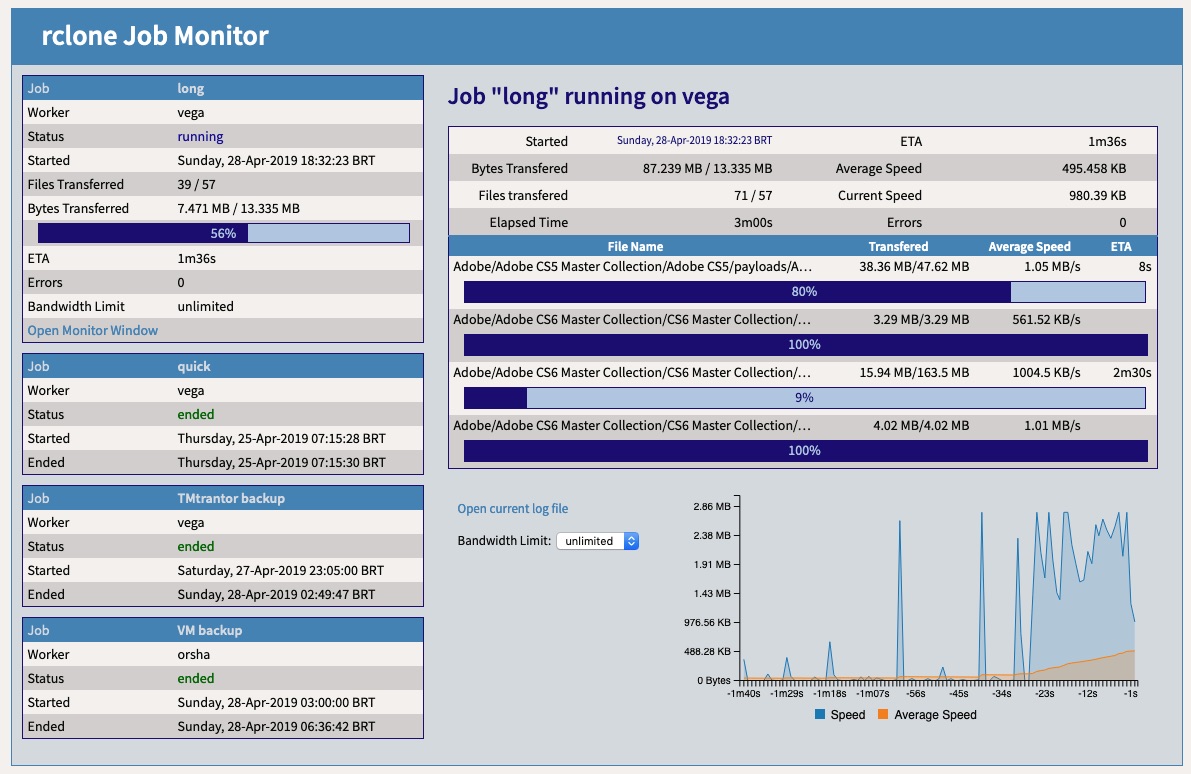
Web based remote monitor for rclone jobs - Version 0.9b
rcloneMon is a set tools focused on monitoring rclone jobs. Its main objetive it to manage (babysit) rclone jobs that have a reasonably long run time or run constantly in the background. It can, however, monitor any rclone job, provided that it runs long enogh to allow monitoring.
rcloneMon is made of 3 major components:
- A wrapper script for rclone, that provides enhanced real-time transfer progress statistics (that are currently not available with
rclone), as well as create persistent job run information. - A web based monitor for
rclonejobs, that usesrclone's Remote Control feature to obtain progress information in real-time. Optionally, it can use the enhanced statistics provided by the wrapper script. - A job dashboard that allow monitoring/babysiting multiple jobs on different machines that integrates the web based monitor.
All components share a common configuration file (config.json). This allow a seamless flow of information for a tight integration.
Although the main target for rcloneMon are jobs running on headless boxes (such as NAS boxes), it can be used to monitor any rclone job running on the local desktop or remote hosts.
- Web based interface
- Graphical progress information at the job and file levels
- Bandwidth usage graph (per job)
- Bandwidth limit control
- Persistent job statistics and results
- Dashboard with extensive job statistics, even for finished or failed jobs
- job status notification (using external exit)
- Support for multiple simultaneous jobs running on multiple hosts
Currently rclone support two types of jobs:
- A single synchronous
rclonejob, that are the ones started directly by therclonecommand. - Multiple asynchorous
rclonejobs, that are started withrcloneRemote Control (rclone rccommand) to run on arcloneremote controlled daemon, started withrclone rcd.
The ideal and more efficient scenario for monitorable jobs is to use asynchronous rclone jobs. However, the current Remote Control API does not provide fine grain progress information on a per job basis.
