ZenStack is a Node.js/TypeScript toolkit that simplifies the development of a web app's backend. It enhances Prisma ORM with a flexible Authorization layer and auto-generated, type-safe APIs/hooks, unlocking its full potential for full-stack development.
Our goal is to let you save time writing boilerplate code and focus on building real features!
Read full documentation at 👉🏻 zenstack.dev. Join Discord for feedback and questions.
ZenStack incrementally extends Prisma's power with the following four layers:
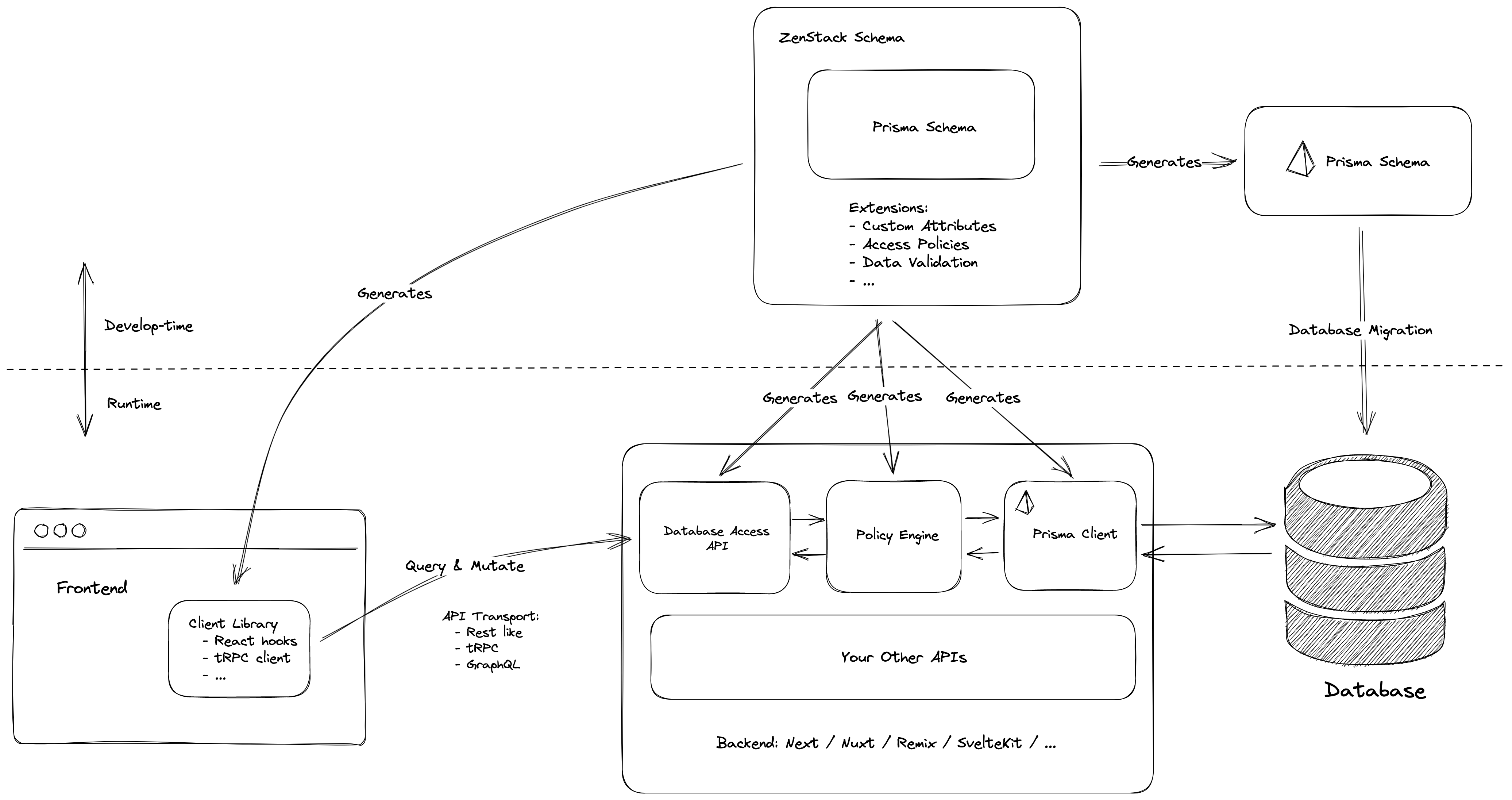
ZenStack introduces a data modeling language called "ZModel" - a superset of Prisma schema language. It extended Prisma schema with custom attributes and functions and, based on that, implemented a flexible access control layer around Prisma.
