function in separate batches via map_reduce
result = \
compute_device_pool.map_reduce(f=my_gpu_function,
reduction=my_reduction_function,
initial_value=...,
host_to_device_transfer_function=...,
device_to_host_transfer_function=...,
args_list=args_list
kwargs_list=kwargs_list)
The reduction function iteratively aggregates two results from the list of results generated by
my_gpu_function from left to right, beginning at initial_value (i.e. reducing
initial_value and the result of my_gpu_function corresponding to the first batch).
The list of results is in the same order to the list of args and kwargs.
If the function requires input arrays on the GPU, it must be provided to map_reduce as
a NumPy array. The data is then sent to the process managing the GPU assigned to this
batch, where it is moved to the GPU device by a host_to_device_transfer_function.
This function needs to be implemented by the user.
Likewise, results that involve GPU arrays are transferred to the host via a user-supplied
device_to_host_transfer_function and are then sent back to the main process before
reduction takes place.
map_combine is a variation of map_reduce, in which a combination function aggregates the
list of results in a single step.
Please refer to the documentation of cocos.multi_processing.device_pool.ComputeDevicePool.map_reduce as well as
cocos.multi_processing.device_pool.ComputeDevicePool.map_combine for further details.
See 'examples/heston_pricing_multi_gpu_example.py' for a fully worked example.
It is common for modern standard desktop computers to support up to support up to 128GB of RAM. Video cards by contrast only feature a small fraction of VRAM. The consequence is that algorithms that work well on a CPU can experience into memory limitations when run on a GPU device.
In some cases this problem can be resolved by running the computation in batches or chunks and transferring results from the GPU to the host after each batch has been processed.
Using map_reduce_single_device and map_combine_single_device found in
cocos.multi_processing.single_device_batch_processing, computations on a single GPU can be split into chunks
and run sequentially. The interface is modeled after the multi GPU functionality described in the previous section.
Calls to map_reduce_single_device and map_combine_single_device can be nested in a multi GPU computation,
which is how multi GPU evaluation of kernel density estimates is realized in Cocos
(see cocos.scientific.kde.gaussian_kde.evaluate_in_batches_on_multiple_gpus).
- Estimating Pi via Monte Carlo
- Option Pricing in a Stochastic Volatility Model via Monte Carlo
- Numeric evaluation of SymPy array expressions on the GPU
- Kernel Density Estimation
The following code estimates Pi via Monte-Carlo simulation. Since Cocos offers a NumPy-like API, the same code works on the both the GPU and the CPU via NumPy.
import time
import cocos.device as cd
def estimate_pi(n: int, gpu: bool = True) -> float:
if gpu:
import cocos.numerics as np
import cocos.numerics.random as random
else:
import numpy as np
import numpy.random as random
x = np.random.rand(n)
y = np.random.rand(n)
in_quarter_circle = (x * x + y * y) <= 1.0
estimate = int(np.sum(in_quarter_circle))
return estimate / n * 4
# initialize cocos device - the architecture is selected automatically
# the architecture can be specified explitly by providing one of
# 'cpu', 'cuda', and 'opencl'
cd.init()
# print information regarding the available devices in the machine
cd.info()
# number of draws
n = 100000000
print(f'simulating {n} draws')
# run estimation of Pi on the cpu via NumPy
pi_cpu = estimate_pi(n, gpu=False)
print(f'Estimate of Pi on cpu: {pi_cpu}')
# run estimation of Pi on the gpu via Cocos
pi_gpu = estimate_pi(n, gpu=True)
print(f'Estimate of Pi on gpu: {pi_gpu}')
# run a benchmark - repeating the simulation R times on both cpu and gpu
R = 10
# on gpu
tic = time.time()
for r in range(R):
pi_gpu = estimate_pi(n, gpu=True)
cd.sync()
time_on_gpu = time.time() - tic
print(f'time elapsed on gpu: {time_on_gpu}')
# on cpu
tic = time.time()
for r in range(R):
pi_cpu = estimate_pi(n, gpu=False)
time_on_cpu = time.time() - tic
print(f'time elapsed on cpu: {time_on_cpu}')
# compute and print the speedup factor
print(f'speedup factor on gpu: {time_on_cpu/time_on_gpu}')
In this example, we are simulating sample paths of the logarithmic price of an underlying security under the risk-neutral probability measure via the Euler–Maruyama discretization method.
The stochastic process is Heston's classical 1992 setup of a security price subject to stochastic volatility. The log price and its instantanous variance are governed by the following system of stochastic differential equations (SDE):
The simulation code below demonstrates how to write code that supports both CPU and GPU computing. The complete code is available under examples.
def simulate_heston_model(T: float,
N: int,
R: int,
mu: float,
kappa: float,
v_bar: float,
sigma_v: float,
rho: float,
x0: float,
v0: float,
gpu: bool = False) -> tp.Tuple:
"""
This function simulates R paths from the Heston stochastic volatility model
over a time horizon of length T divided into N steps.
:param T: time horizon of the simulation
:param N: number of steps
:param R: number of paths to simulate
:param mu: expected return
:param kappa: mean-reversion speed of volatility
:param v_bar: long-run mean of volatility
:param sigma_v: volatility of volatility
:param rho: instantaneous correlation of shocks to price and to volatility
:param x0: initial log price
:param v0: initial volatility
:param gpu: whether to compute on the GPU
:return: a tuple of two R-dimensional numeric arrays for log price and
volatility
"""
if gpu:
import cocos.numerics as np
import cocos.numerics.random as random
else:
import numpy as np
import numpy.random as random
Delta_t = T / float(N - 1)
x = [np.full((R,), x0, dtype=numpy.float32),
np.zeros((R,), dtype=numpy.float32)]
v = [np.full((R,), v0, dtype=numpy.float32),
np.zeros((R,), dtype=numpy.float32)]
sqrt_delta_t = math.sqrt(Delta_t)
sqrt_one_minus_rho_square = math.sqrt(1 - rho ** 2)
# m = np.array([[rho, sqrt_one_minus_rho_square]])
m = np.zeros((2,), dtype=numpy.float32)
m[0] = rho
m[1] = sqrt_one_minus_rho_square
zero_array = np.zeros((R,), dtype=numpy.float32)
t_current = 0
for t in range(1, N):
t_previous = (t + 1) % 2
t_current = t % 2
# generate antithetic standard normal random variables
dBt = random.randn(R, 2) * sqrt_delta_t
sqrt_v_lag = np.sqrt(v[t_previous])
x[t_current] = x[t_previous] \
+ (mu - 0.5 * v[t_previous]) * Delta_t \
+ np.multiply(sqrt_v_lag, dBt[:, 0])
v[t_current] = v[t_previous] \
+ kappa * (v_bar - v[t_previous]) * Delta_t \
+ sigma_v * np.multiply(sqrt_v_lag, np.dot(dBt, m))
v[t_current] = np.maximum(v[t_current], 0.0)
x = x[t_current]
v = np.maximum(v[t_current], 0.0)
return x, v
The following code computes the option price from simulated price paths of the underlying. It demonstrates how to dynamically choose between Cocos and NumPy based on the type input array. Note that in this particular setup, one would typically use Fourier techniques to price the option rather than Monte Carlo simulation. Simulation techniques can be useful when considering stochastic processes outside the affine framework or more generally whenever the conditional characteristic function of the transition density is costly to evaluate or when considering path-dependent options.
def compute_option_price(r: float,
T: float,
K: float,
x_simulated,
num_pack: tp.Optional[types.ModuleType] = None):
"""
Compute the function of a plain-vanilla call option from simulated
log-returns.
