- Overview
- Prerequisites
- Installation Steps
- 1. Clone installation GIT repository locally
- 2. Create the inventory hosts file
- 3. Check the connection with the OpenShift cluster
- 4. Log into OpenShift
- 5. Install all products from a single playbook
- 6. Install each product individually
- 7. Check the installation
- Uninstalling Integreatly
- Troubleshooting
The purpose of this repository is to provide a set of Ansible playbooks that can be used to install a range of Red Hat middleware products on Openshift.
These products include:
-
Single Sign On
-
Managed Services Broker
-
EnMasse
-
Eclipse Che
-
Launcher
-
3Scale
Requirement |
Version |
Ansible |
>= v2.6 |
Openshift Container Platform |
>= v3.10 |
Openshift CLI (OC) |
>= v3.10 |
|
|
|
The following section demonstrates how to install each of the products listed above on an existing Openshift cluster.
git clone https://github.com/integr8ly/installation.git-
Create the host file based on the template(
../evals/inventories/hosts.default). Following the an example.$ cp evals/inventories/hosts.template evals/inventories/hosts
-
Update the host file to connect in your OpenShift cluster
Prior to running the playbooks the master hostname and associated SSH username must be set in the inventory host file to match the target cluster configuration. The following example sets the SSH username to evals and the master hostname to master.evals.example.com:
~/installation/evals/inventories/hosts [local:vars] ansible_connection=local [local] 127.0.0.1 [OSEv3:children] master [OSEv3:vars] ansible_user=evals [master] master.evals.example.comℹ️It is possible to add the variable ansible_ssh_private_key_filefor the master host when the ssh connection requires a public key.(E.g`ansible_ssh_private_key_file=~/.ssh/ocp-workshop.pem`)
Run the following command in order to check the connection with the OpenShift cluster from the /installation/evals.
$ ansible -m ping allFollowing an example of the expected output.
$ ansible -m ping all
127.0.0.1 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
master.example.openshiftworkshop.com | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}Before run the scripts it is required login via oc client tool to the master/OCP. Following an example.
oc login master.example.openshiftworkshop.com -u <user> -p <password>You can install Integreatly using either of the following options:
All products can be installed using the install.yml playbook located in the evals/playbooks/ directory.
Before running the installer, please consider the following variables:
Variable |
Description |
eval_self_signed_certs |
Whether the OpenShift cluster uses self-signed certs or not. Defaults to |
eval_threescale_enable_wildcard_route |
Whether 3Scale enables wildcard routing. Defaults to |
github_client_id |
GitHub OAuth client ID to enable GitHub authorization for Launcher. If not defined, GitHub authorization for Launcher will be disabled |
github_client_secret |
GitHub OAuth client secret to enable GitHub authorization for Launcher. If not defined, GitHub authorization for Launcher will be disabled |
prerequisites_install |
Boolean var that skips the installation of system wide tools/packages that are required by the installer if set to false (needs to be set to false when running the installer in a linux container) - defaults to true. |
-
Login into GitHub
-
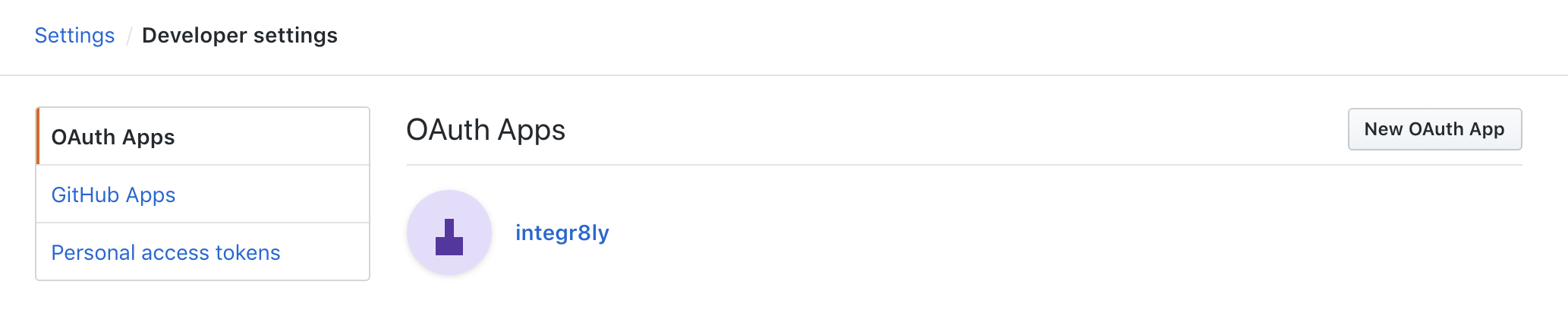
Go to
Settings >> Developer Settings >> New OAuth App. Following an image as example to ilustrate this area. -
Add the following fields values
Table 3. Fields values descriptions Field
Value
Application Name
Any value
Home Page URL
Authorization callback URL
❗The callback URL is a placeholder for now and will be changed after the installation playbook is finished. -
Click on
Register Application -
The values found in GitHub OAuth App,
Client IDandClient Secret, will be required in the next step to install Integreatly enabling GitHub authorization for Launcher. Following an example of this screen.
