整个项目源码:GitHub 整个项目数据集:车辆数据集、无车辆数据集
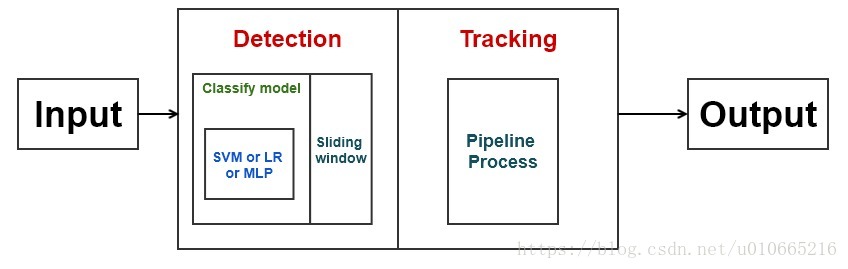
本次分享主要介绍,如何对道路上的汽车进行识别与跟踪。这里我们实现一个简单的demo。后续我们还会对前面的代码及功能进行重构,从而进一步丰富我们的功能。
- 在有标签的训练数据集上进行Histogram of Oriented Gradients(HOG)特征提取
- Normalize 这些特征,并随机化数据集
- 训练线性SVM分类器
- 实现一个滑动窗口技术,并使用训练好的分类器在图片中寻找车辆
- 实现一个流处理机制,并通过一帧一帧地创建循环检测的热图来去除异常值及跟踪车辆
- 为检测到的车辆估计一个边界框
本项目,我们使用一些有标签的训练数据:汽车图片、无汽车图片,训练数据在all文件夹中可以找到 有汽车地图片标签为1,无汽车的图片标签为0 我们先读取数据,看下数据的分布
# import libs
import glob
import matplotlib.image as mpimg
import numpy as np
from skimage.feature import hog
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
import time
import pickle
SEED = 2018
%matplotlib inline
# Read dataset image
vehicle_images = glob.glob('all/vehicles/GTI*/*.png')
none_vehicle_images = glob.glob('all/non-vehicles/*/*.png')
cars = []
notcars = []
for image in vehicle_images:
cars.append(image)
for image in none_vehicle_images:
notcars.append(image)
print('Dataset size:Cars {} | NotCars {}'.format(len(cars),len(notcars)))
rate = len(cars)/len(notcars)*1.0
if rate<2 and rate>0.5:
print('DataSet is balance')
else:
print('DataSet is not balance')Dataset size:Cars 2826 | NotCars 8968
DataSet is not balance
接下来我们分别随机选取一张有汽车及无汽车的图片
# random choose
rand_car = np.random.choice(len(cars))
rand_notcar = np.random.choice(len(notcars))
this_car = mpimg.imread(cars[rand_car])
this_notcar = mpimg.imread(notcars[rand_notcar])
print('The size of car is {}'.format(len(this_car)))
print('The size of notcar is {}'.format(len(this_notcar)))
plt.figure(1)
plt.subplot(121)
plt.title('Car:class 1')
plt.imshow(this_car)
plt.subplot(122)
plt.title('Not a Car:class 0')
plt.imshow(this_notcar)
plt.show()The size of car is 64
The size of notcar is 64
接下来,我们来提取Histogram of oriented Gradients(HOG)特征。 有关HOG特征相关的信息,大家可以参考:HOG 提取HOG特征的基本步骤如下:
- 第一阶段为了减少图像亮度的影响需要对图片做一个全局的归一化。
- 第二阶段计算图像的一阶导数,从而捕捉图像的轮廓及纹理信息。
- 第三阶段旨在产生对局部图像内容敏感的编码(cell)
- 第四阶段,归一化(block)
- 最后将HOG descriptor 转化成分类器需要的特征向量
##
def get_hog_features(img,orient,pix_per_cell,cell_per_block,vis=False,feature_vec=True):
'''
function:Extract HOG image and HOG features of a given image
orient: number of bins for the orientation
pix_per_cell: size of a cell
cell_per_block: nber of cells per block
vis(Boolean) :visualize the HOG image
feature_vec(Boolean):return the features as a feature vector
By default,the function uses transform_sqrt(apply power law compression to normalize the image before processing)
'''
if vis == True:
features,hog_image = hog(img,orientations=orient,
pixels_per_cell=(pix_per_cell,pix_per_cell),
cells_per_block = (cell_per_block,cell_per_block),
transform_sqrt=True,
visualise=vis,feature_vector=feature_vec)
return features,hog_image
else:
features = hog(img,orientations=orient,
pixels_per_cell=(pix_per_cell,pix_per_cell),
cells_per_block=(cell_per_block,cell_per_block),
transform_sqrt=True,
visualise=vis,feature_vector=feature_vec)
return features
def bin_spatial(img,size=(32,32)):
'''
Binned Color Feature
img:original image
size:target size of the image
output:feature vector
'''
features = cv2.resize(img,size).ravel()
#print(cv2.resize(img,size).shape)(8,8,3)=>192
return features
def color_hist(img,nbins=32,bins_range=(0,256)):
'''
Color histogram features for each channel of the original image
img: original image
nbins: number of bins of the histogram
output:concatenate feature vector
'''
