-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 4
gke aks multi cloud small top 1.3 ahr manual
This mission of this collection of workthroughs is to provide end-to-end experiences of designing and/or setting up topologies of Apigee Hybrid. From a single region to multi-region on a single cloud to multi-cloud deployment.
From the end-to-end point of view, it is important to start from a clean slate networking-wise.
We are assuming no default networks or default range allocations. We are going to plan our network layout. Up to a last CIDR. Then we will execute our plan.
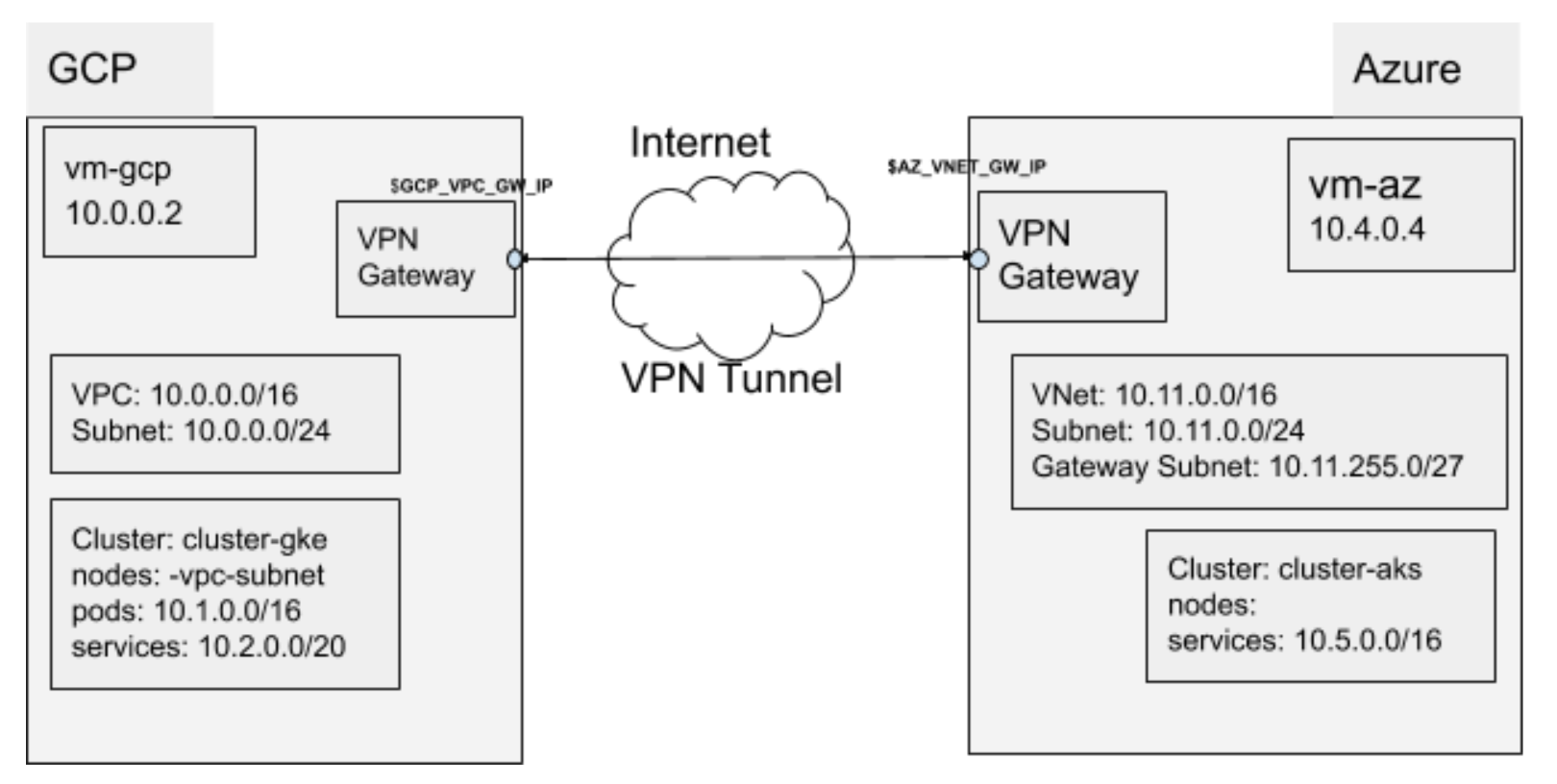
?. Let's be organized and tidy and put all installation files into one directory.
export HYBRID_HOME=~/mch-hybrid-install
mkdir -p $HYBRID_HOME
?. The multicloud-gke-ask.env file contains variables we need to set up networking in and across GCP and Azure clouds.