$ oc login https://<openshift-master-url> -u <user> -p <password>
$ cd evals/
$ $ ansible-playbook -i inventories/hosts playbooks/install.yml -e github_client_id=<your_client-id> -e github_client_secret=<your_client_secret>|
💡
|
The following command installs Integreatly without GitHub authorization for Launcher. $ ansible-playbook -i inventories/hosts playbooks/install.yml |
Following and example of the output made at the end of the playbook with this URL.
TASK [debug] *************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
ok: [127.0.0.1] => {
"msg": "All services have been provisioned successfully. Please add 'https://launcher-sso-launcher.apps.example.openshiftworkshop.com/auth/realms/launcher_realm/broker/github/endpoint' as the Authorization callback URL of your GitHub OAuth Application."
}The http://localhost placeholder added in the GitHub OAuth App should be replaced with this value. Following an example.
Each product has an associated install playbook available from the evals/playbooks/ directory.
$ oc login https://<openshift-master-url>
$ cd evals/
$ ansible-playbook -i inventories/hosts playbooks/rhsso.ymlUpon completion, a new identity provider named rh_sso should be presented on the Openshift master console login screen.
|
|
The default login credentials are [email protected] / Password1
|
To configure custom account credentials, simply override the rhsso role environment variables by specifying user parameters as part of the install command:
$ ansible-playbook -i inventories/hosts playbooks/rhsso.yml -e rhsso_evals_username=<username> -e rhsso_evals_password=<password>$ oc login https://<openshift-master-url>
$ cd evals/
$ ansible-playbook -i inventories/hosts playbooks/enmasse.ymlOnce the playbook has completed a service named EnMasse (standard) will be available
in the Service Catalog. This can be provisioned into your namespace to use EnMasse.
Set the following variables:
Variable |
Description |
che_route_suffix |
The router suffix of the OpenShift cluster |
che_keycloak_host |
The route to the previously created SSO, without protocol |
che_keycloak_user |
Username to authenticate as, this would be the admin user by defaul |
che_keycloak_password |
Password of the user |
che_namespace |
The namesapce to provision che into |
che_infra_namespace |
This can usually be the same as |
$ oc login https://<openshift-master-url>
$ cd evals/
$ ansible-playbook -i inventories/hosts playbooks/che-install.ymlThe Launcher playbook also requires information about the existing SSO that was provisioned previously. It needs to know the route of the SSO. This can be retrieved using:
$ oc get route sso -o jsonpath='{.spec.host}' -n rhssoIt also needs to know the realm to interact with. By default this would be
openshift. Finally it needs the credentials of a user to login as, by default
this would be the admin user created by the SSO playbook.
Specify the following variables in the inventory files or as --extra-vars when
running the playbook.
Variable |
Description |
launcher_openshift_sso_route |
The route to the previously created SSO, without protocol |
launcher_openshift_sso_realm |
The realm to create resources in the SSO, this would be |
launcher_openshift_sso_username |
Username to authenticate as, this would be the admin user by default |
launcher_openshift_sso_password |
Password of the user |
If using self signed certs set launcher_sso_validate_certs to no/false.
Without this, an error will be thrown similar to this:
fatal: [127.0.0.1]: FAILED! => {"msg": "The conditional check 'launcher_sso_auth_response.status == 200' failed. The error was: error while evaluating conditional (launcher_sso_auth_response.status == 200): 'dict object' has no attribute 'status'"}
Next, run the playbook.
$ oc login https://<openshift-master-url>
$ cd evals
$ ansible-playbook -i inventories/hosts playbooks/launcher.ymlOnce the playbook has completed it will print a debug message saying to update
the Authorization callback URL of the GitHub OAuth Application. Once this is
done the launcher setup has finished.
|
|
3Scale requires access to ReadWriteMany PVs. As such, it will only work on Openshift clusters that have RWX PVs available. |
$ oc login https://<openshift-master-url>
$ cd evals/
$ ansible-playbook -i inventories/hosts playbooks/3scale.yml -e threescale_route_suffix=<openshift-router-suffix> -e enable_wildcard_route=<true/false>|
❗
|
Once the installation has finished you will no longer be able to login via the Openshift console or oc cli as the admin if there is an sso redirect in place. The new admin user is [email protected] password is Password1
|
The URL for the Integraly view is https://tutorial-web-app-webapp.apps.<domain>/
For example, if the master url is https://master.example.openshiftworkshop.com/, the web app is available at https://tutorial-web-app-webapp.apps.example.openshiftworkshop.com/.