:param r: the risk-free rate
:param T: the time to expiration
:param K: the strike price
:param x_simulated: a numeric array of simulated log prices of the underlying
:param num_pack: a module - either numpy or cocos.numerics
:return: option price
"""
if not num_pack:
use_gpu, num_pack = get_gpu_and_num_pack_by_dtype(x_simulated)
return math.exp(-r * T) \
* num_pack.mean(num_pack.maximum(num_pack.exp(x_simulated) - K, 0))
Cocos can compile symbolic arrays defined using SymPy to GPU or CPU code.
As an example, consider the following vector valued function.
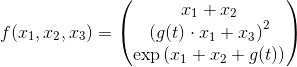 .
.
Here g is a scalar valued function that can be specified at a later point when
numerical evaluation is of interest.
One reason for this setup would be to retain generality.
Another reason might be that a symbolic representation of this function is not
available but one has access to an algorithm (a Python function) that can compute g.
The goal is to evaluate this function at many x = (x_1, x_2, x_3) in parallel on a GPU.
In order to specify this function using SumPy, begin by defining symbolic arguments
x1, x2, x3, t = sym.symbols('x1, x2, x3, t')
Separate the state symbols 'x1', 'x2', and 'x3' from the time symbol 't' and collect them in a tuple
argument_symbols = (x1, x2, x3)
Declare an as of yet unspecified function g
g = sym.Function('g')
Define the function f
f = sym.Matrix([[x1 + x2], [(g(t) * x1 + x3) ** 2], [sym.exp(x1 + x2 + g(t))]])
Compute the Jacobian of g w.r.t x1, x2, and x3 symbolically
jacobian_f = f.jacobian([x1, x2, x3])
Specify the concrete form of g as g(t) = ln(t)
def numeric_time_function(t: float):
return np.log(t)
Convert the symbolic array expression to an object that can evaluated numerically on the cpu or gpu
jacobian_f_lambdified \
= LambdifiedMatrixExpression(
argument_symbols=argument_symbols,
time_symbol=t,
symbolic_matrix_expression=jacobian_f,
symbolic_time_function_name_to_numeric_time_function_map={'g': numeric_time_function})
Generate n = 10000000 random vectors for x1, x2, and x3 at which to evaluate the function in parallel
n = 10000000 X_gpu = cn.random.rand(n, 3) X_cpu = np.array(X_gpu)
Numerically evaluate the Jacobian on the GPU for t=1
jacobian_f_numeric_gpu = \
(jacobian_f_lambdified
.evaluate_with_kwargs(x1=X_gpu[:, 0],
x2=X_gpu[:, 1],
x3=X_gpu[:, 2],
t=1.0))
Numerically evaluate the Jacobian on the CPU for t=1
jacobian_f_numeric_gpu = \
(jacobian_f_lambdified
.evaluate_with_kwargs(x1=X_cpu[:, 0],
x2=X_cpu[:, 1],
x3=X_cpu[:, 2],
t=1.0))
Verify that the results match
print(f'numerical results from cpu and gpu match: '
f'{np.allclose(jacobian_f_numeric_gpu, jacobian_f_numeric_cpu)}')
cocos.scientific.kde import gaussian_kde is a replacement for SciPy's
scipy.stats.kde.gaussian_kde class that works on the GPU.
GPU support is turned on by setting gpu=True in its constructor.
Evaluating a kernel density estimate from a dataset in the NumPy array points
on a grid in the NumPy array grid works as follows:
from cocos.scientific.kde import gaussian_kde gaussian_kde = gaussian_kde(points, gpu=True) density_estimate = gaussian_kde_cocos.evaluate(grid)
To preserve GPU memory, the evaluation of the KDE can proceed sequentially in batches as follows
density_estimate = gaussian_kde_cocos.evaluate_in_batches(grid, maximum_number_of_elements_per_batch)
where the maximum_number_of_elements_per_batch is the maximum number of data points times
evaluation points to process in a single batch.
The Kernel density estimate can be computed on different points on multiple GPUs in parallel
using the method evaluate_in_batches_on_multiple_gpus as follows
comnpute_device_pool = ComputeDevicePool()
gaussian_kde = gaussian_kde(points, gpu=False)
density_estimate = \
gaussian_kde_cocos.evaluate_in_batches_on_multiple_gpus(grid,
maximum_number_of_elements_per_batch,
comnpute_device_pool)
Note that the gpu parameter in the gaussian_kde constructor must be set to false for multi gpu
support and points must be a a NumPy array.
This benchmark compares the runtime performance of the Monte Carlo pi example using NumPy on 1 through 8 cpu cores as well as 1-2 GPUs using Cocos.
The results were produced on a machine with an Intel Core i7 9700K with 128GB of RAM and a NVidia GeForce GTX 1060 running Windows 10. A total of 1000000000 points are drawn in 20 batches.
| Total Time in Seconds | Speedup Compared to NumPy | |
|---|---|---|
| Single Core NumPy | 17.2867612 | 1.0 |
| NumPy with 1 CPU core(s) | 17.1750117 | 1.0065065166738723 |
| NumPy with 2 CPU core(s) | 10.494477000000003 | 1.6472246496895457 |
| NumPy with 3 CPU core(s) | 8.422800300000006 | 2.0523769511667025 |
| NumPy with 4 CPU core(s) | 7.082252900000007 | 2.440856242227665 |
| NumPy with 5 CPU core(s) | 6.365301000000002 | 2.715780636296696 |
| NumPy with 6 CPU core(s) | 5.8881023 | 2.935879901407284 |
| NumPy with 7 CPU core(s) | 5.609009299999997 | 3.081963369181793 |
| NumPy with 8 CPU core(s) | 5.667201699999993 | 3.0503169139012685 |
| Cocos Single GPU | 0.17866180000000043 | 96.75689599007711 |
| Cocos with 1 GPU(s) | 0.1841428000000036 | 93.87693246762655 |
| Cocos with 2 GPU(s) | 0.09644749999999647 | 179.23493299464096 |
Package versions used:
- arrayfire: 3.6.4
- arrayfire-python: 3.6.20181017
- cocos: 0.1.14
- CUDA: 9.2
- cupy-cuda92: 6.2.0
- NumPy: 1.16.4
- Python: 3.7.3
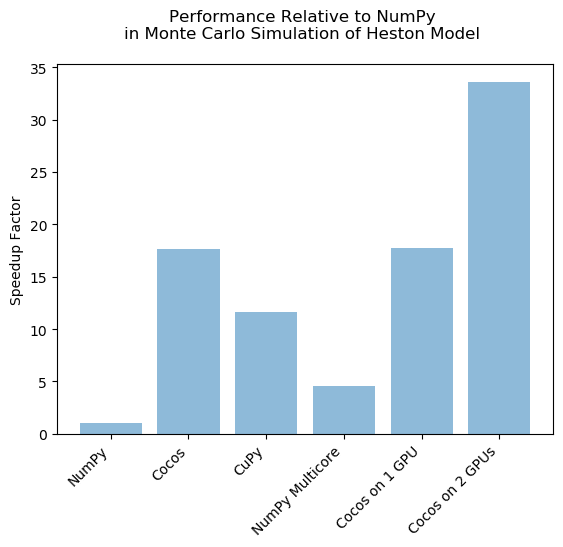
This benchmark compares the runtime performance of the option pricing example under a Heston stochastic volatility model on the CPU using NumPy on a single core as well as on all cores simultaneously and the GPU using Cocos and CuPy. CuPy is another package that provides a NumPy-like API for GPU computing.
