BezierKit is a comprehensive Bezier Path library written in Swift.
Please note that BezierKit is currently pre-release software. Its releases follow semantic versioning which means that until it reaches 1.0 status the API may not be stable or backwards compatible.
- Constructs linear (line segment), quadratic, and cubic Bézier curves
- Draws curves via CoreGraphics
- Determines positions, derivatives, and normals along curves
- Lengths of curves via Legendre-Gauss quadrature
- Intersects curves and computes cubic curve self-intersection to any degree of accuracy
- Determines bounding boxes, extrema,
- Locates nearest on-curve location to point
- to any degree of accuracy
- Splits curves into subcurves
- Offsets and outlines curves
- Comprehensive Unit and Integration Test Coverage
- Complete Documentation
The recommended way to install BezierKit is via CocoaPods, however you may also find that dropping the contents of Library into your project also works.
CocoaPods is a dependency manager for Cocoa projects. You can install it with the following command:
$ gem install cocoapodsTo integrate BezierKit into your Xcode project using CocoaPods, add it to your target in your Podfile:
target '<Your Target Name>' do
pod 'BezierKit', '>= 0.6.1'
endThen, run the following command:
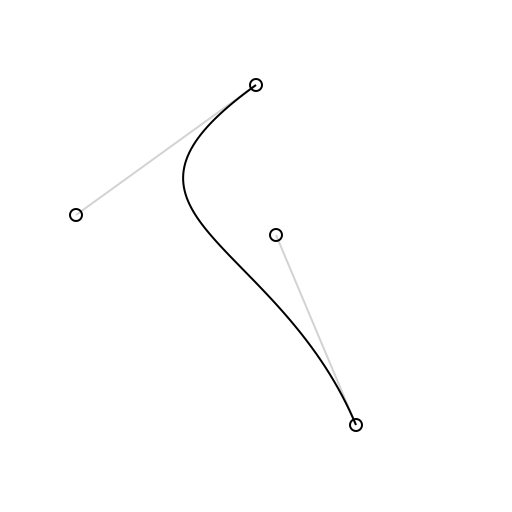
$ pod installBezierKit supports cubic Bezier curves (CubicCurve) and quadratic Bezier curves (QuadraticCurve) as well as line segments (LineSegment) each of which adopts the BezierCurve protocol that encompasses most API functionality.
import BezierKit
let curve = CubicCurve(
p0: CGPoint(x: 100, y: 25),
p1: CGPoint(x: 10, y: 90),
p2: CGPoint(x: 110, y: 100),
p3: CGPoint(x: 150, y: 195)
)
let context: CGContext = ... // your graphics context here
Draw.drawSkeleton(context, curve) // draws visual representation of curve control points
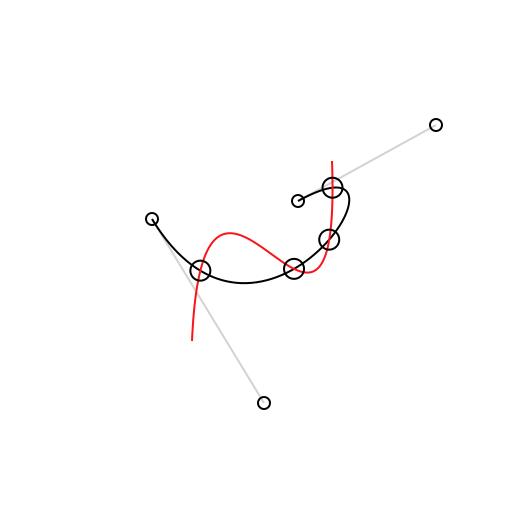
Draw.drawCurve(context, curve) // draws the curve itselfThe intersections(with curve: BezierCurve) -> [Intersection] method determines each intersection between self and curve as an array of Intersection objects. Each intersection has two fields: t1 represents the t-value for self at the intersection while t2 represents the t-value for curve at the intersection. You can use the compute(_:) method on either of the curves to calculate the coordinates of the intersection by passing in the corresponding t-value for the curve.
Cubic curves may self-intersect which can be determined by calling the selfIntersections() method.
let intersections: [Intersection] = curve1.intersections(with: curve2)
let points: [CGPoint] = intersections.map { curve1.compute($0.t1) }
Draw.drawCurve(context, curve: curve1)
Draw.drawCurve(context, curve: curve2)
for p in points {
Draw.drawPoint(context, origin: p)
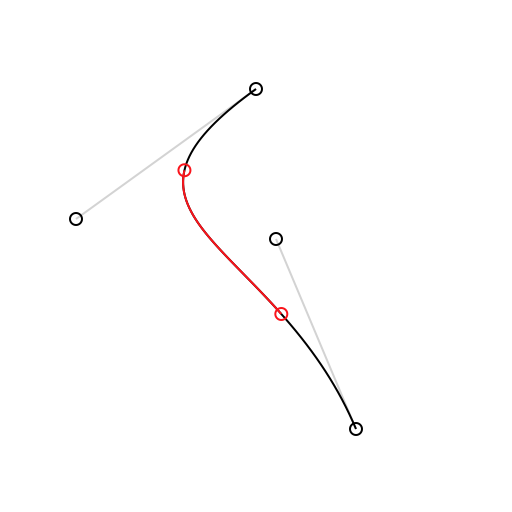
}The split(from:, to:) method produces a subcurve over a given range of t-values. The split(at:) method can be used to produce a left subcurve and right subcurve created by splitting across a single t-value.
Draw.setColor(context, color: Draw.lightGrey)
Draw.drawSkeleton(context, curve: curve)
Draw.drawCurve(context, curve: curve)
let subcurve = curve.split(from: 0.25, to: 0.75) // or try (leftCurve, rightCurve) = curve.split(at:)
Draw.setColor(context, color: Draw.red)
Draw.drawCurve(context, curve: subcurve)
Draw.drawCircle(context, center: curve.compute(0.25), radius: 3)
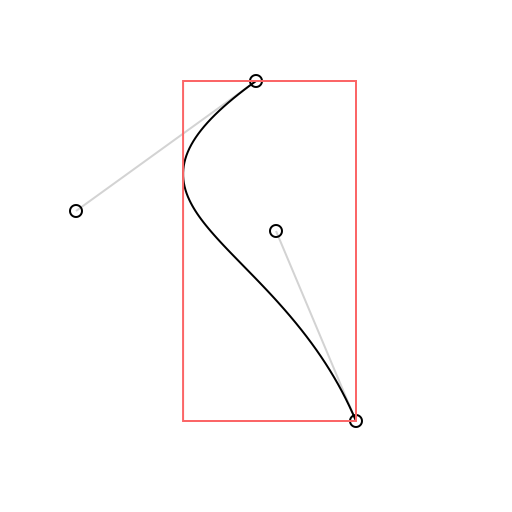
Draw.drawCircle(context, center: curve.compute(0.75), radius: 3)let boundingBox = curve.boundingBox
Draw.drawSkeleton(context, curve: curve)
Draw.drawCurve(context, curve: curve)
Draw.setColor(context, color: Draw.pinkish)
Draw.drawBoundingBox(context, boundingBox: curve.boundingBox)BezierKit is a powerful library with a lot of functionality. For the time being the best way to see what it offers is to build the MacDemos target and check out each of the provided demos.
BezierKit is released under the MIT license. See LICENSE for details.