____ __ ____ __
/ __ )________ ____ ______/ /_ / __ \____ _____/ /___ ______
/ __ / ___/ _ \/ __ `/ ___/ __ \/ /_/ / __ `/ __ / __ `/ ___/
/ /_/ / / / __/ /_/ / /__/ / / / _, _/ /_/ / /_/ / /_/ / /
/_____/_/ \___/\__,_/\___/_/ /_/_/ |_|\__,_/\__,_/\__,_/_/
Krystian Bajno 2024
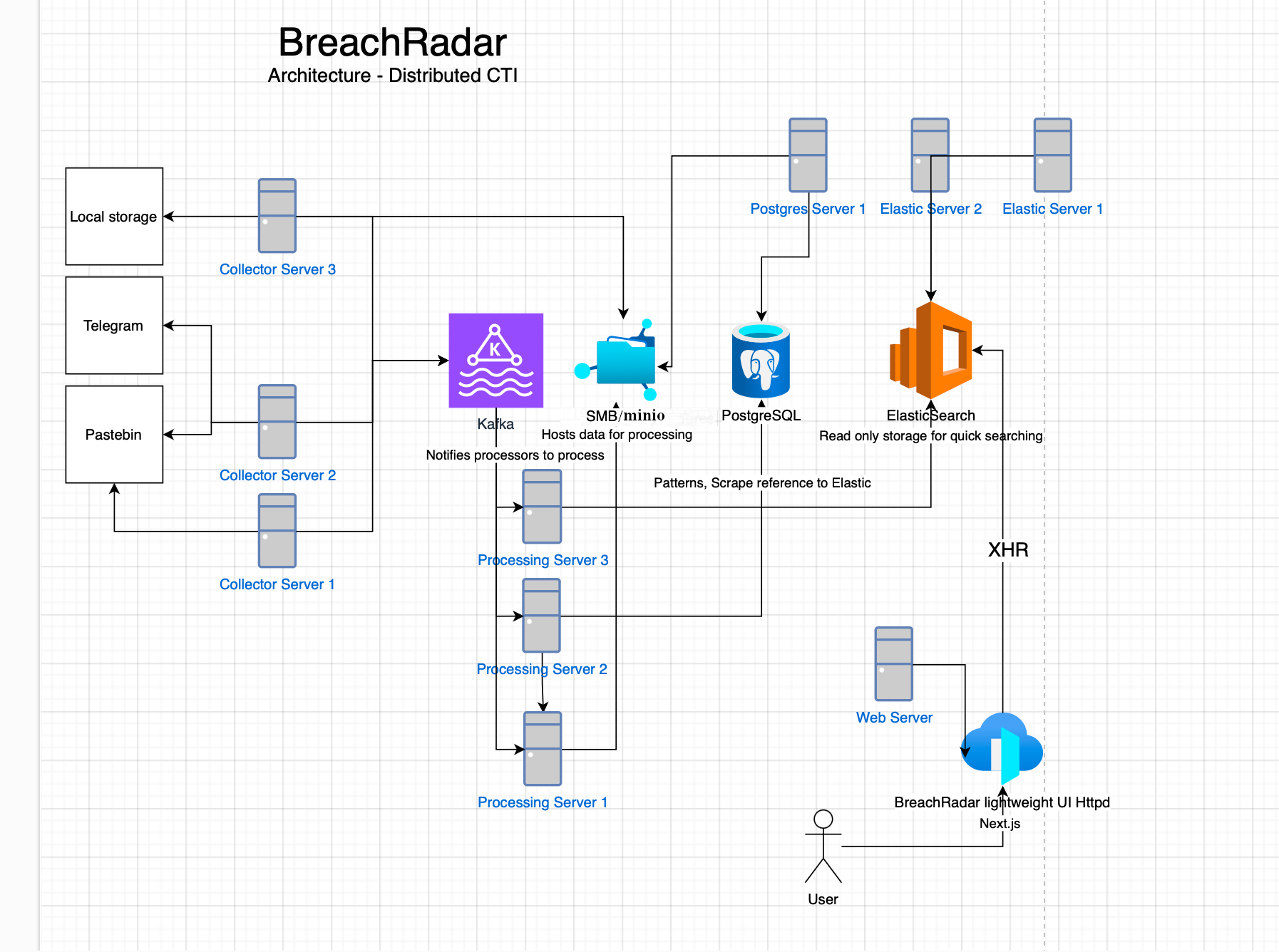
BreachRadar is an open-source Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) platform designed to collect and process data from various sources to detect potential security breaches and leaked credentials. It operates using Elasticsearch, PostgreSQL, SMB/min.io, and Kafka. The plugin-based system allows for integration of new collectors, processors, and data analysis tools.
Swiss-army knife for credentials. A lightweight Rust CLI tool for local data ingestion and Elastic search using CLI, compatible with BreachRadar.
# commands/microradar
cd commands/microradar
cargo build --release
./microradar ingest <input directory> # ingest data from selected directory
./microradar search <searchterm> # search elastic using CLI
./microradar scan <file> # scan file for credentials inside.
./microradar scan <file> --offline # do not use postgreSQL when scanningCopy the plugin into plugins/ directory. The framework will detect and run it automatically. To disable the plugin, navigate to plugin directory and edit config.yaml. Set enabled to false.
Due to sensitive nature of sources and operations, plugins are kept private and separate from core..
- local_plugin - Read data from the local storage -
./data/local_ingestdirectory (default).
- Run
python3 -m venv venv,source venv/bin/activate, andpip install -r requirements.txt - Run
docker-compose upto start Kafka, PostgreSQL, and ElasticSearch. - Compile rust_bindings as they contain Rust PyO3, using
maturin build --releaseandpip install target/wheels/*.whl. - Compile plugins if needed, as they may contain Rust PyO3, using
maturin build --releaseandpip install target/wheels/*.whl. - Run
main.pyto setup the database, indexes, and start collection and processing services. - Run
npm install,npm run build, andnpm run startinwebui/directory to start Web UI service.
You can distribute and scale these components on many machines in order to get a good performance through terabytes of data.
In order to disable processing or collection, modify config.yaml and set
processing: false
# or
collecting: falseThe core system consists of the following main components:
- Collection and processing agent (
main.py) - ElasticSearch - Stores processed data and provides powerful search capabilities.
- Kafka - Is an event queue.
- min.io/SMB Server - Hosts scrapes data to process.
- PostgreSQL - Stores scrap metadata, tracks processing.
- WebUI - Allows to search and analyze data through a web interface connected to ElasticSearch.
- Follow the directory structure of
local_plugin. - Collectors' classnames must end with
Collector, Processors' classnames must end withProcessor, Providers' classnames must end withProvider. - Plugins must have a provider registering the plugin in
registermethod and must extendPluginProviderclass. - In order to register and use a service inside plugin, use the
Appobject passed to a plugin provider and the.make()and.bind()methods.
- Plugins can use
Corecomponents freely. - Collectors implement PluginCollectorInterface and must define a
collectmethod. - Collectors implement PluginCollectorInterface and must define a
postprocessmethod. - Processors implement PluginProcessorInterface with
can_processandprocessmethods. - Processors decide whether they can process a scrap based on
can_process.
- OpenCTI integration
- RecordedFuture integration
- Implement analysis and
basic_analysisplugin.