Crazydoc is a Python library to parse one of the most common DNA representation formats: the joyfully coloured and stylishly annotated MS-Word document.
Crazydoc returns Biopython records of the sequences contained in an MS-Word document, with record features corresponding to the various sequence highlightings (background color, boldness, italics, case change, etc.). The records can saved as GenBanks or easily plotted.
Motivation
While other standards such as FASTA or Genbank are better supported by modern sequence editors, none enjoys the same popularity among molecular biologist as MS-Word's .docx format, which is limited only by the sophistication and creativity of the user.
Relying on a loose syntax and unclear specifications, this format has however suffered from a lack of support in the developers community and is generally incompatible with mainstream software pipelines. This library allows to convert MS-Word DNA sequences to more computing friendly formats: Biopython records, FASTA, or annotated Genbanks.
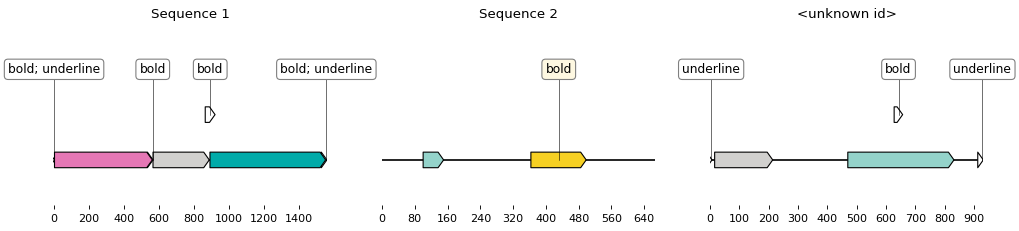
To obtain all sequences contained in a docx as annotated Biopython records (such as this one):
from crazydoc import CrazydocParser
parser = CrazydocParser(['highlight_color', 'bold', 'underline'])
biopython_records = parser.parse_doc_file("./example.docx")You can then plot the obtained records:
from crazydoc import CrazydocSketcher
sketcher = CrazydocSketcher()
for record in biopython_records:
sketch = sketcher.translate_record(record)
ax, _ = sketch.plot()
ax.set_title(record.id)
ax.figure.savefig('%s.png' % record.id)To write the sequences down as Genbank records, with annotations:
from crazydoc import records_to_genbank
records_to_genbank(biopython_records)Note that records_to_genbank() will truncate the record name to 20 characters,
to fit in the GenBank format. Additionally, slashes (/) will be replaced with
hyphens (-) in the filenames. To read protein sequences, pass is_protein=True:
biopython_records = parse_doc_file(protein_path, is_protein=True)This will return protein records, which will be saved with a GenPept extension
(.gp) by records_to_genbank(biopython_records, is_protein=True),
unless specified otherwise with extension=.
You can also save annotated sequences as colourful Word docs.
write_crazydoc() takes a SeqRecord, the qualifier key to use as a feature name,
and a path to save the document to.
# Load an annotated sequence with Biopython
from Bio import SeqIO
from crazydoc import write_crazydoc
seq = SeqIO.read("examples/examples_outputs/Sequence 1.gbk", "genbank")
# Most features will already have some name qualifier but you can add your own
for i,f in enumerate(seq.features):
f.qualifiers['product'] = f"feature{i}"
# Save the annotated sequence as a docx
write_crazydoc(seq, 'product', 'test.docx')You can install crazydoc through PIP:
pip install crazydoc
Alternatively, you can unzip the sources in a folder and type:
python setup.py install
Crazydoc is an open-source software originally written at the Edinburgh Genome Foundry by Zulko and released on Github under the MIT licence (Copyright 2018 Edinburgh Genome Foundry).
Everyone is welcome to contribute!

Crazydoc is part of the EGF Codons synthetic biology software suite for DNA design, manufacturing and validation.