-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 170
Home
Ganglia Web 2 (gweb2) is a refresh of the Ganglia PHP UI. We plan to continue adding new features, and bringing the Ganglia web code up to date after some years of inattention. This page details some of the main new features which will be available in an upcoming release.
It is recommended that you install the PHP JSON extension. It isn't *required*, but it provides better performance than the Net_JSON PEAR extension. The extension is included in PHP 5.2 and later; if you are on 5.1 use `pecl` to install e.g.
pecl install json
`pecl` is part of `php-pear` package on RHEL/CentOS. Make sure you add extension.json to your PHP extensions ie.
# cat /etc/php.d/json.ini extension=json.so
On RHEL/CentOS 4, you will also need `phpize` which comes with the `php-devel` package.
You will also need PHP XML support which is part of e.g. `php-xml` or `php5-xml` package. Without it export of graphs in CSV and JSON format will not work.
Latest release of Ganglia Web 2 can be downloaded from https://sourceforge.net/projects/ganglia/files/gweb/. Download the gweb tarball and unarchive it somewhere in your web tree then rename the resulting directory to a URL you want e.g. `/var/www/ganglia2` (Ubuntu/Debian) or `/var/www/html/ganglia2` (Centos/RHEL) e.g.
tar xvf gweb-1.9.9.2607M.tar.gz mv gweb-1.9.9.2607M ganglia2
You can run Ganglia Web 2 in parallel to your existing Ganglia UI if you so desire. You can now opt to either run make to create the necessary directory structure or conduct a manual install.
Please edit the Makefile found in the tarball. Adjust the `DESTDIR` to where you copied the files e.g. `/var/www/ganglia2` and `APACHE_USER` is the name of the user that runs the Apache server e.g. `apache` or `www-data` (Ubuntu/Debian). When done type
make install
To install it manually execute following
bash APACHE_USER="apache" DEST_DIR="/var/www/ganglia2" sed -e "s|@varstatedir@|/var/lib|" conf_default.php.in > conf_default.php install -o $APACHE_USER -d /var/lib/ganglia/dwoo install -o $APACHE_USER -d /var/lib/ganglia/conf chown -R $APACHE_USER $DEST_DIR/conf rsync -a $DEST_DIR/conf/ /var/lib/ganglia/conf/
You should now be able to access Ganglia in your browser by going to e.g. http://server/ganglia2/
- you need to copy `/var/www/ganglia2/apache.conf` (Ubuntu/Debian) or `/var/www/html/ganglia2/apache.conf` (CentOS/RHEL) to `/etc/apache2/sites-enabled`.
- In most cases, you need to modify the above apache.conf to make sure the alias /ganglia refers to `/var/www/ganglia2` (Ubuntu up to 13.10/Debian) or `/var/www/html/ganglia2` (CentOS/RHEL/Ubuntu 14.04+) .
- In most cases, you need to modify `/var/www/ganglia2/conf.php` (Ubuntu/Debian) to make sure `gweb_confdir` refers to the directory where the directories of `conf` and `dwoo` locate in, such as `/var/lib/ganglia-web` or `/var/lib/ganglia`.
- Make sure you have the dir of rrds under `gmetad_root` e.g. /var/lib/ganglia/rrds
- Make sure the above RRD files are owned by the same user as one running as gmetad e.g. nobody
All of Ganglia configuration options can be found in `conf_default.php`. If you want to override them you will need to create a `conf.php` file. This way even if you upgrade Gweb 2.0 you will retain your customizations. For example I use the following override file
php
<?php
$conf['default_metric'] = "cpu_report";
$conf['graphreport_stats'] = false;
$conf['rrdtool'] = "env RRD_DEFAULT_FONT='DejaVuSansMono-Roman' /usr/bin/rrdtool";
$conf['rrdcached_socket'] = "/var/run/rrdcached/rrdcached.sock";
$conf['auth_system'] = "disabled";
?>
WARNING: If you end up changing `$conf['gmetad_root']` variable please check any other variables that depend on it like `$conf['conf_dir']` and `$conf['views_dir']`.
You can zoom to arbitrary time on the graph by clicking on any of the graphs in cluster and host views. Click and hold the mouse when you do an outline will show up which will allow you to select time range you want. Once you release the mouse button the whole page will reload and show the new range.
Ganglia has supported the definition of custom graphs via PHP files for some time. Gweb2 continues to support PHP-based graphs, and adds support for JSON-based graphs as well. Defining graphs in JSON is much simpler (you don't need to know any `rrdtool` syntax) and will probably suit most cases. If you need more flexibility than in possible given the syntax supported by the JSON format, then defining a graph in PHP is still an option. In order migrate your PHP-based graphs to Gweb2, you will need to Migrating PHP Graphs to Gweb 2 to your graphs as you copy them to the new install.