// base.zmodel
abstract model Base {
id String @id
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId String
// 🔐 allow full CRUD by author
@@allow('all', author == auth())
}// schema.zmodel
import "base"
model Post extends Base {
title String
published Boolean @default(false)
// 🔐 allow logged-in users to read published posts
@@allow('read', auth() != null && published)
}The zenstack CLI transpiles the ZModel into a standard Prisma schema, which you can use with the regular Prisma workflows.
At runtime, transparent proxies are created around Prisma clients for intercepting queries and mutations to enforce access policies.
import { enhance } from '@zenstackhq/runtime';
// a regular Prisma client
const prisma = new PrismaClient();
async function getPosts(userId: string) {
// create an enhanced Prisma client that has access control enabled
const enhanced = enhance(prisma, { user: userId });
// only posts that're visible to the user will be returned
return enhanced.post.findMany();
}Server adapter packages help you wrap an access-control-enabled Prisma client into backend CRUD APIs that can be safely called from the frontend. Here's an example for Next.js:
// pages/api/model/[...path].ts
import { requestHandler } from '@zenstackhq/next';
import { enhance } from '@zenstackhq/runtime';
import { getSessionUser } from '@lib/auth';
import { prisma } from '@lib/db';
// Mount Prisma-style APIs: "/api/model/post/findMany", "/api/model/post/create", etc.
// Can be configured to provide standard RESTful APIs (using JSON:API) instead.
export default requestHandler({
getPrisma: (req, res) => enhance(prisma, { user: getSessionUser(req, res) }),
});Plugins can generate strong-typed client libraries that talk to the aforementioned APIs. Here's an example for React:
// components/MyPosts.tsx
import { useFindManyPost } from '@lib/hooks';
const MyPosts = () => {
// list all posts that're visible to the current user, together with their authors
const { data: posts } = useFindManyPost({
include: { author: true },
orderBy: { createdAt: 'desc' },
});
return (
<ul>
{posts?.map((post) => (
<li key={post.id}>
{post.title} by {post.author.name}
</li>
))}
</ul>
);
};The following diagram gives a high-level architecture overview of ZenStack.
- Access control and data validation rules right inside your Prisma schema
- Auto-generated OpenAPI (RESTful) specifications, services, and client libraries
- End-to-end type safety
- Extensible: custom attributes, functions, and a plugin system
- A framework-agnostic core with framework-specific adapters
- Uncompromised performance
- Prisma schema generator
- Zod schema generator
- SWR and TanStack Query hooks generator
- OpenAPI specification generator
- tRPC router generator
- 🙋🏻 Request for a plugin
- Next.js (including support for the new "app directory" in Next.js 13)
- Nuxt
- SvelteKit
- Fastify
- ExpressJS
- NestJS
- 🙋🏻 Request for an adapter
- Custom attributes and functions
- Multi-file schema and model inheritance
- Polymorphic Relations
- Strong-typed JSON field (coming soon)
- 🙋🏻 Request for an extension
The sample repo includes the following patterns:
- ACL
- RBAC
- ABAC
- Multi-Tenancy
You can use this blog post as an introduction.
Check out the Multi-tenant Todo App for a running example. You can find different implementations below:
- Next.js 13 + NextAuth + SWR
- Next.js 13 + NextAuth + TanStack Query
- Next.js 13 + NextAuth + tRPC
- Nuxt V3 + TanStack Query
- SvelteKit + TanStack Query
- RedwoodJS
- Next.js 13 + Pages Route + SWR
- Next.js 13 + App Route + ReactQuery
- Next.js 13 + App Route + tRPC
- Nuxt V3 + TanStack Query
- SvelteKit
- Remix
- NestJS Backend API
- Express Backend API
- Clerk Integration
Join our discord server for chat and updates!
If you like ZenStack, join us to make it a better tool! Please use the Contributing Guide for details on how to get started, and don't hesitate to join Discord to share your thoughts.
Please also consider sponsoring our work to speed up the development. Your contribution will be 100% used as a bounty reward to encourage community members to help fix bugs, add features, and improve documentation.
Thank you for your generous support!
Marblism |
Mermaid Chart |
CodeRabbit |
Johann Rohn |
Benjamin Zecirovic |
Ulric |
Fabian Jocks |
Thanks to all the contributors who have helped make ZenStack better!