-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 3.7k
Logic
Boolean logic is a simple mathematical system that has two values:
- true
- false
Logic blocks are generally used to control conditional blocks and repeat blocks.
Here's an example:

If the value of the variable x is greater than 100, the condition is true, and the text "What a big number!" is printed. If the value of x is not greater than 100, the condition is false, and "That's not very big." is printed.
Boolean values can also be stored in variables and passed to functions, the same as number, text, and list values.
If a block expects a Boolean value as an input, it usually interprets an absent input as false. An example is provided below. Non-Boolean values cannot be directly plugged in where Boolean values are expected, although it is possible (but inadvisable) to store a non-Boolean value in a variable, then plug that into the input. Neither of these practices are recommended, and their behaviour could change in future versions of Blockly.
A single block, with a dropdown specifying either true or false, can be used to get a Boolean value:

There are six comparison operators. Each takes two inputs (normally numbers) and returns true or false depending on how the inputs compare with each other.

The six operators are: equals, not equals, less than, greater than, less than or equal, greater than or equal.
The and block will return true only if both of its two inputs are also true.
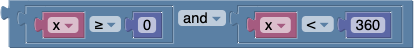
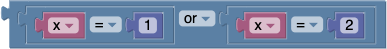
The or block will return true if either of its two inputs are true.
The not block converts its Boolean input into its opposite. For example, the result of:

is false.
As mentioned above, if no input is provided, a value of true is assumed, so the following block produces the value false:

Leaving an input empty is not recommended, however.
The ternary block acts like a miniature if-else block. It takes three inputs; the first input is the Boolean condition to test, the second input is the value to return if the test was true, the third input is the value to return if the test was false. In the example below, if the variable x is less than 10, then the variable colour is set to red, otherwise the variable colour is set to green.

A ternary block can always be replaced by an if-else block. The following two examples are exactly the same as each other.