As a result rcloneMon currently uses synchronous rclone jobs. When the remote control API is enhanced to provides per job statistics rcloneMon will provide support for asynchronous jobs.
rcloneMon bases its operation on the following roles:
As expected, the host is the actual computer where an instance of rclone is running. It's defined by one IP address or host name.
A worker is one instance of rclone running on a host with Remote Control active. It's defined by the host IP address or name, the TCP port that the Remote Control is answering requests on and protocol (HTTP or HTTPS).
There can be multiple workers in a host, provided that they are assigned (bind) to different TCP ports (using rclone option --rc-addr).
A job is a rclone operation that will be executed by a particular worker. There can be several jobs associated with a single worker.
At this time, rcloneMon only supports workers for synchronous job. This (temporary) limitation will restrict a single active job per worker. rcloneMon does not perform any check for multiples jobs for a worker, but rclone will fail to start because the TCP port is already in use by the other instace of the worker (synchronous).
Once (and if) rclone provides per job statistics (for asynchronous jobs in a single rclone instance),
rcloneMon will be enhanced to allow multiple asynchronous simultaneous jobs on a worker.
Current goals are:
- Support asynchronous jobs [require feature change in rclone]
- Create a modular component
- Job run history
First and foremost, the wrapper scripts were written and tested under Linux, but should run without problems on other *nix flavors (such as macOS). Running under Windows will require several adaptations, not possible at this time.
All rcloneMon files served over HTTP are static. rcloneMon don't require a dedicated webserver. rclone can act as a web server for regular (static) files when running with the --rc-files option, combined with the --rc option or running in Remote Control Daemon mode rcd).
However, it can make use of an existing web server (such as Apache) for serving all the static files, while rclone will still be used to provide real-time statistics over HTTP.
One can rely on an instance of rclone that is running a job to serve static files, along with servicing real-time statistics. The drawback here is that when the job finishes, the web server will also terminate, and it will no longer be possible to obtain job status for the dashboard.
There are two ways to overcome this limitation:
- Run a dedicated
rcloneinstance (rclone rcd --rc-filesplus other options) just to serve the static files. - Run a separate web server, such as Apache, for these files.
When using rclone as the sole web server there are no extra CORS considerations. When running with another web server it may be necessary to properly configure the server for CORS, if multiple servers are involved.
For Apache, the proper htaccess file (to be renamed to .htaccess) is provided to allow cross-domain requests to be properly handled as needed.
rcloneMon componenents have the following dependecies:
- Bandwidth usage graphics use C3.js, as well as its dependency D3.js.
- The wrapper script is written in
PHP(5.6+), as handling JSON data in regularshorbashis not a very sane option. This should not be a big problem as PHP is readly available (normally built-in) on most modern OS, including popular NAS boxes (such as QNAP and Synology).
All project files, including C3.js (please use c3.min.js and c3.min.css) and D3.js (d3.min.js) must be placed in a single directory accessible by the selected web server.
Like any other *unix scripts, PHP scripts requires the first line to contain the path to the PHP executable/interpreter, PLEASE UPDATE the shebang (first line, that starts with #!) to reflect the location of the PHP binary on your system, and if necessary the location of the php.ini file (if using non standard PHP settings). Note that PHP shebangs cannot have more than a single option and it moust not have blanks. Therefore, use -c/pathto/php.ini and not -c /pathto/php.ini or it will not work.
Most of the time the default PHP instalation and configuration will sufice, being the only change that may be necessary is to define a default "timezone" (that can be also specified directly on the rcloneMon config.json file).
The wrapper script is actually a collection of at least 3 scripts:
myrclone- that is the main script, and is used to start a job:
myrclone jobname [basedir]
proclog- that is used to attach to and process the log file while it's being written byrclone, to produce the real-time and persistent status file.notify- a sample notification exit, also written in PHP, that will be called bymyrcloneat the start and end of a job, receiving as parameter the full path of the status file. By examining the status file the script can send a message (using any available method) or email to the appropriate user. Writting and configuring this exit is beyond the scope of rcloneMon.
myrclone script is suitable for use with cron. Just follow these simple rules to properly integrate with cron:
- As with any script, it's better to invoke the shell passing the script as a parameter. For example (your PHP may be at a differnent location).
- Divert
STDOUTto/dev/null. The technique used to hook to the log file may cause problems if the job is running without an attached TTY.
/sbin/php myclone jobname > /dev/null
Proper settings for path and URLs are required to allow all the components to find the information they need. There are two files specified in config.json:
- The log file: this is the log file that is generated by the
rcloneworker that must run with the-voption in order to write overall job progress statistics. - The status file: this file is generated and updated by wrapper script to provide missing progress information as well as persistent job information. Status files are served as static files by the selected web server.