channel1_hist = np.histogram(img[:,:,0],bins=nbins,range=bins_range)
channel2_hist = np.histogram(img[:,:,1],bins=nbins,range=bins_range)
channel3_hist = np.histogram(img[:,:,2],bins=nbins,range=bins_range)
#Concatenate the histograms into a sigle feature vector
hist_features = np.concatenate((channel1_hist[0],channel2_hist[0],channel3_hist[0]))#48
#print(channel1_hist)
# Return the individual histograms into a single feature vector
return hist_features
def extract_features(imgs,color_space="RGB",spatial_size=(32,32),
hist_bins=32,orient=9,
pix_per_cell=8,cell_per_block=2,hog_channel=0,
spatial_feat=True,hist_feat=True,hog_feat=True,
hog_vis=False):
'''
Feature extractor:extract features from a list of images
The function calls bin_spatial(),color_hist() and get_hog_features
'''
#create a list to append feature vectors to
features = []
# Iterate through the list of images
for file in imgs:
file_features = []
# Read in each one by one
image = mpimg.imread(file)
if hog_vis == False:
image = image.astype(np.float32)/255
# apply color conversion if other than 'RGB'
# color conversion
if color_space in ['HSV','LUV','HLS','YUV','YCrCb']:
feature_image = cv2.cvtColor(image,eval('cv2.COLOR_RGB2'+color_space))
else: feature_image = np.copy(image)
# Image size: add all pixels of reduced image as vector
if spatial_feat == True:
spatial_features = bin_spatial(feature_image,size=spatial_size)
#print('spatial features shape:',spatial_features.shape)
file_features.append(spatial_features)
# Histogram of reduced image: add histogram as a vector
if hist_feat == True:
hist_features = color_hist(feature_image,nbins=hist_bins)
file_features.append(hist_features)
#HOG of reduced image: add HOG as feature vector
if hog_feat == True:# Call get_hog_features() with vis=False ,feature_vec = True
if hog_channel == 'ALL':
hog_features = []
for channel in range(feature_image.shape[2]):
if hog_vis:
hog_feature,hog_image = get_hog_features(feature_image[:,:,channel],
orient,pix_per_cell,cell_per_block,
vis=True,feature_vec=True)
#print(cv2.cvtColor(image,cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY).dtype)
res = cv2.addWeighted(cv2.cvtColor(image,cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY),0.1,
((hog_image/np.max(hog_image))*255).astype(np.float32),0.1,0.0)
# Plot the examples
fig = plt.figure()
plt.title(channel)
plt.subplot(131)
plt.imshow(image,cmap='gray')
plt.title('Original Image')
plt.subplot(132)
plt.imshow(hog_image,cmap='gray')
plt.title('HOG')
plt.subplot(133)
plt.imshow(res,cmap='gray')
plt.title('overlapped')
plt.show()
else:
hog_feature = get_hog_features(feature_image[:,:,channel],
orient,pix_per_cell,cell_per_block,
vis=False,feature_vec=True)
#print('hog feature shape:',hog_feature.shape)
hog_features.append(hog_feature)
hog_features = np.ravel(hog_features)
else:
hog_features = get_hog_features(feature_image[:,:,hog_channel],orient,
pix_per_cell,cell_per_block,vis=False,feature_vec = True)
#Append the new feature vector to the features list
#print('hog features shape:',hog_features.shape)
file_features.append(hog_features)
features.append(np.concatenate(file_features))
#print(np.concatenate(file_features).shape)
# return list of feature vectors
return featurescolor_space = 'YCrCb' # ['RGB','HSV','LUV','HLS','YUV',''YCrCb']
orient = 12#HOG orientations
pix_per_cell = 8#HOG pixels per cell
