Creating a server-client application with C socket.
Clone the project and cd in to the main directory.
Open a terminal and setup your server with the following command:
./server [port]You should get a result like this:
Listening on 0.0.0.0:8080After that connect to the server with your client using this command:
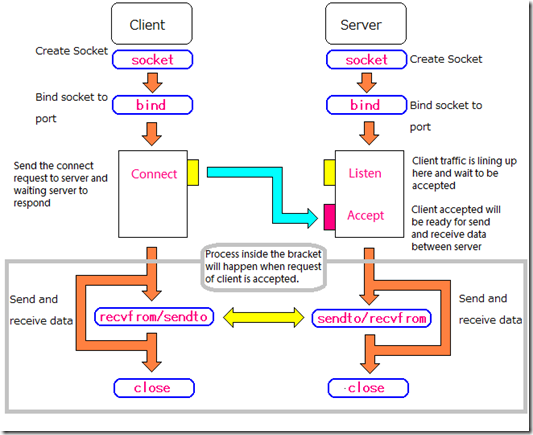
./client [IP] [port]Socket programming is a way of connecting two nodes on a network to communicate with each other. One socket(node) listens on a particular port at an IP, while other socket reaches out to the other to form a connection. Server forms the listener socket while client reaches out to the server.
int sockfd = socket(domain, type, protocol)- sockfd: socket descriptor, an integer (like a file-handle)
- domain: integer, communication domain e.g., AF_INET (IPv4 protocol) , AF_INET6 (IPv6 protocol)
- type: communication type
- SOCK_STREAM: TCP(reliable, connection oriented)
- SOCK_DGRAM: UDP(unreliable, connectionless)
- protocol: Protocol value for Internet Protocol(IP), which is 0. This is the same number which appears on protocol field in the IP header of a packet.(man protocols for more details)
int bind(int sockfd, const struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t addrlen);After creation of the socket, bind function binds the socket to the address and port number specified in addr(custom data structure). In the example code, we bind the server to the localhost, hence we use INADDR_ANY to specify the IP address.
int listen(int sockfd, int backlog);It puts the server socket in a passive mode, where it waits for the client to approach the server to make a connection. The backlog, defines the maximum length to which the queue of pending connections for sockfd may grow. If a connection request arrives when the queue is full, the client may receive an error with an indication of ECONNREFUSED.
int new_socket = accept(int sockfd, struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t *addrlen);It extracts the first connection request on the queue of pending connections for the listening socket, sockfd, creates a new connected socket, and returns a new file descriptor referring to that socket. At this point, connection is established between client and server, and they are ready to transfer data.
int connect(int sockfd, const struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t addrlen);The connect() system call connects the socket referred to by the file descriptor sockfd to the address specified by addr. Server’s address and port is specified in addr.
pthread_t thread_id;
pthread_create(&thread_id, NULL, client_handler, (void *)&client_socket);Using pthread to create a thread for each of our clients and handle them with a specific method.