Both files need to be accessed by the scripts and served over the web, so it's necessary to have the proper path and URL settings for each one.
Paths that are not absolute (start with a /) will have the basedir prepended. For the basedir the following defaults apply, in order, to compute the actual value used:
- the directory where the script is located
- the directory passed as the second parameter for the wrapper script
- the
basedirspecification for the worker - the
basedirspecification for the job
Like paths, any relative URL will be anchored at baseUR with the following defaults, in order, to compute the actual value used:
- The base for the current page (means located at the same directory as the page)
- the
baseurlspecification for the worker - the
baseurlspecification for the job
The config.json file must be placed on the same directory as all other files. It defines all jobs and associated workers, as well as some OS enviroment related settings (used only by the wrapper script).
The file contains a single JSON object with the following keys:
The workers value is an array of objects, each one defining a worker. For each worker the following keys are available:
name- an arbritary string used to identify this worker for linking jobs to it (using theworkerkey on the job).description- an arbritrary string to describe the worker. At this time it serves only as a comment.url- a string with the URL that is used to submit Remote Control commands to this server.bandwidth- an object with 2 keys:speedcap- an integer defining the maximum bandwidth in bytes available for this worker. If defined, will be used to prevent out-of-bounds errors (outliers) in speed calculations.settings- an object that contains the values for the bandwidth setting dropdown menu. The key is the what gets send torcloneand the value is what is displayed on the monitor GUI for selection. The first pair must match the default bandwidth setting for all jobs that will use this worker.
notify- a string with the full path for the notification exit (see bellow) executable.basedir- a string defining the base directory path that will be prepended to the statusfile and logfile for all jobs associated with the worker. It can be overwritten at the job level.baseurl- a string defining the base URL path that will be prepended to the statusfile and logfile URLs for all jobs associated with the worker. It can be overwritten at the job level.statusfile- a string defining the name and path of the status file to use. If the path is relative, it will be prepended by the computedbasedir. It can be overwritten at the job level.logfile- a string defining the name and path of the log file to use. If the path is relative, it will be prepended by the computedbasedir. It can be overwritten at the job level.
The jobs value is an array of objects, each one defining a job. For each job the following keys are available:
name- an arbritary string used to identify this job. Used for starting the monitor (passed in the URL query string) and for identifying the job in the dashbord.description- an arbritrary string to describe the job. At this time it serves only as a comment.worker- a string that will be used to link (identify) to the worker that will used to run the job. Must match thenameof the worker.command- a string with the completerclonecommand to be executed by the wrapper script. Must include all necessary parameters for running in Remote Control mode (--rc,--rc-addr,-v), set the log file location (to match the logfile specification that will be computed, set any authentication paramters, thercloneaction to be performed and, if necessary, the root for the integrated web server (--rc-files).basedir- a string defining the base directory path that will be prepended to the statusfile and logfile for all jobs associated with the worker.baseurl- a string defining the base URL path that will be prepended to the statusfile and logfile URLs for all jobs associated with the worker.statusfile- a string defining the name and path of the status file to use. If the path is relative, it will be prepended by the computedbasedir.logfile- a string defining the name and path of the log file to use. If the path is relative, it will be prepended by the computedbasedir.
The enviroment value is an object, with each key defining a setting of the operating enviroment. The following keys are available:
timezone- [optional] PHP does not use the system defined time zone. You may alternatively define it in the php.ini that will be used by the scripts (see PHP notes above). Defaults to UTC.systemp- [optional] path to the system temporary directory that is wiped out on every boot. Defaults to/var/run.
Here is a sample config.json. It will not work without modifications.