cell_per_block = 2 #HOG cells per block
hog_channel = 'ALL' # ['0','1','ALL']
spatial_size = (8,8) #Spatial binning dimensions
hist_bins = 16 #Number of histogram bins
hist_range = bins_range = (0,256)
spatial_feat = True #spatial features
hist_feat = False # histogram features
hog_feat = True # hog features# randomly select example
rand_img = np.random.choice(np.arange(0,len(notcars),1))
print('Image adress:',notcars[rand_img])
feat = extract_features([notcars[rand_img]],color_space=color_space,
spatial_size=spatial_size,hist_bins=hist_bins,
orient=orient,pix_per_cell=pix_per_cell,
cell_per_block=cell_per_block,
hog_channel=hog_channel,spatial_feat=spatial_feat,
hist_feat=hist_feat,hog_feat=hog_feat,hog_vis=True
)Image adress: all/non-vehicles/GTI/image1686.png
/home/ora/anaconda3/envs/tensorflow/lib/python3.6/site-packages/skimage/feature/_hog.py:119: skimage_deprecation: Default value of `block_norm`==`L1` is deprecated and will be changed to `L2-Hys` in v0.15
'be changed to `L2-Hys` in v0.15', skimage_deprecation)
car_features = extract_features(cars,color_space=color_space,
spatial_size=spatial_size,hist_bins=hist_bins,orient=orient,
pix_per_cell=pix_per_cell,cell_per_block=cell_per_block,
hog_channel=hog_channel,spatial_feat=spatial_feat,
hist_feat=hist_feat,hog_feat=hog_feat)
notcar_features = extract_features(notcars,color_space=color_space,
spatial_size=spatial_size,hist_bins=hist_bins,
orient=orient,pix_per_cell=pix_per_cell,
cell_per_block=cell_per_block,
hog_channel=hog_channel,spatial_feat=spatial_feat,
hist_feat=hist_feat,hog_feat=hog_feat)
# Group cars and notcars images in a single array
X = np.vstack((car_features,notcar_features)).astype(np.float64)
# Define the labels vector
y = np.hstack((np.ones(len(car_features)),np.zeros(len(notcar_features))))
#Normalize data:fit a per-column scaler
X_scaler = StandardScaler().fit(X)
scaled_X = X_scaler.transform(X)
#Split up data into randomized training and test sets(shuffe included)
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(scaled_X,y,test_size=0.2,random_state=SEED)
print('Using:',orient,'orientations',pix_per_cell,
'pixels per cell and ',cell_per_block,'cells per block')
print('Feature vector length:',len(X_train[0]))
print('Mean of example 0{}|std {}'.format(np.mean(X_train[10]),np.std(X_train[0])))/home/ora/anaconda3/envs/tensorflow/lib/python3.6/site-packages/skimage/feature/_hog.py:119: skimage_deprecation: Default value of `block_norm`==`L1` is deprecated and will be changed to `L2-Hys` in v0.15
'be changed to `L2-Hys` in v0.15', skimage_deprecation)
Using: 12 orientations 8 pixels per cell and 2 cells per block
Feature vector length: 7248
Mean of example 0-0.05479098608161728|std 0.8436106482861411
这里我们运行线性支持向量机
svc = LinearSVC()
# Check the training time for the SVC
t = time.time()
svc.fit(X_train,y_train)
t2 = time.time()
print(round(t2-t,2),'Seconds to train SVC...')
# Check the score of the SVC
print('Train Accuracy of SVC=',round(svc.score(X_train,y_train),4))
print('Test Accuracy of SVC=',round(svc.score(X_test,y_test),4))
# Check the prediction time for a single sample
t = time.time()
n_predict = 10
print('My SVC predicts:',svc.predict(X_test[0:n_predict]))
print('For these',n_predict,'labels:',y_test[0:n_predict])
t2 = time.time()
print(round(t2-t,5),'Seconds to predict',n_predict,'labels with SVC')22.9 Seconds to train SVC...