If a given report is defined in both PHP and JSON, the PHP file takes precedence.
| Key | Expected Value |
|---|---|
| report_name | Textual name of this report, used to identify the report to the engine. This should be the filename without the '.json' extension. |
| report_type | `standard` or `template`. Use `template` when you are using Graphite rendering, and want GWeb to replace `HOST_CLUSTER` in your Graphite config string with the actual name of the host the graph is for. This value is ignored when rendering with `rrdtool`. |
| graphite | Ampersand separated list of arguments to be passed to Graphite targets. |
| percent | Usually omitted. When specified with a value of '1', the graph is formed with all values being represented as a percentage of the aggregate total of all metrics. |
| title | Used to label the top of the graph. |
| vertical_label | Label for the y-axis. |
| scale | Scaling factor. All values are multiplied by this number before being graphed or displayed in the legend. (Normally omitted, which is equivalent to specifying "1") |
| series | An array of hashes, describing which metrics should be part of the graph. |
| show_total | If defined and set to '1', this adds an aggregate total for all of the displayed metrics to the graph legend. |
`series` member hashes should contain the following values
| Key | Expected Value |
|---|---|
| metric | The name of the metric to graph. Corresponds to an rrd file. |
| color | A hex value to color the line/area for this metric. |
| label | Label text for use in the graph's legend. |
| type | `line`, `stack`, `area` or `percentile`. Difference between stack and area are that if you specify something as a stack is that all stacked values will be stacked on top of each other whereas area types will not be stacked on top of each other. Percentile is a vertical line that displays percentile value for particular metric. Valid values are 0-100. |
| line_width | '1', '2', or '3'. Only relevant for `type`==`line` or `type`==`percentile`. |
| percentile | You need specify percentile value for the percentile line e.g. 75, 95 etc. |
There are certain such as number of nodes (servers) in a cluster that will show only in meta and cluster contexts. You can define those metrics by adding a contexts array to the JSON definition for an item. You can also override the DS (datasource name) to be something other than the default "sum".
json
{
"metric": "cpu_num",
"color": "00FF00",
"label": "Nodes",
"line_width": "2",
"type": "line",
"ds": "num",
"contexts": [ "cluster", "meta" ]
}
If you are using the graphite integration features in GWeb2, you may add additional syntax to a JSON graph file to configure your graph for Graphite rendering. See link:https://github.com/ganglia/ganglia-web/blob/master/graph.d/apache_response_report.json[apache_response_report.json] for an example.
The https://github.com/ganglia/ganglia-web/blob/master/graph.d/[graph.d] directory contains many examples.
link:https://github.com/ganglia/ganglia-web/blob/master/graph.d/network_report.json[network] is a good basic example of a simple 2-line graph.
json
{
"report_name" : "network_report",
"report_type" : "standard",
"title" : "Network",
"vertical_label" : "Bytes/sec",
"series" : [
{ "metric": "bytes_in", "color": "33cc33", "label": "In", "line_width": "2", "type": "line" },
{ "metric": "bytes_out", "color": "5555cc", "label": "Out", "line_width": "2", "type": "line" }
]
}
Example network report graph:

This link:https://github.com/ganglia/ganglia-web/blob/master/graph.d/cpu_report.json[CPU] is set up for use with Graphite. Note that it would be possible to also define a `series` key here, and the report would work with `rrdtool` as well.