The results were produced on a machine with an Intel Core i7 9700K with 128GB of RAM and two NVidia GeForce GTX 1060 running Windows 10. Two Million paths are being simulated with 500 time steps per year.
| Total Time in Seconds | Speedup Compared to NumPy | |
|---|---|---|
| NumPy | 32.782310247421265 | 1.0 |
| Cocos | 1.856126070022583 | 17.661682994960795 |
| CuPy | 2.815166473388672 | 11.64489224964396 |
| NumPy Multicore | 7.143897294998169 | 4.588855199580479 |
| Cocos on 1 GPU | 1.8460988998413086 | 17.757613229843344 |
| Cocos on 2 GPUs | 0.9753890037536621 | 33.60947285776512 |
Package versions used:
- arrayfire: 3.6.4
- arrayfire-python: 3.6.20181017
- cocos: 0.1.14
- CUDA: 9.2
- cupy-cuda92: 6.2.0
- NumPy: 1.16.4
- Python: 3.7.3
Most differences between NumPy and Cocos stem from two sources:
- NumPy is row-major (C style) whereas ArrayFire is column-major (Fortran style).
- Only part of NumPy's functionality is present in ArrayFire, which Cocos is based on.
| Attribute | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| T | Same as self.transpose(), except that self is returned if self.ndim < 2. | |
| H | Conjugate transpose. | attribute is not present in NumPy |
| data | Python buffer object pointing to the start of the array’s data. | attribute not implemented |
| dtype | Data-type of the array’s elements. | |
| flags | Information about the memory layout of the array. | attribute not implemented |
| flat | A 1-D iterator over the array. | attribute not implemented |
| imag | The imaginary part of the array. | |
| real | The real part of the array. | |
| size | Number of elements in the array. | |
| itemsize | Length of one array element in bytes. | |
| nbytes | Total bytes consumed by the elements of the array. | |
| ndim | Number of array dimensions. | |
| shape | Tuple of array dimensions. | |
| strides | Tuple of bytes to step in each dimension when traversing an array. | |
| ctypes | An object to simplify the interaction of the array with the ctypes module. | attribute not implemented |
| base | Base object if memory is from some other object. | attribute not implemented |
| Method | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| all(axis=None) | Returns True if all elements evaluate to True. | parameters "out" and "keepdims" are not supported |
| any(axis=None) | Returns True if any of the elements of a evaluate to True. | parameters "out" and "keepdims" are not supported |
| argmax(axis=None) | Return indices of the maximum values along the given axis. | parameter "out" is not supported |
| argmin(axis=None) | Return indices of the minimum values along the given axis of a. | parameter "out" is not supported |
| argpartition | Returns the indices that would partition this array. | method not implemented |
| argsort(axis=-1, ascending=True) | Returns the indices that would sort this array. | has additional parameter "ascending"; does not support parameters "kind" and "order" |
| astype(dtype) | Copy of the array, cast to a specified type. | does not support parameters "order", "casting", "subok", and "copy" |
| byteswap | Swap the bytes of the array elements | method not implemented |
| choose | Use an index array to construct a new array from a set of choices. | method not implemented |
| clip(min, max) | Return an array whose values are limited to [min, max]. | parameter "out" is not supported |
| compress | Return selected slices of this array along given axis. | method not implemented |
| conj() | Complex-conjugate all elements. | |
| conjugate() | Return the complex conjugate, element-wise. | |
| copy() | Return a copy of the array. | |
| cumprod | Return the cumulative product of the elements along the given axis. | method not implemented |
| cumsum(axis=-1) | Return the cumulative sum of the elements along the given axis. | parameters "dtype" and "out" are not supported |
| diagonal(offset = 0) | Return specified diagonals. | parameters "axis1" and "axis2" are not supported |
| dot(a, b) | Dot product of two arrays. | parameter "out" is not supported |
| dump | Dump a pickle of the array to the specified file. | method not implemented |
| dumps | Returns the pickle of the array as a string. | method not implemented |
| fill(value) | Fill the array with a scalar value. | |
| flatten() | Return a copy of the array collapsed into one dimension. | parameter "order" is not supported; flattens array column by column in contrast to numpy, which operates row by row (may be changed in the future) |
| getfield | Returns a field of the given array as a certain type. | method not implemented |
| item(*args) | Copy an element of an array to a standard Python scalar and return it. | implemented indirectly and therefore slow |
| itemset(*args) | Insert scalar into an array (scalar is cast to array’s dtype, if possible) | implemented indirectly and therefore slow |
| max(axis=None) | Return the maximum along a given axis. | parameter "out" is not supported; different criterion from numpy for complex arrays |
| mean(axis=None) | Returns the average of the array elements along given axis. | parameters "dtype", "out", and "keepdims" are not supported |
| min(axis=None) | Returns the average of the array elements along given axis. | parameter "out" is not supported; different criterion from numpy for complex arrays |
| newbyteorder | Return the array with the same data viewed with a different byte order. | method not implemented |
| nonzero | Return the indices of the elements that are non-zero. | does not support arrays with more than three axis |
| partition | Rearranges the elements in the array in such a way that value of the element in kth position is in the position it would be in a sorted array. | method not implemented |
| prod(axis=None) | Return the product of the array elements over the given axis | parameters "dtype", "out", and "keepdims" are not supported |
| ptp | Peak to peak (maximum - minimum) value along a given axis. | parameter "out" is not supported; different output from numpy for complex arrays due to differences of min and max criteria compared to numpy |
| put | Set a.flat[n] = values[n] for all n in indices. | method not implemented; straightforward once the attribute "flat" has been implemented |
| ravel | Return a flattened array. | method not implemented |
| repeat(repeats, axis=None) | Repeat elements of an array. | order is reversed compared to numpy (see remarks for the method flatten) |
| reshape(shape) | Returns an array containing the same data with a new shape. | parameter "order" is not supported |
| resize(newshape) | Change shape and size of array in-place. | method not implemented |
| round() | Return a with each element rounded to the given number of decimals. | parameters "decimals" and "out" are not supported |
| searchsorted | Find indices where elements of v should be inserted in a to maintain order. | method not implemented |
| setfield | Put a value into a specified place in a field defined by a data-type. | method not implemented |
| setflags | Set array flags WRITEABLE, ALIGNED, and UPDATEIFCOPY, respectively. | method not implemented |
| sort(axis=-1, ascending=True) | Sort an array, in-place. | has additional parameter "ascending"; parameters "kind" and "order" are not supported |
| squeeze(axis=None) | Remove single-dimensional entries from the shape of a. | |
| std(axis=None) | Returns the standard deviation of the array elements along given axis. | parameters "dtype", "out", "ddof", and "keepdims" are not supported |
| sum(axis=None) | Return the sum of the array elements over the given axis. | parameters "dtype", "out, and "keepdims" are not supported |
| swapaxes | Return a view of the array with axis1 and axis2 interchanged. | method not implemented |
| take | Return an array formed from the elements of a at the given indices. | method not implemented |
| tobytes | Construct Python bytes containing the raw data bytes in the array. | method not implemented; could be implemented by first converting to numpy array for instance |
| tofile | Write array to a file as text or binary (default). | method not implemented; could be implemented by first converting to numpy array for instance |