Train Accuracy of SVC= 1.0
Test Accuracy of SVC= 0.9818
My SVC predicts: [0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0.]
For these 10 labels: [0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0.]
0.00101 Seconds to predict 10 labels with SVC
接下来我们运行逻辑回归分类器
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
lrc = LogisticRegression(max_iter=10)
t = time.time()
lrc.fit(X_train,y_train)
t2 = time.time()
print(round(t2-t,2),'Seconds to train LRC...')
# Check the score of the LRC
print('Train Accuracy of LRC=',round(lrc.score(X_train,y_train),4))
print('Test Accuracy of LRC=',round(lrc.score(X_test,y_test),4))
# Check the prediction time for a single sample
t = time.time()
n_predict = 10
print('My LRC predicts:',lrc.predict(X_test[0:n_predict]))
print('For these',n_predict,'labels:',y_test[0:n_predict])
t2 = time.time()
print(round(t2-t,5),'Seconds to predict',n_predict,'labels with LRC')27.1 Seconds to train LRC...
Train Accuracy of LRC= 1.0
Test Accuracy of LRC= 0.9852
My LRC predicts: [0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0.]
For these 10 labels: [0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0.]
0.00169 Seconds to predict 10 labels with LRC
最后我们来运行多层感知分类器
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier
mlp = MLPClassifier(random_state=SEED)
t = time.time()
mlp.fit(X_train,y_train)
t2 = time.time()
print(round(t2-t,2),'Seconds to train MLP...')
# Check the score of the LRC
print('Train Accuracy of MLP=',round(mlp.score(X_train,y_train),4))
print('Test Accuracy of MLP=',round(mlp.score(X_test,y_test),4))
# Check the prediction time for a single sample
t = time.time()
n_predict = 10
print('My MLP predicts:',mlp.predict(X_test[0:n_predict]))
print('For these',n_predict,'labels:',y_test[0:n_predict])
t2 = time.time()
print(round(t2-t,5),'Seconds to predict',n_predict,'labels with LRC')21.28 Seconds to train MLP...
Train Accuracy of MLP= 1.0
Test Accuracy of MLP= 0.9953
My MLP predicts: [0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0.]
For these 10 labels: [0. 1. 0. 0. 1. 1. 0. 0. 1. 0.]
0.00294 Seconds to predict 10 labels with LRC
保存模型
model_combine = 'model.p'
try:
with open(model_combine,'wb') as pfile:
pickle.dump(
{
'X_dataset':X,
'y_dataset':y,
'svc':svc,
'lrc':lrc,
'mlp':mlp,
'X_scaler':X_scaler,
'color_space':color_space,
'spatial_size':spatial_size,
'hist_bins':hist_bins,
'orient':orient,
'pix_per_cell':pix_per_cell,
'cell_per_block':cell_per_block,
'hog_channel':hog_channel,
'spatial_feat':spatial_feat,
'hist_feat':hist_feat,
'hog_feat':hog_feat
},
pfile,pickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL)
except Exception as e:
print('Unable to save data to',model,':',e)
raiseimport glob
import matplotlib.image as mpimg
import numpy as np
from skimage.feature import hog
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from scipy.ndimage.measurements import label
import time
from sklearn.externals import joblib
import pickle
from moviepy.editor import VideoFileClip
from IPython.display import HTML
# from skimage import measure
SEED = 2018
%matplotlib inlinedef get_hog_features(img,orient,pix_per_cell,cell_per_block,vis=False,feature_vector=True):
'''
function:Extract HOG image and HOG features of a given image
orient: number of bins for the orientation
pix_per_cell: size of a cell
cell_per_block: nber of cells per block
vis(Boolean) :visualize the HOG image
feature_vec(Boolean):return the features as a feature vector
By default,the function uses transform_sqrt(apply power law compression to normalize the image before processing)