json
{
"report_name" : "cpu_report",
"report_type" : "template",
"title" : "CPU",
"graphite" : "target=alias(HOST_CLUSTER.cpu_user.sum,'User')&target=alias(HOST_CLUSTER.cpu_nice.sum%2C'Nice')&target=alias(HOST_CLUSTER.cpu_system.sum,'System')&target=alias(HOST_CLUSTER.cpu_wio.sum,'Wait')&target=alias(HOST_CLUSTER.cpu_idle.sum%2C'Idle')&areaMode=stacked&max=100&colorList=3333bb,ffea00,dd0000,ff8a60,e2e2f2"
}
- http://vuksan.com/blog/2011/02/20/json-representation-for-graphs-in-ganglia/
- http://linux.die.net/man/1/rrdgraph_graph
Aggregate graphs allow you to overlay same metric
.Example aggregate stacked graph
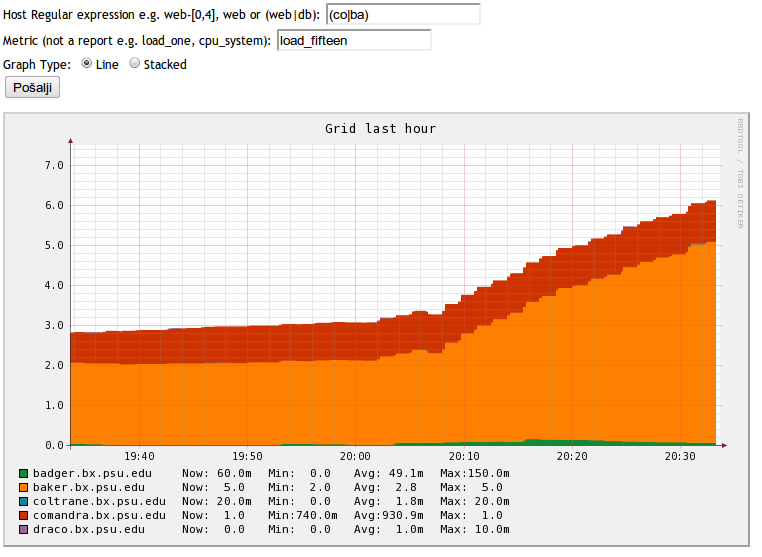
Views are arbitrary collection of metrics. They are useful if you want to have an easy overview of e.g. load on the webservers, DB servers, as well as number of SQL queries on host1.
There are two ways to create/modify views. One is via the Web GUI and the other one programatically by defining views using JSON.
To create views click on the Views tab then Click Create View. Type your name then click Create. Next step is to add metrics to a view.
Above or below each metric or composite graph is a plus sign. Click on it. A window will pop up. Select the view you want the metric to be added. Repeat the process for consecutive metrics.
Views are stored as JSON files in the conf_dir. Default for the conf_dir is in /var/lib/ganglia/conf. You can change that by specifying an alternate directory in conf.php ie.
php $conf['conf_dir'] = "/var/www/html/conf";
You can create or edit existing files. Name for a view needs to start with view_ and end with .json e.g. view_1.json or view_jira_servers.json. It needs to be unique. This is an example definition of a view which will result with a view with 3 different graphs.
| Key | Expected Value |
|---|---|
| view_name | Name of the view |
| view_type | Standard or Regex. Regex view allows you to specify regex to match hosts |
| items | An array of hashes, describing which metrics should be part of the view. |
`items` member hashes should contain the following values
| Key | Expected Value |
|---|---|
| hostname | Hostname of the host for which we want metric/graph displayed |
| metric | Name of the metric e.g. load_one. |
| graph | Graph Name e.g. cpu_report, load_report. You can use only metric or graph keys but not both |
| aggregate_graph | If this value exists and is set to true item defines an aggregate graph. This item needs a hash of regular expressions and a description |
If you add `aggregate_graph` item you need to specify a host_regex_hash that contains list of of regex elements. Please check the example for guidance on how to do it.
You can also embed composite graph/reports as described in the JSON definition above. The only difference is that you are required to add a unique key called item_id to identify the graph e.g.
json
{
"item_id": "abcde",
"report_name" : "load_all_report",
"report_type" : "standard",
"title" : "Load All Report",
"vertical_label" : "load",
"series" : [
{ "hostname": "localhost", "clustername": "unspecified", "metric": "load_one", "color": "9933bb", "label": "95th percentile", "percentile": 95, "line_width": "2", "type": "percentile" },
{ "hostname": "localhost", "clustername": "unspecified", "metric": "load_one", "color": "3333bb", "label": "Load 1", "line_width": "2", "type": "line" },
]
}
json
{
"view_name":"jira",
"items":[
{ "hostname":"web01.domain.com","graph":"cpu_report"},
{ "hostname":"web02.domain.com","graph":"load_report"},
{ "aggregate_graph":"true",
"host_regex":[
{"regex":"web[2-7]"},
{"regex":"web50"}
],
"metric_regex":[
{"regex":"load_one"}
],
"graph_type":"stack",
"title":"Location Web Servers load"
}
],
"view_type":"standard"
}
Automatic rotation is a feature aimed for people in data centers that need to continuously rotate metrics to help spot early signs of trouble. It is intended to work in conjunction with views. To activate it click on Automatic Rotation then select the view you want rotated. Metrics will be rotated until the browser window is closed. You can change the view while the view is rotated and changes will be reflected within one full rotation.
Another powerful thing about automatic rotation is that if you have multiple monitors you can invoke different views to be rotated on different monitors.
Mobile is a mobile optimized view for Ganglia. It is intended for any mobile browsers supported by jQueryMobile toolkit. This covers most WebKit implementations ie. Android, iPhone iOS, HP webOS and Blackberry OS 6+. Interface intends to provide a better experience viewing Ganglia on your mobile phone by eliminating panning and zooming.