{
"workers": [ {
"name":"worker1",
"description":"Description of worker #1",
"url":"http://server1.example.com:5572",
"baseurl":"http://server1.example.com/rclone/",
"bandwidth":{"speedcap":2883584,"settings":{"off":"unlimited","500k":"500KBps","1M":"1MBps","1.500M":"1.5MBps","2M":"2MBps","2.500M":"2.5MBps","3M":"3MBps"}},
"notify":"/usr/share/rclone/notify"
},
{
"name":"worker2",
"description":"Description of worker #2",
"url":"http://server2.example.com:5572",
"baseurl":"http://server2.example.com/rclone/",
"bandwidth":{"speedcap":2883584,"settings":{"off":"unlimited","500k":"500KBps","1M":"1MBps","1.500M":"1.5MBps","2M":"2MBps","2.500M":"2.5MBps","3M":"3MBps"}},
"notify":"/usr/share/rclone/notify"
} ],
"jobs": [ {
"name":"Backup1",
"description":"Backup Job #1",
"worker":"worker1",
"command":"/usr/bin/rclone --rc --rc-addr=0.0.0.0:5572 -v --log-file=/usr/share/rclone/backup1/rclone.log --tpslimit=3 --checkers=3 --drive-chunk-size=32M --rc-files=/usr/share/rclone --rc-user=xxxx --rc-pass=xxxx sync /file/tobackup1 remote:backup1",
"basedir":"/usr/share/rclone",
"logfile":"backup1/rclone.log",
"statusfile":"backup1/rclone.status"
},
{
"name":"Backup2",
"description":"Backup Job #2",
"worker":"worker2",
"command":"/usr/bin/rclone --rc --rc-addr=0.0.0.0:5572 -v --log-file=/usr/share/rclone/backup2/rclone.log --tpslimit=3 --checkers=3 --drive-chunk-size=32M --rc-files=/usr/share/rclone --rc-user=xxxx --rc-pass=xxxx sync /file/tobackup2 remote:backup2",
"basedir":"/usr/share/rclone",
"logfile":"backup2/rclone.log",
"statusfile":"backup2/rclone.status"
},
{
"name":"quick1",
"description":"Quick rclone test for worker #1",
"worker":"worker1",
"command":"/usr/bin/rclone -v --log-file=/usr/share/rclone/test/quick.log lsf remote:",
"basedir":"/usr/share/rclone",
"logfile":"test/quick.log",
"statusfile":"test/quick.status"
},
{
"name":"long1",
"description":"Long rclone test for worker #1",
"worker":"worker1",
"command":"/usr/bin/rclone --rc --rc-addr=0.0.0.0:5572 -v --log-file=/usr/share/rclone/test/long.log --tpslimit=3 --checkers=3 --drive-chunk-size=32M --rc-files=/usr/share/rclone --rc-user=xxxx --rc-pass=xxxx sync /file/junkpile remote:garbage1",
"basedir":"/usr/share/rclone",
"logfile":"test/long.log",
"statusfile":"test/long.status"
},
{
"name":"quick2",
"description":"Quick rclone test for worker #2",
"worker":"worker2",
"command":"/usr/bin/rclone -v --log-file=/usr/share/rclone/test/quick.log lsf remote:",
"basedir":"/usr/share/rclone",
"logfile":"test/quick.log",
"statusfile":"test/quick.status"
},
{
"name":"long2",
"description":"Long rclone test for worker #2",
"worker":"worker2",
"command":"/usr/bin/rclone --rc --rc-addr=0.0.0.0:5572 -v --log-file=/usr/share/rclone/test/long.log --tpslimit=3 --checkers=3 --drive-chunk-size=32M --rc-files=/usr/share/rclone --rc-user=xxxx --rc-pass=xxxx sync /file/junkpile remote:garbage2",
"basedir":"/usr/share/rclone",
"logfile":"test/long.log",
"statusfile":"test/long.status"
} ],
"environment": {
"timezone":"America/New_York",
"systemp":"/var/run"
}
}
When connecting to rclone for statistics or when using it as the main web server, basic authentication --rc-user + --rc-pass or --rc-htpasswd can be used without problems and the web browser will ask for the authentication only once per session.
If using another web server and authentication is required, please follow the appropriate instructions for configuring basic authentication.
rcloneMon allows the definition of a notification exit that will be called when the job is started and again when it ends.
The exit program, along with any optional parameters, is specified in the config.json file. The actual command to be executed will have the full path to the status file appended.
The exit program (that can be a binary or a script) must read the status file to determine the current state of the job.
Send the actual notification and the actual proceedure to do it is not part of rcloneMon or this document.
Note file notify.template contain a sample notification exit written in PHP to serve as a starting point.
The status file contain a single JSON object with the following keys:
status- Current job status ('running', 'ended' or 'failed')job- job nameworker- worker namestart- start timestamp (in seconds since the UNIX EPOCH)starttime- formated start timeend- end timestamp (in seconds since the UNIX EPOCH)endtime- formated end timeelapsed- seconds elapsed since the start (formated)ETA- ETA (as estimated byrclone)bandwidth- current bandwitdh limit (see below)transferredbytes- bytes transferredtransferredfiles- files transferredtotalbytes- total bytes estimated to be transferred by the jobtotalfiles- total files estimated to be transferred by the joberrors- number of errorslastrc- last exit code fromrclone
Notes:
- Not all keys will be present at all times.
- Bandwith limitation cannot be queried, so initially it's set to the first value specified in the
config.jsonbandwidth settings, and will correctly change to when set in the GUI or externally directly with Remote Control. - totalbytes and totalfiles may change as
rclonerevises these numbers (running checks).
Once the web server (stand alone or rclone) is running, open the URL pointing to the dashboard (dashboard.html) on your favorite web browser.
Alternatively, you may monitor a running job directly by connecting to the monitor url and passing the job name.
http://server1.example.com:5572/rcloneMon.html?job=jobname