cat <<"EOF" > $HYBRID_HOME/multicloud-gke-aks.env
### gcp-r1.env
#
# GCP/GKE
#
export GCP_REGION=${REGION:-europe-west1}
export GCP_ZONE=${ZONE:-europe-west1-b}
export GCP_VPC=$GCP_REGION-vpc
export GCP_VPC_SUBNET=$GCP_VPC-subnet
export GCP_VPC_GW_NAME=$GCP_REGION-gw
export GCP_VPC_GW_IP_NAME=$GCP_VPC_GW_NAME-gw-ip
export GCP_VPC_TARGET_GW=$GCP_REGION-tgt-gw
export GCP_VPN_TUNNEL=$GCP_REGION-vpn-tunnel
export GCP_VPC_VPN_ROUTE=$GCP_REGION-route-az
export GCP_VPC_CIDR=10.0.0.0/14
export GCP_VPC_SUBNET_CIDR=10.0.0.0/16
### az-r2.env
#
# AZ/AKS
#
export RESOURCE_GROUP=yuriyl
export AZ_REGION=westeurope
export AZ_VNET=$RESOURCE_GROUP-vnet-$AZ_REGION
export AZ_VNET_SUBNET=$AZ_VNET-subnet
export AZ_VNET_GW_IP_NAME=$RESOURCE_GROUP-vnet-$AZ_REGION-gw-ip
export AZ_VNET_GW=$RESOURCE_GROUP-vnet-$AZ_REGION-gateway
# CIDR: VNet/VPN
export AZ_VNET_CIDR=10.4.0.0/14
export AZ_VNET_SUBNET_CIDR=10.4.0.0/16
export AZ_VNET_GW_SUBNET_CIDR=10.7.255.0/27
EOF
source $HYBRID_HOME/multicloud-gke-aks.env
?. Check the configuration values against the illustration. Observe:
- CIDRs do not overlap;
- There are no public _IP addresses yet for a tunnel;
It is your personal preference how to do your job. Saying that, if you do not have a preference yet, I would recommend doing all the work in GCP Cloud Shell. Open 4 tabs and allocate session positionally for following purposes:
- tab 1: Main session, working control tab for both clouds;
- tab 2: An editor of your choice to edit/view files and navigate around a file system (vi, emacs, mc, etc);
- tab 3: A GKE session;
- tab 4: An AKS session;
?. Set up gcp project variable and config setting
export PROJECT=$(gcloud projects list|grep qwiklabs-gcp|awk '{print $1}')
gcloud config set project $PROJECT
REF: In case of GCP we are going to follow this document to creating a classic VPN using static routing: https://cloud.google.com/network-connectivity/docs/vpn/how-to/creating-static-vpns Follow the link for additional explanations.
?. Create a VPC Network
gcloud compute networks create $GCP_VPC \
--subnet-mode=custom \
--bgp-routing-mode=regional \
--mtu=1460
?. Create a network subnet
gcloud compute networks subnets create $GCP_VPC_SUBNET \
--network=$GCP_VPC \
--range=$GCP_VPC_SUBNET_CIDR \
--region=$GCP_REGION
?. Firewall Rules for internal, 22, and icmp traffic
gcloud compute firewall-rules create $GCP_VPC-allow-internal --network $GCP_VPC --allow tcp,udp,icmp --source-ranges $GCP_VPC_CIDR
gcloud compute firewall-rules create fr-$GCP_VPC-ssh --network $GCP_VPC --allow tcp:22
gcloud compute firewall-rules create fr-$GCP_VPC-icmp --network $GCP_VPC --allow icmp
We are going to follow Azure instructions on creation of VPN Gateway using CLI. You can refer to this page for more detailed explanations: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/vpn-gateway/vpn-gateway-howto-site-to-site-resource-manager-cli
?. Install az command with default settings:
NOTE: Use this if you wish to run an interactive version:
curl -L https://aka.ms/InstallAzureCli | bash
pip3 install azure-cli
?. Install script configures PATH for az command as well as bash completion. Re-init your PATH variable to add ~/.local/bin directory, where the az is installed.
source ~/.profile
?. Authenticate into your az account
az login
az network vnet create --name $AZ_VNET --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --address-prefix $AZ_VNET_CIDR --location $AZ_REGION --subnet-name $AZ_VNET_SUBNET --subnet-prefix $AZ_VNET_SUBNET_CIDR
az network vnet subnet create --address-prefix $AZ_VNET_GW_SUBNET_CIDR --name GatewaySubnet --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --vnet-name $AZ_VNET
REF: https://cloud.google.com/network-connectivity/docs/vpn/how-to/creating-static-vpns
?. Create the resources for the Cloud VPN gateway:
b. Reserve a regional external (static) IP address:
gcloud compute addresses create $GCP_VPC_GW_IP_NAME \
--region $GCP_REGION \
--project $PROJECT
?. Note the IP address (we are going to you use it when we will be configuring our peer VPN gateway):
export GCP_VPC_GW_IP=$(gcloud compute addresses describe $GCP_VPC_GW_IP_NAME \
--region $GCP_REGION \
--project $PROJECT \
--format='value(address)' )
A Local Network Gateway represents your 'on-premises' site.