| tolist | Return the array as a (possibly nested) list. | method not implemented; could be implemented by first converting to numpy array for instance |
| tostring | Construct Python bytes containing the raw data bytes in the array. | method not implemented; could be implemented by first converting to numpy array for instance |
| trace(offset=0) | Return the sum along diagonals of the array. | parameters "axis1", "axis2", "dtype", and "out" are not supported |
| transpose() | Returns a new array with axes transposed. | parameter "*axis" is not supported; look into arrayfire function "moddims" to support *axis; new array is not a view on the old data |
| var(axis=None, ddof=0) | Returns the variance of the array elements, along given axis. | parameters "dtype", "out", and "keepdims" are not supported |
| view | New view of array with the same data. | method not implemented |
| Function | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| amin | Return the minimum of an array or minimum along an axis. | function not implemented |
| amax | Return the maximum of an array or maximum along an axis. | function not implemented |
| nanmin | Return minimum of an array or minimum along an axis, ignoring any NaNs. | function not implemented |
| nanmax | Return the maximum of an array or maximum along an axis, ignoring any NaNs. | function not implemented |
| ptp(a, axis=None) | Range of values (maximum - minimum) along an axis. | parameter "out" not supported |
| percentile | Compute the qth percentile of the data along the specified axis. | function not implemented |
| nanpercentile | Compute the qth percentile of the data along the specified axis, while ignoring nan values. | function not implemented |
| Function | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| median | Compute the median along the specified axis. | parameters "out", "overwrite_input"=False, and "keepdims" are not supported |
| average(a, axis=None, weights=None) | Compute the weighted average along the specified axis. | parameter "returned" is not supported; does not work on Mac OS X with AMD chip when weights are given |
| mean(a, axis=None) | parameters "dtype", "out", and "keepdims" are not supported | |
| std(a, axis=None, ddof=0) | Compute the arithmetic mean along the specified axis. | parameters "dtype", "out", and "keepdims" are not supported |
| var(a, axis=None, ddof=0) | Compute the variance along the specified axis. | parameters "dtype", "out", and "keepdims" are not supported |
| nanmedian | Compute the median along the specified axis, while ignoring NaNs. | function not implemented |
| nanmean | Compute the arithmetic mean along the specified axis, ignoring NaNs. | function not implemented |
| nanstd | Compute the standard deviation along the specified axis, while ignoring NaNs. | function not implemented |
| nanvar | Compute the variance along the specified axis, while ignoring NaNs. | function not implemented |
| Function | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| corrcoeff(x, bias=False, ddof=None | Return Pearson product-moment correlation coefficients. | parameters "y" and "rowvar" are not supported |
| correlate | Cross-correlation of two 1-dimensional sequences. | function not implemented |
| cov(m, bias=False, ddof=None) | Estimate a covariance matrix, given data and weights. | parameters "y", "rowvar", "fweights", and "aweights" are not supported |
| Function | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| histogram | Compute the histogram of a set of data. | function not implemented |
| histogram2d | Compute the bi-dimensional histogram of two data samples. | function not implemented |
| histogramdd | Compute the multidimensional histogram of some data. | function not implemented |
| bincount | Count number of occurrences of each value in array of non-negative ints. | function not implemented |
| digitize | Return the indices of the bins to which each value in input array belongs. | function not implemented |
| Function | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| empty | Return a new array of given shape and type, initializing entries to zero. | in contrast to numpy it initializes entries to zero just like zeros |
| empty_like | Return a new array with the same shape and type as a given array. | in contrast to numpy it initializes entries to zero just like zeros |
| eye(N, M=None, k=0, dtype=np.float32) | Return a 2-D array with ones on the diagonal and zeros elsewhere. | |
| identity(n, dtype=np.float32) | Return the identity array. | |
| [ones(shape, dtype=np.float32)](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.ones.html#numpy.ones) | Return a new array of given shape and type, filled with ones. | parameter "order" is not supported |
| [ones_like(a, dtype=None)](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.ones.html#numpy.ones_like) | Return an array of ones with the same shape and type as a given array. | parameters "order" and "subok" are not supported |
| [zeros(shape, dtype=n.float32)](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.ones.html#numpy.zeros) | Return a new array of given shape and type, filled with zeros. | parameter "order" is not supported |
| [zeros_like(a, dtype=None)](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.ones.html#numpy.zeros_like) | Return an array of zeros with the same shape and type as a given array. | parameters "order" and "subok" are not supported |
| [full(shape, fill_value, dtype=n.float32)](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.ones.html#numpy.full) | Return a new array of given shape and type, filled with fill_value. | parameter "order" is not supported |
| [full_like(a, fill_value, dtype=None)](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.ones.html#numpy.full_like) | Return a full array with the same shape and type as a given array. | parameters "order" and "subok" are not supported |
| Function | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| array(object, dtype=None) | Create an array. | parameters "copy", "order", "subok", and "ndmin" are not supported |
| asarray | Convert the input to an array. | function not implemented |
| asanyarray | Convert the input to an ndarray, but pass ndarray subclasses through. | function not implemented |
| ascontiguousarray | Return a contiguous array in memory (C order). | function not implemented |
| asmatrix | Interpret the input as a matrix. | function not implemented |
| copy(a) | Return an array copy of the given object. | parameter "order" is not supported |
| frombuffer | Interpret a buffer as a 1-dimensional array. | function not implemented |
| fromfile | Construct an array from data in a text or binary file. | function not implemented |
| fromfunction | Construct an array by executing a function over each coordinate. | function not implemented |
| fromiter | Create a new 1-dimensional array from an iterable object. | function not implemented |
| fromstring | A new 1-D array initialized from raw binary or text data in a string. | function not implemented |
| loadtxt | Load data from a text file. | function not implemented |
| Function | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| diag(v, k=0) | Extract a diagonal or construct a diagonal array. | |
| diagflat(v, k=0) | Create a two-dimensional array with the flattened input as a diagonal. | |
| tri | An array with ones at and below the given diagonal and zeros elsewhere. | function not implemented |
| tril(m) | Lower triangle of an array. | parameter "k" is not supported |
| triu(m) | Upper triangle of an array. | parameter "k" is not supported |
| vander | Generate a Vandermonde matrix. | function not implemented |
| Function | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| copyto | Copies values from one array to another, broadcasting as necessary. | function not implemented |
| Function | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| reshape(a, newshape) | Gives a new shape to an array without changing its data. | parameter "order" is not supported |
| ravel | Return a contiguous flattened array. | function not implemented |
