-
http://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/learn_matlab/matrices-and-arrays.html#responsive_offcanvas
http://www.tutorialspoint.com/matlab/ -
separate the elements in a single row with either a comma (,) or a space.
[1 2 3 4] [1,2,3,4]
-
separate the rows with semicolons or 'return'
a = [1 2 3; 4 5 6; 7 8 10] a = [1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 10] -
All variables of all data types in MATLAB are multidimensional arrays.
A vector is a one-dimensional array and a matrix is a two-dimensional array.
Special Arrays in MATLAB
zeros(n), ones(m,n),eye(n), rand(m.n) ,magic(n)
- Matrix and Array Operations
a = [1 2 3; 4 5 6; 7 8 10]
a + 10
sin(a)
a' ; transpose(a)
p = a*inv(a)
format long
p
format short
p
- element-wise operators
p = a.*a
a.^3
- Concatenation
A = [a,a]
A = [a; a]
- Complex Numbers
sqrt(-1)
c = [3+4i, 4+3j; -i, 10j]
- Array Indexing
A = magic(4)
A(4,2) %The most common way is to specify row and column subscripts
A(8) %use a single subscript that traverses down each column in order:
A(1:3,2) %use the colon operator, which allows you to specify a range of the form start:end
A(3,:) %The colon alone, without start or end values, specifies all of the elements in that dimension.
- The colon operator also allows you to create an equally spaced vector of values using the more general form start:step:end.
B = 0:10:100
- Deleting a Row or a Column in a Matrix
a = [ 1 2 3 4 5; 2 3 4 5 6; 3 4 5 6 7; 4 5 6 7 8];
a( 4 , : ) = [] %delete the fourth row of a
- Array Functions
size,length,ndims,diag ,numel,sort
x = [7.1, 3.4, 7.2, 28/4, 3.6, 17, 9.4, 8.9];
length(x) % length of x vector
y = rand(3, 4, 5, 2);
ndims(y) % no of dimensions in array y
s = ['Zara', 'Nuha', 'Shamim', 'Riz', 'Shadab'];
numel(s) % no of elements in s
sort(x)
m = [2 6 4; 5 3 9; 2 0 1] % two dimensional array
sort(m, 1) % sorting m along the row
sort(m, 2) % sorting m along the column
size(m)
- Multidimensional Arrays
a
a(:, :, 2)= [ 7 6 3; 1 9 2; 4 8 5]
- We can also create multidimensional arrays using the ones(), zeros() or the rand() functions.
b = rand(4,3,2)
- some commands
clc , clear, close all
help
who ,whos
save,load
-
The simplest type of MATLAB® program is called a script. A script is a file with a .m extension
that contains multiple sequential lines of MATLAB commands and function calls.
You can run a script by typing its name at the command line. -
edit a script file named "plotrand.m" as following:
% Generate random data from a uniform distribution
% and calculate the mean. Plot the data and the mean.
n = 50; % 50 data points
r = rand(n,1);
plot(r)
% Draw a line from (0,m) to (n,m)
m = mean(r);
hold on
plot([0,n],[m,m])
hold off
title('Mean of Random Uniform Data')
- Save the file in the current folder. To run the script, type its name at the command line:
plotrand
- A function is a group of statements that together perform a task.
In MATLAB, functions are defined in separate files.
The name of the file and of the function should be the same.
Syntax of a function statement is:
function [out1,out2, ..., outN] = myfun(in1,in2,in3, ..., inN)
function max = mymax(n1, n2, n3, n4, n5)
%This function calculates the maximum of the
% five numbers given as input
max = n1;
if(n2 > max)
max = n2;
end
if(n3 > max)
max = n3;
end
if(n4 > max)
max = n4;
end
if(n5 > max)
max = n5;
end
help mymax
mymax(34, 78, 89, 23, 11)
- Graphing
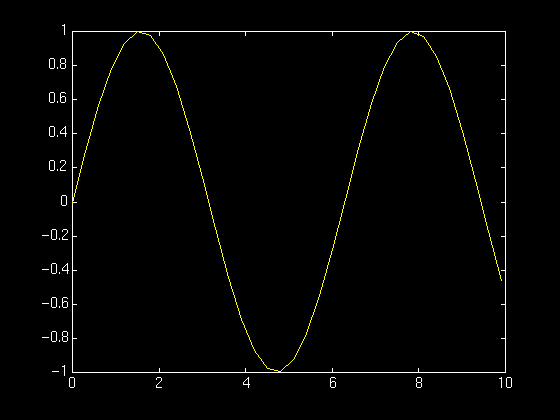
- Functions of one variable
t = 0:.3:10;
y = sin(t);
plot(t,y)
- Functions of two variables
[x,y] = meshgrid(-2:.2:2, -2:.2:2); z = x .* exp(-x.^2 - y.^2); surf(x,y,z)