Search allows you to find hosts and metrics quickly. It has multiple purposes ie.
- Find a particular metric - especially useful if a metric is rare e.g. outgoing_sms_queue
- Quickly find a host regardless of a cluster
- First a list of matching hosts
- Second list of matching metrics. If the search term matches metric on multiple hosts all hosts will be shown.
New in Gweb 2.0 is the ability to generate graphs using link:http://graphite.wikidot.com[Graphite] as the graphing engine as opposed to RRDtool.
First, install Graphite on the server that have direct access to the RRD files generated by Gmetad and RRDtool. You can follow the instructions found link:http://graphite.readthedocs.org/en/latest/install.html[here].
For integration with Ganglia, you only need to install `whisper` and the graphite webapp.
After Graphite has been installed, it needs to be patched to work with Ganglia. Get the respective patch for the version of Graphite you have installed link:https://github.com/vvuksan/ganglia-misc/tree/master/graphite[here].
If you are using version 0.9.8 of Graphite, you might also want to apply the following patches:
- http://bazaar.launchpad.net/~graphite-dev/graphite/main/diff/373
- http://bazaar.launchpad.net/~graphite-dev/graphite/main/revision/345.1.52/webapp/graphite/render/glyph.py
php $conf['graph_engine'] = "graphite";
You may or may not need to adjust the following configuration options in `conf.php` depending on your Graphite setup (these options should also be found in `conf_default.php`):
php $conf['graphite_url_base'] = "http://127.0.0.1/render"; $conf['graphite_rrd_dir'] = "/opt/graphite/storage/rrd";
The directory structure of your RRD files will be symlinked to `$conf['graphite_rrd_dir']` with some minor changes (such as replacing space with "_"). The actual RRD files will not be duplicated.
WARNING: Certain reports (such as CPU Report) currently does not work correctly as the JSON representation does not support certain metric calculations
You will notice little CSV and JS icons next to graphs displayed. Clicking on these will export graph values for the displayed time period in a CSV (comma separated values) or JSON format. If there are multiple metrics used to create graphs like in e.g. CPU report all metrics will be exported.
By default when you click on a host view all of the metric groups are expanded. You can change that so that only metric graph titles are showing and you have to click on the metric group to expand the view. To default to metric groups initially collapsed add following setting in conf.php
php $conf['metric_groups_initially_collapsed'] = true;
If you'd like to display only certain hosts in the cluster view you can filter them out using the text box that is located next to the Show Node drop down. Filter accepts regular expressions ie. you can show any host that has web in it's name by putting `web`
or to filter out webservers web10-web17 you could type `web1[0-7]`
or show me web03 and web04 and all mysql servers `(web-0[3,4]|mysql)`
This feature has existed before but has been enhanced. This feature is intended to speed up cluster view rendering when you have lots of hosts in a cluster ie. hundreds or thousands. This will result in large load times as all images are rendered and downloaded. Instead you can opt to show only first X graphs. Rest of the graphs will not be loaded and will be replaced with a placeholder showing current metric value. You can do that on the fly by selecting from the drop down menu. You can also set a default by setting it in conf.php ie.
php $conf['max_graphs'] = 100;
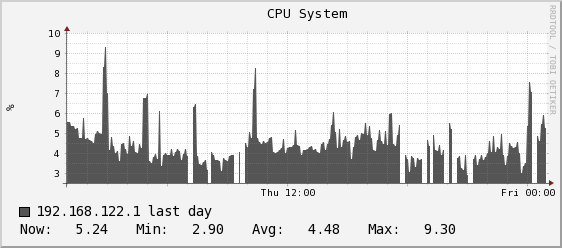
You can now enable slope mode for your RRDtool graphs. This option is disabled by default. Slope mode is defined in RRDtool documentation as http://oss.oetiker.ch/rrdtool/doc/rrdgraph.en.html
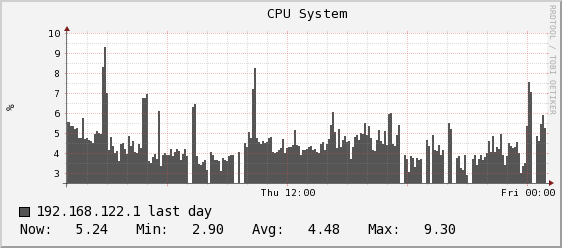
RRDtool graphs are composed of stair case curves by default. This is in line with the way RRDtool calculates its data. Some people favor a more 'organic' look for their graphs even though it is not all that true.
Here is an example of two different presentations. First one is standard and the second is one with slope mode turned on
.Graph with slope mode off
.Graph with slope mode on
From Trac wiki version 43.