| ndarray.flat | A 1-D iterator over the array. | function not implemented |
| ndarray.flatten | Return a copy of the array collapsed into one dimension. | parameter "order" is not implemented |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| moveaxis | Move axes of an array to new positions. | function not implemented |
| rollaxis(a, axis[, start]) | Roll the specified axis backwards, until it lies in a given position. | function not implemented |
| swapaxes(a, axis1, axis2) | Interchange two axes of an array. | function not implemented |
| ndarray.T | Same as self.transpose(), except that self is returned if self.ndim < 2. | |
| transpose(a) | Permute the dimensions of an array. | parameter "axes" is not supported |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| atleast_1d(*arys) | Convert inputs to arrays with at least one dimension. | function not implemented |
| atleast_2d(*arys) | View inputs as arrays with at least two dimensions. | function not implemented |
| atleast_3d(*arys) | View inputs as arrays with at least three dimensions. | function not implemented |
| broadcast | Produce an object that mimics broadcasting. | function not implemented |
| broadcast_to(array, shape[, subok]) | Broadcast an array to a new shape. | function not implemented |
| broadcast_arrays(*args, **kwargs) | Broadcast any number of arrays against each other. | function not implemented |
| expand_dims(a, axis) | Expand the shape of an array. | function not implemented |
| [squeeze(a, axis=None)](https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-1.13.0/reference/generated/numpy.squeeze.html) | Remove single-dimensional entries from the shape of an array. |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| asarray(a[, dtype, order]) | Convert the input to an array. | function not implemented |
| asanyarray(a[, dtype, order]) | Convert the input to an ndarray, but pass ndarray subclasses through. | function not implemented |
| asmatrix(data[, dtype]) | Interpret the input as a matrix. | function not implemented |
| asfarray(a[, dtype]) | Return an array converted to a float type. | function not implemented |
| asfortranarray(a[, dtype]) | Return an array laid out in Fortran order in memory. | function not implemented |
| ascontiguousarray(a[, dtype]) | Return a contiguous array in memory (C order). | function not implemented |
| asarray_chkfinite(a[, dtype, order]) | Convert the input to an array, checking for NaNs or Infs. | function not implemented |
| asscalar(a) | Convert an array of size 1 to its scalar equivalent. | |
| require(a[, dtype, requirements]) | Return an ndarray of the provided type that satisfies requirements. | function not implemented |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| concatenate((a1, a2, ...), axis=0) | Join a sequence of arrays along an existing axis. | |
| stack(arrays[, axis]) | Join a sequence of arrays along a new axis. | function not implemented |
| column_stack(tup) | Stack 1-D arrays as columns into a 2-D array. | function not implemented |
| dstack(tup) | Stack arrays in sequence depth wise (along third axis). | |
| hstack(tup) | Stack arrays in sequence horizontally (along second axis). | |
| vstack(tup) | Stack arrays in sequence vertically (along first axis). | |
| block(arrays) | Assemble an nd-array from nested lists of blocks. | function not implemented |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| split(ary, indices_or_sections[, axis]) | Split an array into multiple sub-arrays. | function not implemented |
| array_split(ary, indices_or_sections[, axis]) | Split an array into multiple sub-arrays. | function not implemented |
| dsplit(ary, indices_or_sections) | Split array into multiple sub-arrays along the 3rd axis (depth). | function not implemented |
| hsplit(ary, indices_or_sections) | Split an array into multiple sub-arrays horizontally (column-wise). | function not implemented |
| vsplit(ary, indices_or_sections) | Split an array into multiple sub-arrays vertically (row-wise). | function not implemented |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| tile(A, reps) | Construct an array by repeating A the number of times given by reps. | |
| repeat(a, repeats[, axis]) | Repeat elements of an array. | function not implemented |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| delete(arr, obj[, axis]) | Return a new array with sub-arrays along an axis deleted. | function not implemented |
| insert(arr, obj, values[, axis]) | Insert values along the given axis before the given indices. | function not implemented |
| append(arr, values[, axis]) | Append values to the end of an array. | function not implemented |
| resize(a, new_shape) | Return a new array with the specified shape. | function not implemented |
| trim_zeros(filt[, trim]) | Trim the leading and/or trailing zeros from a 1-D array or sequence. | function not implemented |
| unique(ar[, return_index, return_inverse, ...]) | Find the unique elements of an array. | function not implemented |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| flip(m, axis) | Reverse the order of elements in an array along the given axis. | |
| fliplr(m) | Flip array in the left/right direction. | |
| flipud(m) | Flip array in the up/down direction. | |
| reshape(a, newshape) | Gives a new shape to an array without changing its data. | parameter "order" is not supported |
| roll(a, shift, axis=None) | Roll array elements along a given axis. | |
| rot90(m[, k, axes]) | Rotate an array by 90 degrees in the plane specified by axes. | function not implemented |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| bitwise_and(x1, x2) | Compute the bit-wise AND of two arrays element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", and "extobj" are not supported |
| bitwise_or(x1, x2) | Compute the bit-wise OR of two arrays element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", and "extobj" are not supported |
| bitwise_xor(x1, x2) | Compute the bit-wise XOR of two arrays element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", and "extobj" are not supported |
| invert(x) | Compute bit-wise inversion, or bit-wise NOT, element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", and "extobj" are not supported |
| left_shift(x1, x2) | Shift the bits of an integer to the left. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", and "extobj" are not supported |
| right_shift(x1, x2) | Shift the bits of an integer to the right. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", and "extobj" are not supported |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| take(a, indices[, axis, out, mode]) | Take elements from an array along an axis. | function not implemented |
| choose(a, choices[, out, mode]) | Construct an array from an index array and a set of arrays to choose from. | function not implemented |
| compress(condition, a[, axis, out]) | Return selected slices of an array along given axis. | function not implemented |
| diag(v, k=0) | Extract a diagonal or construct a diagonal array. | |
| diagonal(a[, offset, axis1, axis2]) | Return specified diagonals. | function not implemented |
| select(condlist, choicelist[, default]) | Return an array drawn from elements in choicelist, depending on conditions. | function not implemented |
| lib.stride_tricks.as_strided(x[, shape, ...]) | Create a view into the array with the given shape and strides. | function not implemented |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| place(arr, mask, vals) | Change elements of an array based on conditional and input values. | function not implemented |
| put(a, ind, v[, mode]) | Replaces specified elements of an array with given values. | function not implemented |
| putmask(a, mask, values) | Changes elements of an array based on conditional and input values. | function not implemented |
| fill_diagonal(a, val[, wrap]) | Fill the main diagonal of the given array of any dimensionality. | function not implemented |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| nditer | Efficient multi-dimensional iterator object to iterate over arrays. | function not implemented |