|
💡
|
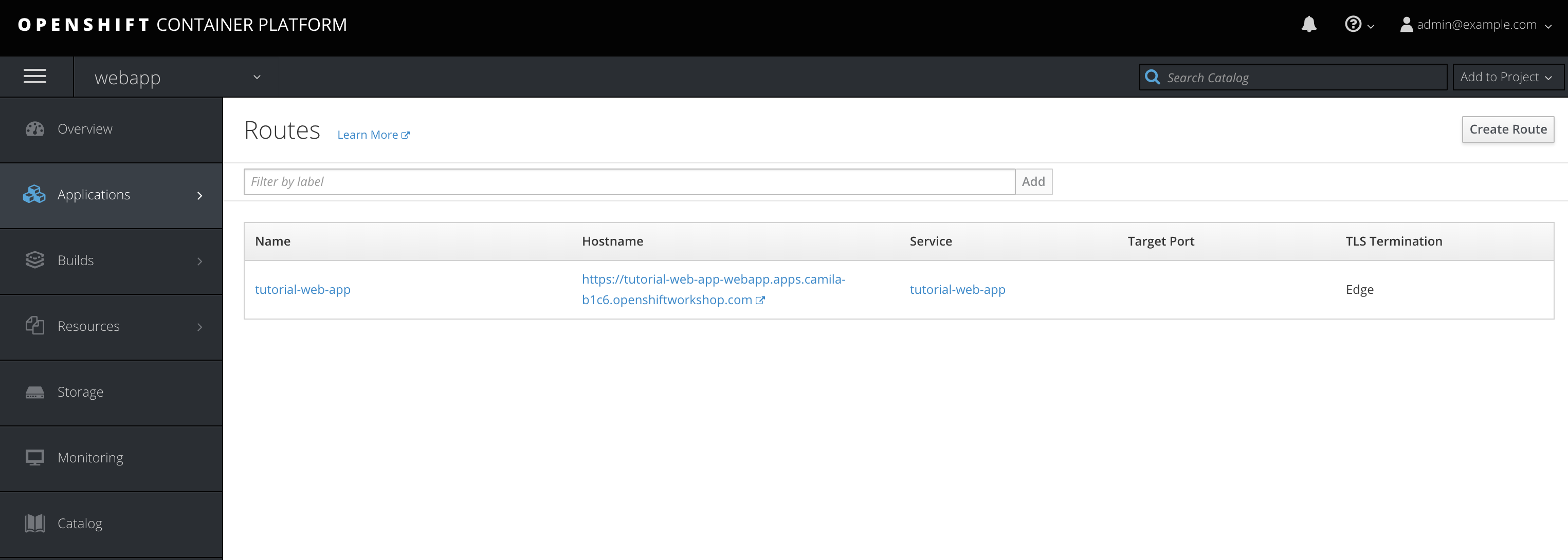
The project Webapp is responsible for the Integraly interface. You can find the URL looking for the router created for this project. As the following example. |
Also, with the evals users created by the installer is possible to check the services in the OpenShift catalog.
|
❗
|
The default login credentials are [email protected] / Password1
|
Following an image of this console as example.
Run the uninstall.yml playbook from inside the evals directory:
$ cd evals/
$ ansible-playbook -i inventories/hosts playbooks/uninstall.ymlBy default this will delete all user-created namespaces as well, if you wish to keep these namespaces then add the following flag:
-e keep_namespaces=true
The issue means that python version used by Ansible has not this required module. In order to fix it is required to install the missing module. Following the command to install it via pip.
$ pip install jmespath|
ℹ️
|
The module need to be installed in the same version of python used by Ansible. Use the command $ ansible --version to check this path.
|
The issue means that python version used by Ansible has not this required module. In order to fix it is required to install the missing module. Following the command to install it via pip.
$ pip install jsonpointerAlso, you might need to use the varible ansible_python_interpreter in the host file to fix it, for example:
[local:vars]
ansible_connection=local
ansible_python_interpreter=python|
💡
|
The module need to be installed in the same version of python used by Ansible. Use the command $ ansible --version to check this path.
|
If your cluster is using a self signed (non CA) certificate, there are a couple of things that needs to be noted.
-
Che will only allow the creation of one workspace when self signed certificates are used.
-
When a workspace is created, the following errors may appear on the workspace:
Connection failed with terminal Some error happened with terminal WebSocket connection
Failed to import project
-
In order to solve these issues, you will need to accept the certs for all the routes that was created for that workspace. These routes are listed in the workspace deployment within the Che namespace.