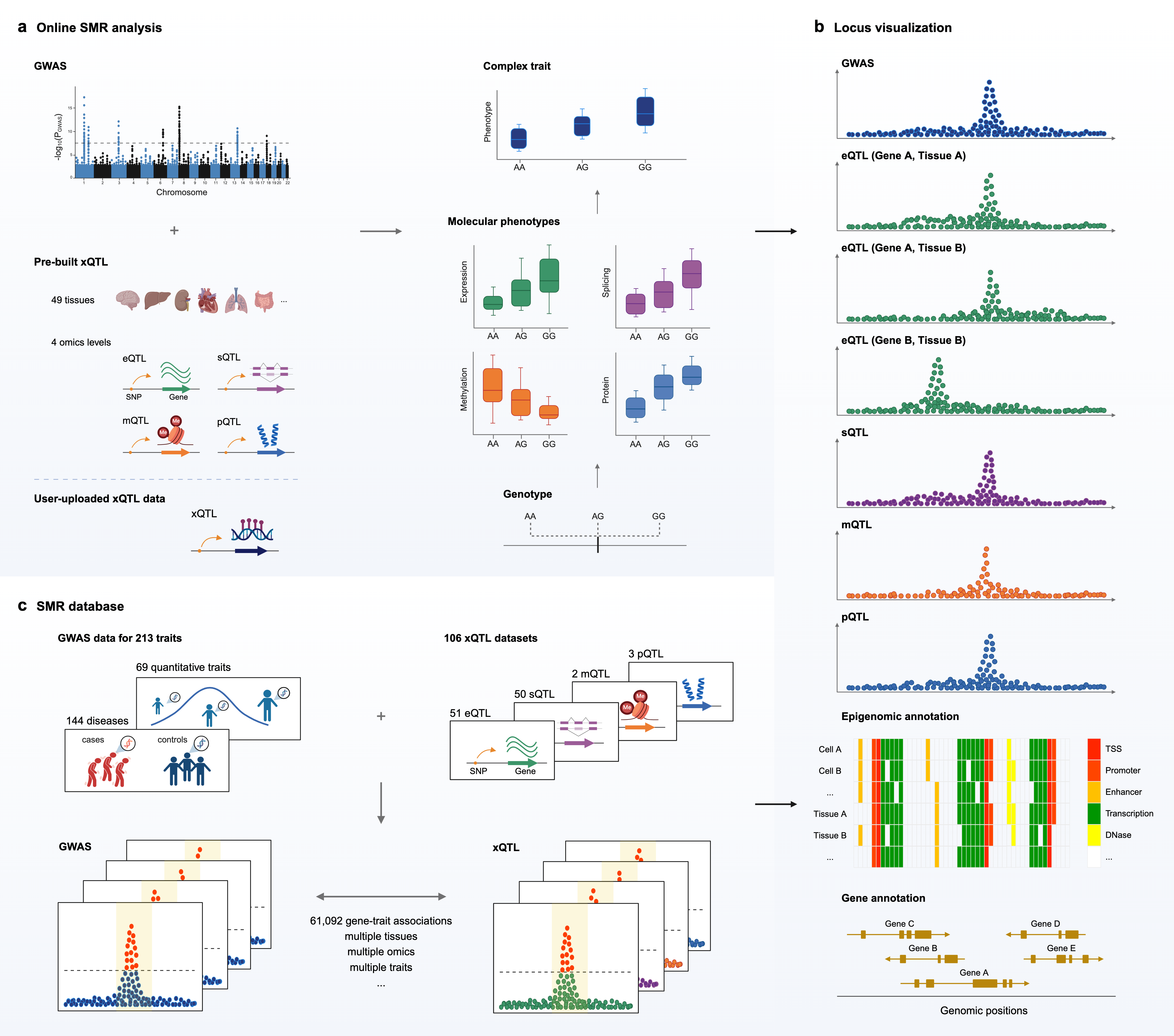
SMR Portal is a web-based platform designed for the integrative analysis of genome-wide association study (GWAS) and molecular quantitative trait locus (xQTL) summary statistics to identify genes associated with complex traits, including diseases, using the summary-data-based Mendelian Randomization (SMR) and HEIDI (Heterogeneity in Dependent Instruments) methods. It comprises three modules: online SMR analysis, locus visualization, and SMR database. It aims to facilitate the discovery of complex trait genes, to elucidate the regulatory mechanisms underlying GWAS signals, and to enhance the accessibility of these gene-trait associations for the research community.
The online SMR analysis module simplifies the SMR & HEIDI analysis processes so that users only need to provide GWAS summary statistics for a trait of interest. The platform provides users with access to 106 pre-built xQTL summary datasets, including 51 eQTL, 50sQTL, 2 mQTL and 3 pQTL datasets, spanning 4 omics layers, and 49 tissues (SMR_Portal_Supplementary.xlsx). Additionally, it offers users the flexibility to upload their own customized xQTL data. An online log file is available for users to monitor the progress of the analysis. Upon completion of the online SMR analyses, an email notification containing a hyperlink is sent to the designated email address, allowing users to access and visualize the results in the SMR-Portal.
The SMR database is a continuously updated resource with visualization capabilities for pre-computed SMR results, covering a broad spectrum of complex traits with available large-scale GWAS summary statistics. It catalogues over 61,092 significant gene-trait associations derived from SMR & HEIDI analyses, encompassing 213 GWAS traits (SMR_Portal_Supplementary.xlsx) and 106 xQTL datasets. Users can query a gene or trait of interest, and the database will display significant gene-trait associations across various xQTL datasets, spanning multiple omics layers and tissues.
The locus visualization module provides interactive tools for visualizing GWAS, xQTL, and SMR association signals, along with genomic and epigenomic annotations in the locus identified by SMR & HEIDI. The visualization begins with the GWAS locus plot and the xQTL locus plots for molecular phenotypes associated with traits; the primary purpose of these plots is to show whether the GWAS signals coincide with the xQTL signals (i.e., the pleiotropy or causality model). Below the locus plots, a heatmap illustrates the chromatin states of the specified region across different cell types or tissues, using data from the Roadmap Epigenomics Mapping Consortium (REMC). These epigenomic annotations assist users in identifying functional elements, such as promoters, transcribed regions, and enhancers, along with their potential cell or tissue type specificity. In summary, the locus visualization module enhances our understanding of genetic regulatory mechanisms by demonstrating how genetic variants, potentially located within functional elements, affect one or more traits through molecular phenotypes.
SMR Portal (https://yanglab.westlake.edu.cn/software/smr_portal)
SMR software (https://yanglab.westlake.edu.cn/software/smr)
Yang Lab (https://yanglab.westlake.edu.cn)
For those interested in exploring the SMR Portal, a tutorial is available at Tutorial.md
To ensure the security of your data, you must log in to submit your GWAS summary data for the online SMR analysis. If you have not yet registered, you can do so here. For those interested, a demo is available in data/demo.
Should you have any questions, suggestions, or encounter any issues, please reach out to us at [email protected].
Online tool and database: Guo Y, Xu T, Luo J, Jiang Z, Chen W, Chen H, Qi T, Yang J (2024) SMR-Portal: an online platform for integrative analysis of GWAS and xQTL data to identify complex trait genes. Nature Methods.
SMR and HEIDI methods: Zhu Z, Zhang F, Hu H, Bakshi A, Robinson MR, Powell JE, Montgomery GW, Goddard ME, Wray NR, Visscher PM & Yang J (2016) Integration of summary data from GWAS and eQTL studies predicts complex trait gene targets. Nature Genetics, 48:481-487.