| ndenumerate(arr) | Multidimensional index iterator. | function not implemented |
| ndindex(*shape) | An N-dimensional iterator object to index arrays. | function not implemented |
| flatiter | Flat iterator object to iterate over arrays. | function not implemented |
| lib.Arrayterator(var[, buf_size]) | Buffered iterator for big arrays. | function not implemented |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| dot(a, b) | Dot product of two arrays. | parameter "out" is not supported |
| linalg.multi_dot(arrays) | Compute the dot product of two or more arrays in a single function call, while automatically selecting the fastest evaluation order. | function not implemented |
| vdot(a, b) | Return the dot product of two vectors. | |
| inner(a, b) | Inner product of two arrays. | function not implemented |
| outer(a, b) | Outer product of two arrays. | function not implemented |
| matmul(a, b[, out]) | Matrix product of two arrays. | only handles 2d arrays |
| tensordot(a, b[, axes]) | Compute tensor dot product along specified axes for arrays >= 1-D. | function not implemented |
| einsum(subscripts, *operands[, out, dtype, ...]) | Evaluates the Einstein summation convention on the operands. | function not implemented |
| linalg.matrix_power(M, n) | Raise a square matrix to the (integer) power n. | function not implemented |
| kron(a, b) | Kronecker product of two arrays. | function not implemented |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| linalg.cholesky(a) | Cholesky decomposition. | |
| linalg.qr(a) | Compute the qr factorization of a matrix. | parameter "mode" is not supported |
| linalg.svd(a[, full_matrices, compute_uv]) | Singular Value Decomposition. |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| linalg.eig(a) | Compute the eigenvalues and right eigenvectors of a square array. | function not implemented |
| linalg.eigh(a[, UPLO]) | Return the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a Hermitian or symmetric matrix. | function not implemented |
| linalg.eigvals(a) | Compute the eigenvalues of a general matrix. | function not implemented |
| linalg.eigvalsh(a[, UPLO]) | Compute the eigenvalues of a Hermitian or real symmetric matrix. | function not implemented |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| linalg.norm(x[, ord, axis, keepdims]) | Matrix or vector norm. | parameter "keepdims" is not supported |
| linalg.cond(x[, p]) | Compute the condition number of a matrix. | function not implemented |
| linalg.det(a) | Compute the determinant of an array. | function not implemented |
| linalg.matrix_rank(M, tol=None) | Return matrix rank of array using SVD method | |
| linalg.slogdet(a) | Compute the sign and (natural) logarithm of the determinant of an array. | function not implemented |
| trace(a, offset=0) | Return the sum along diagonals of the array. | parameters "axis1", "axis2", "dtype", and "out" are not supported |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| linalg.solve(a, b) | Solve a linear matrix equation, or system of linear scalar equations. | additional parameter "trans" indicating whether the argument should be transposed |
| linalg.tensorsolve(a, b[, axes]) | Solve the tensor equation a x = b for x. | function not implemented |
| linalg.lstsq(a, b[, rcond]) | Return the least-squares solution to a linear matrix equation. | function not implemented |
| linalg.inv(a) | Compute the (multiplicative) inverse of a matrix. | |
| linalg.pinv(a[, rcond]) | Compute the (Moore-Penrose) pseudo-inverse of a matrix. | function not implemented |
| linalg.tensorinv(a[, ind]) | Compute the ‘inverse’ of an N-dimensional array. |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| all(a, axis=None) | Test whether all array elements along a given axis evaluate to True. | parameters "out" and "keepdims" are not supported |
| any(a, axis=None) | Test whether any array element along a given axis evaluates to True. | parameters "out" and "keepdims" are not supported |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| isfinite(x) | Test element-wise for finiteness (not infinity or not Not a Number). | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", and "extobj" are not supported |
| isinf(x) | Test element-wise for positive or negative infinity. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", and "extobj" are not supported |
| isnan(x) | Test element-wise for NaN and return result as a boolean array. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", and "extobj" are not supported |
| isneginf(x) | Test element-wise for negative infinity, return result as bool array. | parameter "out" is not supported |
| isposinf(x) | Test element-wise for positive infinity, return result as bool array. | parameter "out" is not supported |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| iscomplex(x) | Returns a bool array, where True if input element is complex. | function not implemented |
| iscomplexobj(x) | Check for a complex type or an array of complex numbers. | |
| isfortran(a) | Returns True if the array is Fortran contiguous but not C contiguous. | |
| isreal(x) | Returns a bool array, where True if input element is real. | function not implemented |
| isrealobj(x) | Return True if x is a not complex type or an array of complex numbers. | |
| isscalar(num) | Returns True if the type of num is a scalar type. |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| logical_and(x1, x2) | Compute the truth value of x1 AND x2 element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| logical_or(x1, x2) | Compute the truth value of x1 OR x2 element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| logical_not(x) | Compute the truth value of NOT x element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| logical_xor(x1, x2) | Compute the truth value of x1 XOR x2 element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| allclose(a, b[, rtol, atol, equal_nan]) | Returns True if two arrays are element-wise equal within a tolerance. | function not implemented |
| isclose(a, b[, rtol, atol, equal_nan]) | Returns a boolean array where two arrays are element-wise equal within a tolerance. | function not implemented |
| array_equal(a1, a2) | True if two arrays have the same shape and elements, False otherwise. | |
| array_equiv(a1, a2) | Returns True if input arrays are shape consistent and all elements equal. | function not implemented |
| greater(x1, x2) | Return the truth value of (x1 > x2) element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| greater_equal(x1, x2) | Return the truth value of (x1 >= x2) element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| less(x1, x2) | Return the truth value of (x1 < x2) element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| less_equal(x1, x2) | Return the truth value of (x1 =< x2) element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| equal(x1, x2) | Return (x1 == x2) element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| not_equal(x1, x2) | Return (x1 != x2) element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| sin(x) | Trigonometric sine, element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| cos(x) | Cosine element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| tan(x) | Compute tangent element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| arcsin(x) | Inverse sine, element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| arccos(x) | Trigonometric inverse cosine, element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| arctan(x) | Trigonometric inverse tangent, element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| hypot(x1, x2) | Given the “legs” of a right triangle, return its hypotenuse. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| arctan2(x1, x2) | Element-wise arc tangent of x1/x2 choosing the quadrant correctly. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| degrees(x, /[, out, where, casting, order, ...]) | Convert angles from radians to degrees. | function not implemented |
| radians(x, /[, out, where, casting, order, ...]) | Convert angles from degrees to radians. | function not implemented |