'''
if vis == True:
features,hog_image = hog(img,orientations=orient,
pixels_per_cell=(pix_per_cell,pix_per_cell),
cells_per_block = (cell_per_block,cell_per_block),
transform_sqrt=True,
visualise=vis,feature_vector=feature_vector)
return features,hog_image
else:
features = hog(img,orientations=orient,
pixels_per_cell=(pix_per_cell,pix_per_cell),
cells_per_block=(cell_per_block,cell_per_block),
transform_sqrt=True,
visualise=vis,feature_vector=feature_vector)
return features
def bin_spatial(img,size=(32,32)):
'''
Binned Color Feature
img:original image
size:target size of the image
output:feature vector
'''
features = cv2.resize(img,size).ravel()
return features
def color_hist(img,nbins=32,bins_range=(0,256)):
'''
Color histogram features for each channel of the original image
img: original image
nbins: number of bins of the histogram
output:concatenate feature vector
'''
channel1_hist = np.histogram(img[:,:,0],bins=nbins,range=bins_range)
channel2_hist = np.histogram(img[:,:,1],bins=nbins,range=bins_range)
channel3_hist = np.histogram(img[:,:,2],bins=nbins,range=bins_range)
#Concatenate the histograms into a sigle feature vector
hist_features = np.concatenate((channel1_hist[0],channel2_hist[0],channel3_hist[0]))
# Return the individual histograms into a single feature vector
return hist_features
def color_cvt(img,cspace):
'''
image conversion to different color space
cspace avaliable:'HSV','LUV','YUV','YCrCb'
'''
if cspace in ['HSV','LUV','HLS','YUV','YCrCb']:
return cv2.cvtColor(img,eval('cv2.COLOR_RGB2'+cspace))
else:
return np.copy(img)这里选用svc分类器
data_file = 'model.p'
with open(data_file,mode='rb') as f:
data = pickle.load(f)
svc = data['svc']
X_scaler = data['X_scaler']
color_space = data['color_space']
spatial_size = data['spatial_size']
hist_bins = data['hist_bins']
orient = data['orient']
pix_per_cell = data['pix_per_cell']
cell_per_block = data['cell_per_block']
hog_channel = data['hog_channel']
spatial_feat = data['spatial_feat']
hist_feat = data['hist_feat']
hog_feat = data['hog_feat']# 此处列表的更新,可以使用固定长的队列存储,这里是固定更新的
class Buffer():
def __init__(self,buffer_sz):
self.buffer_sz = buffer_sz
self.hot_windows = []
self.heat_mframe = []
self.hotwindows_mframe = []
self.nwindow_mframe = []
def add_hotwindows(self,new_val):
self.hot_windows.append(new_val)
def update_hotwindows_historic(self,new_val):
self.hotwindows_mframe.extend(new_val)
self.nwindow_mframe.append(len(new_val))
if len(self.nwindow_mframe) > self.buffer_sz:
self.hotwindows_mframe = self.hotwindows_mframe[self.nwindow_mframe[0]:]
self.nwindow_mframe = self.nwindow_mframe[-self.buffer_sz:]
def update_heat_historic(self,new_heat):
self.heat_mframe.append(new_heat)
if len(self.heat_mframe) > self.buffer_sz:
self.heat_mframe = self.heat_mframe[-self.buffer_sz:]
buffer = Buffer(buffer_sz=40)接下来实现一个函数来提取特征及作出预测
def find_cars(img,ystart,ystop,cells_per_step,scale,svc,X_scale,cspace,orient,pix_per_cell,
cell_per_block,spatial_feat,spatial_size,hist_feat,hist_bins):
'''
uses a single HOG feature extraction on the entire image
sliding_window = {'scale':[0.6, 0.8, 1.2, 1.6, 2, 2.2],
'ystart':[400, 400, 400, 350, 350, 350],
'ystop': [520, 520, 620, 620, 656, 656],
'cells_per_step': [3, 3, 1, 1, 1, 1]}
img.shape: (720,1280,3)
'''
draw_img = np.copy(img)
#Normalize pixel intensity
img = img.astype(np.float32)/255
#确定搜索车辆的区域
img_tosearch = img[ystart:ystop,700::]
#print(img_tosearch.shape)
ctrans_tosearch = color_cvt(img_tosearch,cspace=cspace)
if scale!=1:
imshape = ctrans_tosearch.shape
