This repo contains the code of my submission for the Algorithms and Data Structure class.
The objective was to write a memory and speed efficient program in C that imitates a social-like platform. The different commands are: adding new entities, new relations types between entities, some entities may be deleted, some relations may be deleted, and there is a report call which calls for the output made in a specific way: for each relation type, print the entities that receive that relation type the most. You can find a more detailed explanation in the “General guidelines” file or by looking at the code
The project received a 30/30 cum laude, completing all the tests well under the time and memory limits.
I wanted to try out something different compared to the most classical and intuitive approach, which would be a hash table with binary trees, probably red-and-black to speed things up. Another of the approaches to store relationships can be the use of a 2D matrix but having multiple relationship types and having some heavy memory restriction makes is a failing approach. That’s why I went for a more complex and heavily personalized structure.
The result is a relatively short code with some great time-complexity results. The code in the repo is the one I submitted with a better formatting and clearer comments. With more time I would have tried other optimization ideas such as rb instead of lists instead of lists in the NodeReport list, and make the code run for more than 10k entities and 20 relation types.
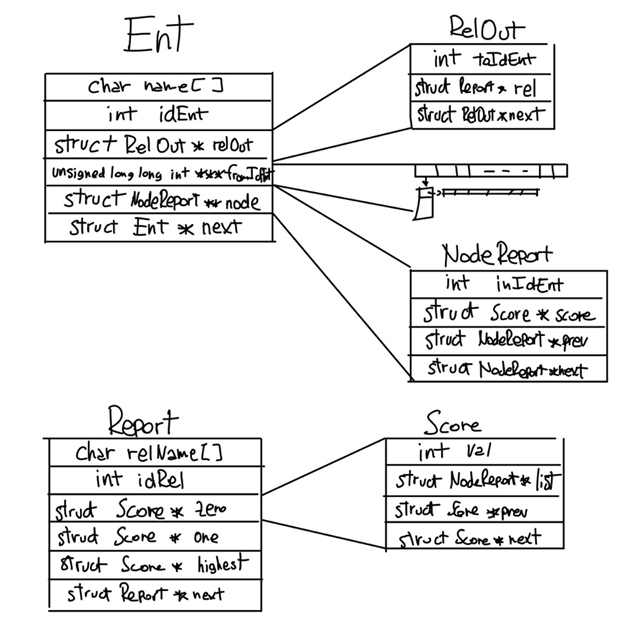
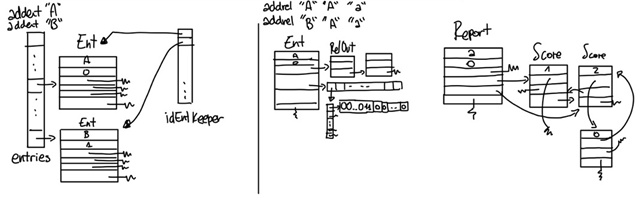
The picture at the bottom is probably the most intuitive way to describe the data structure. There is a hash table of all the created and non-deleted entities. When an entity is created an ID (progressive number) is assigned. In the entIDKeeper array a pointer to that entity is placed in the cell equal to the ID. This makes finding the entity by ID extremely fast and we can use the ID to build the rest of the structure in a very memory-efficient way.
NodeReport and fromIdEnt are closely connected: in NodeReport there is the pointer to the specific node in the Report, in fromIdEnt there is a 2D matrix that signals if that entity receives a relation of that type from the entity depending if the bit appears as 1 or 0. RelOut is just a list of the relations going out from that Ent.
The Report is composed of a list all the relation types. Each has a ranking system made of a list of values. When a node is made it is placed in one, then it is moved higher or lower in the Score list depending on the relations that are added or deleted.
The most common algorithms and data structure work great, but sometimes trying out new things may even be better, especially if the problem has some strict time and memory limits. It is probably more time consuming and bug prone, but it is the most rewarding.
Another thing is the use of specialized tools to analyze memory leaks and time consumed for tasks. Some solution may appear working properly but may hide some huge memory leaks or some time consumption that may not come to mind.