| unwrap(p[, discont, axis]) | Unwrap by changing deltas between values to 2*pi complement. | function not implemented |
| deg2rad(x, /[, out, where, casting, order, ...]) | Convert angles from degrees to radians. | function not implemented |
| rad2deg(x, /[, out, where, casting, order, ...]) | Convert angles from radians to degrees. | function not implemented |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| sinh(x) | Hyperbolic sine, element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| cosh(x) | Hyperbolic cosine, element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| tanh(x) | Compute hyperbolic tangent element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| arcsinh(x) | Inverse hyperbolic sine element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| arccosh(x) | Inverse hyperbolic cosine, element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| arctanh(x) | Inverse hyperbolic tangent element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| around(a[, decimals, out]) | Evenly round to the given number of decimals. | function not implemented |
| round_(a[, decimals, out]) | Evenly round to the given number of decimals. | function not implemented |
| rint(x, /[, out, where, casting, order, ...]) | Round elements of the array to the nearest integer. | function not implemented |
| fix(x[, out]) | Round to nearest integer towards zero. | function not implemented |
| floor(x) | Return the floor of the input, element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| ceil(x) | Return the ceiling of the input, element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| trunc(x) | Return the truncated value of the input, element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| prod(a, axis=None) | Return the product of array elements over a given axis. | parameters "dtype", "out", and "keepdims" are not supported |
| sum(a, axis=None) | Sum of array elements over a given axis. | parameters "dtype", "out", and "keepdims" are not supported |
| nanprod(a[, axis, dtype, out, keepdims]) | Return the product of array elements over a given axis treating Not a Numbers (NaNs) as ones. | function not implemented |
| nansum(a[, axis, dtype, out, keepdims]) | Return the sum of array elements over a given axis treating Not a Numbers (NaNs) as zero. | function not implemented |
| cumprod(a[, axis, dtype, out]) | Return the cumulative product of elements along a given axis. | function not implemented |
| cumsum(a, axis=None) | Return the cumulative sum of the elements along a given axis. | parameters "dtype" and "out" are not supported |
| nancumprod(a[, axis, dtype, out]) | Return the cumulative product of array elements over a given axis treating Not a Numbers (NaNs) as one. | function not implemented |
| nancumsum(a[, axis, dtype, out]) | Return the cumulative sum of array elements over a given axis treating Not a Numbers (NaNs) as zero. | function not implemented |
| diff(a, n=1, axis=-1) | Calculate the n-th discrete difference along given axis. | |
| ediff1d(ary[, to_end, to_begin]) | The differences between consecutive elements of an array. | function not implemented |
| gradient(f, *varargs, **kwargs) | Return the gradient of an N-dimensional array. | function not implemented |
| cross(a, b[, axisa, axisb, axisc, axis]) | Return the cross product of two (arrays of) vectors. | function not implemented |
| trapz(y[, x, dx, axis]) | Integrate along the given axis using the composite trapezoidal rule. | function not implemented |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| exp(x) | Calculate the exponential of all elements in the input array. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| expm1(x) | Calculate exp(x) - 1 for all elements in the array. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| exp2(x) | Calculate 2**p for all p in the input array. | function not implemented |
| log(x) | Natural logarithm, element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| log10(x) | Return the base 10 logarithm of the input array, element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| log2(x) | Base-2 logarithm of x. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| log1p(x) | Return the natural logarithm of one plus the input array, element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| logaddexp(x1, x2, /[, out, where, casting, ...]) | Logarithm of the sum of exponentiations of the inputs. | function not implemented |
| logaddexp2(x1, x2, /[, out, where, casting, ...]) | Logarithm of the sum of exponentiations of the inputs in base-2. | function not implemented |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| i0(x) | Modified Bessel function of the first kind, order 0. | function not implemented |
| sinc(x) | Return the sinc function. | function not implemented |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| signbit(x, /[, out, where, casting, order, ...]) | Returns element-wise True where signbit is set (less than zero). | function not implemented |
| copysign(x1, x2, /[, out, where, casting, ...]) | Change the sign of x1 to that of x2, element-wise. | function not implemented |
| frexp(x[, out1, out2], / [[, out, where, ...]) | Decompose the elements of x into mantissa and twos exponent. | function not implemented |
| ldexp(x1, x2, /[, out, where, casting, ...]) | Returns x1 * 2**x2, element-wise. | function not implemented |
| nextafter(x1, x2, /[, out, where, casting, ...]) | Return the next floating-point value after x1 towards x2, element-wise. | function not implemented |
| spacing(x, /[, out, where, casting, order, ...]) | Return the distance between x and the nearest adjacent number. | function not implemented |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| add(x1, x2) | Add arguments element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| reciprocal(x) | Return the reciprocal of the argument, element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| negative(x) | Numerical negative, element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| multiply(x1, x2) | Multiply arguments element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| divide(x1, x2) | Divide arguments element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| power(x1, x2) | First array elements raised to powers from second array, element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| subtract(x1, x2) | Subtract arguments, element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| true_divide(x1, x2) | Returns a true division of the inputs, element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| floor_divide(x1, x2) | Return the largest integer smaller or equal to the division of the inputs. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| float_power(x1, x2, /[, out, where, ...]) | First array elements raised to powers from second array, element-wise. | function not implemented |
| fmod(x1, x2, /[, out, where, casting, ...]) | Return the element-wise remainder of division. | function not implemented |
| mod(x1, x2) | Return the element-wise remainder of division. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| modf(x[, out1, out2], / [[, out, where, ...]) | Return the fractional and integral parts of an array, element-wise. | function not implemented |
| remainder(x1, x2) | Return element-wise remainder of division. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| divmod(x1, x2[, out1, out2], / [[, out, ...]) | Return element-wise quotient and remainder simultaneously. | function not implemented |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| angle(z) | Return the angle of the complex argument. | parameter "deg" is not supported |
| real(val) | Return the real part of the complex argument. | |
| imag(val) | Return the imaginary part of the complex argument. | |
| conj(x) | Return the complex conjugate, element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| convolve(a, v[, mode]) | Returns the discrete, linear convolution of two one-dimensional sequences. | function not implemented |
| convolve(a, v[, mode]) | Returns the discrete, linear convolution of two one-dimensional sequences. | function not implemented |