ctrans_tosearch = cv2.resize(ctrans_tosearch,(np.int(imshape[1]/scale),np.int(imshape[0]/scale)))
ch1 = ctrans_tosearch[:,:,0]
ch2 = ctrans_tosearch[:,:,1]
ch3 = ctrans_tosearch[:,:,2]
#print(ch1.shape[1])
# Define blocks and steps as above(//地板除法,取整数)
nxblocks = (ch1.shape[1]//(pix_per_cell))-1
nyblocks = (ch1.shape[0]//(pix_per_cell))-1
#nfeat_per_block = orient*cell_per_block**2
#64 was the original sampling rate with 8 cells and 8 pix per cell
window = 64
nblocks_per_window = (window//(pix_per_cell))-1
#cells_per_step = 2 instead of overlap ,define how many cells to step cells=>block
nxsteps = (nxblocks-nblocks_per_window)//cells_per_step
nysteps = (nyblocks-nblocks_per_window)//cells_per_step
#print('nxsteps:{},nysteps:{}'.format(nxsteps,nysteps))
# Compute individual channel HOG features for the entire image
hog1 = get_hog_features(ch1,orient,pix_per_cell,cell_per_block,feature_vector=False)
hog2 = get_hog_features(ch2,orient,pix_per_cell,cell_per_block,feature_vector=False)
hog3 = get_hog_features(ch3,orient,pix_per_cell,cell_per_block,feature_vector=False)
current_hot_windows = []
for xb in range(nxsteps):
for yb in range(nysteps):
ypos = yb*cells_per_step
xpos = xb*cells_per_step
#Extract HOG for this patch
hog_feat1 = hog1[ypos:ypos+nblocks_per_window,xpos:xpos+nblocks_per_window].ravel()
hog_feat2 = hog2[ypos:ypos+nblocks_per_window,xpos:xpos+nblocks_per_window].ravel()
hog_feat3 = hog3[ypos:ypos+nblocks_per_window,xpos:xpos+nblocks_per_window].ravel()
hog_features = np.hstack((hog_feat1,hog_feat2,hog_feat3))
xleft = xpos*pix_per_cell
ytop = ypos*pix_per_cell
#Extract the image patch
subimg = cv2.resize(ctrans_tosearch[ytop:ytop+window,xleft:xleft+window],(64,64))
#Get color features
if spatial_feat == True:
spatial_features = bin_spatial(subimg,size=spatial_size)
if hist_feat == True:
hist_features = color_hist(subimg,nbins=hist_bins)
#Scale features and make a prediction
if (spatial_feat== True) and (hist_feat==True) and (hog_feat==True):
test_feature = X_scaler.transform(np.hstack((spatial_features,hist_features,
hog_features)).reshape(1,-1))
elif (spatial_feat==True) and (hist_feat==False) and (hog_feat==True):
test_features = X_scaler.transform(np.hstack((spatial_features,hog_features)).reshape(1,-1))
test_prediction = svc.predict(test_features)
if test_prediction ==1.:
#这里scale系数需要还原
xbox_left = np.int(xleft*scale) + 700
ytop_draw = np.int(ytop*scale)+ystart
win_draw = np.int(window*scale)
buffer.add_hotwindows(((xbox_left,ytop_draw),(xbox_left+win_draw,ytop_draw+win_draw)))
cv2.rectangle(draw_img,(xbox_left,ytop_draw),(xbox_left+win_draw,ytop_draw+win_draw),
(0,0,255),6)
return draw_img前面代码中,我们将检测到汽车的位置存储在hot_windows中。通过hot_windows我们来画出热点图,并在热点图上应用阈值检测来清除错误检测的坐标
def add_heat(heatmap,bbox_list):
'''
iterate through list of positive sliding windows (bbox_list) and add heat
'''
for box in bbox_list:
# Add +=1 for all pixels inside each bbox
# Assuming each 'box' takes the form ((x1,y1),(x2,y2))
heatmap[box[0][1]:box[1][1],box[0][0]:box[1][0]]+=1
# return updated heatmap
return heatmap# Iterate through
def apply_threshold(heatmap,threshold):
'''
Appy threshold on heatmap
return thresholded heatmap where all values below threshold are set to 0
'''
# Zero out pixles below the threshold
heatmap[heatmap<=threshold] = 0
# return thresholded map
return heatmap
def draw_labeled_bboxes(img,labels):
#Iterate through all detected cars
for car_number in range(1,labels[1]+1):
#find pixels with each car_number label value
nonzero = (labels[0]==car_number).nonzero()
# Identify x and y values of those pixels
nonezeroy = np.array(nonzero[0])
nonezerox = np.array(nonzero[1])
# Define a bounding box based on min/max x and y
bbox = ((np.min(nonezerox),np.min(nonezeroy)),(np.max(nonezerox),np.max(nonezeroy)))
# Check car validtion ==> too small then ignore
if(abs(bbox[0][0]-bbox[1][0])>50 and abs(bbox[0][1]-bbox[1][1])>50):#too small rect are ignore
cv2.rectangle(img,bbox[0],bbox[1],(0,255,0),6)
# return image
return imgsliding_window = {'scale':[0.6, 0.8, 1.2, 1.6, 2, 2.2],
'ystart':[400, 400, 400, 350, 350, 350],
'ystop': [520, 520, 620, 620, 656, 656],
'cells_per_step': [3, 3, 1, 1, 1, 1]}def pipline_test(image):
'''
takes an image and returns a image
'''
#initialize for heatmap of current frame
heat_sframe = np.zeros_like(image[:,:,0]).astype(np.float)
#initialize hot_windows recoder
buffer.hot_windows = []
threshold = 50
for idx ,scale in enumerate(sliding_window['scale']):
ystart = sliding_window['ystart'][idx]
ystop = sliding_window['ystop'][idx]
cells_per_step = sliding_window['cells_per_step'][idx]
out_img = find_cars(image,ystart,ystop,cells_per_step,scale,svc,X_scaler,color_space,orient,
pix_per_cell,cell_per_block,spatial_feat,spatial_size,hist_feat,hist_bins)
plt.imshow(out_img)
plt.title('Find cars function output')
plt.show()
#Add heat to each box in box list
#print(buffer.hot_windows)
heat_sframe = add_heat(heat_sframe,buffer.hot_windows)
heat_sframe = apply_threshold(heat_sframe,threshold)
buffer.update_heat_historic(heat_sframe)
smooth_heat = np.zeros_like(image[:,:,0]).astype(np.float)
for h in buffer.heat_mframe:
smooth_heat +=h
smooth_heat = smooth_heat/len(buffer.heat_mframe)
heatmap = np.clip(smooth_heat,0,255)
plt.imshow(heatmap,cmap='hot')
plt.title('Heat Map')
plt.show()
labels = label(heatmap)
new = draw_labeled_bboxes(np.copy(image),labels)
plt.imshow(new)
plt.title('Result image')
plt.show()
return new
# Read test image
test_data = glob.glob('test_images/*.jpg')
for file in test_data:
image = mpimg.imread(file)
new_image = pipline_test(image)#接下来实现 vehicle detector pipeline
def pipline(image):
'''
takes an image and returns a image
'''
#initialize for heatmap of current frame
heat_sframe = np.zeros_like(image[:,:,0]).astype(np.float)
#initialize hot_windows recoder
buffer.hot_windows = []
threshold = 50
for idx ,scale in enumerate(sliding_window['scale']):
ystart = sliding_window['ystart'][idx]
ystop = sliding_window['ystop'][idx]
cells_per_step = sliding_window['cells_per_step'][idx]
out_img = find_cars(image,ystart,ystop,cells_per_step,scale,svc,X_scaler,color_space,orient,
pix_per_cell,cell_per_block,spatial_feat,spatial_size,hist_feat,hist_bins)
heat_sframe = add_heat(heat_sframe,buffer.hot_windows)
heat_sframe = apply_threshold(heat_sframe,threshold)
buffer.update_heat_historic(heat_sframe)
smooth_heat = np.zeros_like(image[:,:,0]).astype(np.float)
for h in buffer.heat_mframe:
smooth_heat +=h
smooth_heat = smooth_heat/len(buffer.heat_mframe)
heatmap = np.clip(smooth_heat,0,255)
labels = label(heatmap)
new = draw_labeled_bboxes(np.copy(image),labels)
return new# Run pipeline on video
video_output = 'project_solution.mp4'
clip1 = VideoFileClip('project_video.mp4')
white_clip = clip1.fl_image(pipline)
%time white_clip.write_videofile(video_output,audio=False)[MoviePy] >>>> Building video project_solution.mp4
[MoviePy] Writing video project_solution.mp4
100%|█████████▉| 1260/1261 [12:31<00:00, 1.70it/s]
[MoviePy] Done.
[MoviePy] >>>> Video ready: project_solution.mp4
CPU times: user 12min 32s, sys: 2.17 s, total: 12min 34s
Wall time: 12min 32s