| clip(a, a_min, a_max) | Clip (limit) the values in an array. | parameter "out" is not supported |
| sqrt(x) | Return the positive square-root of an array, element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| cbrt(x) | Return the cube-root of an array, element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| square(x) | Return the element-wise square of the input. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| absolute(x) | Calculate the absolute value element-wise. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| fabs(x, /[, out, where, casting, order, ...]) | Compute the absolute values element-wise. | function not implemented |
| sign(x) | Returns an element-wise indication of the sign of a number. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| heaviside(x1, x2, /[, out, where, casting, ...]) | Compute the Heaviside step function. | function not implemented |
| maximum(x1, x2) | Element-wise maximum of array elements. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| minimum(x1, x2) | Element-wise minimum of array elements. | parameters "out", "where", "casting", "order", "dtype", "subok", "signature", "extobj" are not supported |
| fmax(x1, x2, /[, out, where, casting, ...]) | Element-wise maximum of array elements. | function not implemented |
| fmin(x1, x2, /[, out, where, casting, ...]) | Element-wise minimum of array elements. | function not implemented |
| nan_to_num(x[, copy]) | Replace nan with zero and inf with finite numbers. | function not implemented |
| real_if_close(a[, tol]) | If complex input returns a real array if complex parts are close to zero. | function not implemented |
| interp(x, xp, fp[, left, right, period]) | One-dimensional linear interpolation. | function not implemented |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| rand(d0, d1, ..., dn) | Random values in a given shape. | |
| randn(d0, d1, ..., dn) | Return a sample (or samples) from the “standard normal” distribution. | |
| randint(low[, high, size, dtype]) | Return random integers from low (inclusive) to high (exclusive). | |
| random_integers(low[, high, size]) | Random integers of type np.int between low and high, inclusive. | function not implemented |
| random_sample([size]) | Return random floats in the half-open interval [0.0, 1.0). | function not implemented |
| random([size]) | Return random floats in the half-open interval [0.0, 1.0). | function not implemented |
| ranf([size]) | Return random floats in the half-open interval [0.0, 1.0). | function not implemented |
| sample([size]) | Return random floats in the half-open interval [0.0, 1.0). | function not implemented |
| choice(a[, size, replace, p]) | Generates a random sample from a given 1-D array | replace=False and p != None are not supported |
| bytes(length) | Return random bytes. | function not implemented |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| shuffle(x) | Modify a sequence in-place by shuffling its contents. | |
| permutation(x) | Randomly permute a sequence, or return a permuted range. |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| beta(a, b, size=None) | Draw samples from a Beta distribution. | |
| binomial(n, p[, size]) | Draw samples from a binomial distribution. | function not implemented |
| chisquare(df, size=None) | Draw samples from a chi-square distribution. | |
| dirichlet(alpha[, size]) | Draw samples from the Dirichlet distribution. | function not implemented |
| exponential(scale=1.0, size=None) | Draw samples from an exponential distribution. | |
| f(dfnum, dfden[, size]) | Draw samples from an F distribution. | function not implemented |
| gamma(shape, scale=1.0, size=None) | Draw samples from a Gamma distribution. | |
| geometric(p[, size]) | Draw samples from the geometric distribution. | function not implemented |
| gumbel([loc, scale, size]) | Draw samples from a Gumbel distribution. | function not implemented |
| hypergeometric(ngood, nbad, nsample[, size]) | Draw samples from a Hypergeometric distribution. | function not implemented |
| laplace([loc, scale, size]) | Draw samples from the Laplace or double exponential distribution with specified location (or mean) and scale (decay). | function not implemented |
| logistic(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=None) | Draw samples from a logistic distribution. | |
| lognormal(mean=0.0, sigma=1.0, size=None) | Draw samples from a log-normal distribution. | |
| logseries(p[, size]) | Draw samples from a logarithmic series distribution. | function not implemented |
| multinomial(n, pvals[, size]) | Draw samples from a multinomial distribution. | function not implemented |
| multivariate_normal(mean, cov[, size, ...) | Draw random samples from a multivariate normal distribution. | function not implemented |
| negative_binomial(n, p[, size]) | Draw samples from a negative binomial distribution. | function not implemented |
| noncentral_chisquare(df, nonc[, size]) | Draw samples from a noncentral chi-square distribution. | function not implemented |
| noncentral_f(dfnum, dfden, nonc[, size]) | Draw samples from the noncentral F distribution. | function not implemented |
| normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=None) | Draw random samples from a normal (Gaussian) distribution. | |
| pareto(a[, size]) | Draw samples from a Pareto II or Lomax distribution with specified shape. | function not implemented |
| poisson([lam, size]) | Draw samples from a Poisson distribution. | function not implemented |
| power(a[, size]) | Draws samples in [0, 1] from a power distribution with positive exponent a - 1. | function not implemented |
| rayleigh([scale, size]) | Draw samples from a Rayleigh distribution. | function not implemented |
| standard_cauchy([size]) | Draw samples from a standard Cauchy distribution with mode = 0. | function not implemented |
| standard_exponential(size=None) | Draw samples from the standard exponential distribution. | |
| standard_gamma(shape, size=None) | Draw samples from a standard Gamma distribution. | |
| standard_normal(size=None) | Draw samples from a standard Normal distribution (mean=0, stdev=1). | |
| standard_t(df[, size]) | Draw samples from a standard Student’s t distribution with df degrees of freedom. | function not implemented |
| triangular(left, mode, right[, size]) | Draw samples from the triangular distribution over the interval [left, right]. | function not implemented |
| uniform(low=0.0, high=1.0, size=None) | Draw samples from a uniform distribution. | |
| vonmises(mu, kappa[, size]) | Draw samples from a von Mises distribution. | function not implemented |
| wald(mean, scale, size=None) | Draw samples from a Wald, or inverse Gaussian, distribution. | |
| weibull(a[, size]) | Draw samples from a Weibull distribution. | function not implemented |
| zipf(a[, size]) | Draw samples from a Zipf distribution. | function not implemented |
| function | description | notes |
|---|---|---|
| seed(seed=None) | Seed the generator. | |
| get_seed() | Returns the current seed of the generator. | function has no counterpart in numpy |
| get_state() | Return a tuple representing the internal state of the generator. | function not implemented |
| set_state(state) | Set the internal state of the generator from a tuple. | function not implemented |
- Requires Python 3.7 or higher.
- Arrays may have no more than 4 axes.
- Cocos provides only a subset of NumPy's functions and methods. In many cases, Cocos does not support all of the parameters of its corresponding NumPy function or method.
- Trailing singleton dimensions are cut off, e.g. there is no difference between an array with shape (2, 2, 1) and an array with shape (2, 2) in Cocos.
- Matrix multiplication is not supported for integer types.
Cocos implements multi-GPU functionality via process-based parallelism (one process per GPU device). It is recommended to have at least one physical CPU core per GPU in the system in order to prevent 'starving' the GPUs.
MIT License
Copyright (c) 2019 Michael Nowotny
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.