az network local-gateway create --gateway-ip-address $GCP_VPC_GW_IP --name $GCP_VPC --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --local-address-prefixes $GCP_VPC_CIDR
A VPN gateway must have a Public IP address. VPN Gateway currently only supports Dynamic Public IP address allocation.
az network public-ip create --name $AZ_VNET_GW_IP_NAME --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --allocation-method Dynamic
WARNING: It does take time 19:04-19:33. You better plan lunch around this operation. " Creating a VPN gateway can take 30 up to 45 minutes or more to complete." ->
NOTE: You can use --no-wait az command option to execute this long-running command in an asynchronous mode. In this case, use the az network vnet-gateway list command to check for a current status. See below.
az network vnet-gateway create --name $AZ_VNET_GW --public-ip-address $AZ_VNET_GW_IP_NAME --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --vnet $AZ_VNET --gateway-type Vpn --vpn-type RouteBased --sku VpnGw1
?. You can check provisioning status using the following command and observing the value for ProvisioningState
az network vnet-gateway list --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --output table
?. Get the public ip address
export AZ_VNET_GW_IP=$(az network public-ip show --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --name $AZ_VNET_GW_IP_NAME --query ipAddress --output tsv)
gcloud compute target-vpn-gateways create $GCP_VPC_TARGET_GW \
--network $GCP_VPC \
--region $GCP_REGION \
--project $PROJECT
These rules instruct Google Cloud to send ESP (IPsec), UDP 500, and UDP 4500 traffic to the gateway. These are the default ports required for IPsec VPN connections
gcloud compute forwarding-rules create fr-$GW_NAME-esp \
--ip-protocol ESP \
--address $GCP_VPC_GW_IP \
--target-vpn-gateway $GCP_VPC_TARGET_GW \
--region $GCP_REGION \
--project $PROJECT
gcloud compute forwarding-rules create fr-$GW_NAME-udp500 \
--ip-protocol UDP \
--ports 500 \
--address $GCP_VPC_GW_IP \
--target-vpn-gateway $GCP_VPC_TARGET_GW \
--region $GCP_REGION \
--project $PROJECT
gcloud compute forwarding-rules create fr-$GW_NAME-udp4500 \
--ip-protocol UDP \
--ports 4500 \
--address $GCP_VPC_GW_IP \
--target-vpn-gateway $GCP_VPC_TARGET_GW \
--region $GCP_REGION \
--project $PROJECT
IKEv2 (Internet Key Exchange version 2) http://www.internet-computer-security.com/VPN-Guide/Policy-based-vs-Route-based-VPN.html
A route based VPN is more flexible, more powerful and recommended over policy based VPN. However a policy based VPN is usually simpler to create.
Supported IKE ciphers https://cloud.google.com/network-connectivity/docs/vpn/concepts/supported-ike-ciphers How to generate: https://cloud.google.com/network-connectivity/docs/vpn/how-to/generating-pre-shared-key
?. Generate PSK
export PSK=$(openssl rand -base64 24)
?. Route based VPN, both the local and remote traffic selectors are 0.0.0.0/0 as defined in routing options and traffic selectors.
gcloud compute vpn-tunnels create $GCP_VPN_TUNNEL \
--peer-address $AZ_VNET_GW_IP \
--ike-version 2 \
--shared-secret $PSK \
--local-traffic-selector=0.0.0.0/0 \
--remote-traffic-selector=0.0.0.0/0 \
--target-vpn-gateway $GCP_VPC_TARGET_GW \
--region $GCP_REGION \
--project $PROJECT
?. A static route for each remote IP range you specified in the --remote-traffic-selector option in the previous step.
gcloud compute routes create $GCP_VPC_VPN_ROUTE \
--destination-range $AZ_VNET_CIDR \
--next-hop-vpn-tunnel $GCP_VPN_TUNNEL \
--network $GCP_VPC \
--next-hop-vpn-tunnel-region $GCP_REGION \
--project $PROJECT
az network vpn-connection create --name VNetToVPC --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --vnet-gateway1 $AZ_VNET_GW --location $AZ_REGION --shared-key $PSK --local-gateway2 $GCP_VPC
It might take some time to establish connection.
?. CLI: GCP VPN Tunnel state: https://cloud.google.com/network-connectivity/docs/vpn/how-to/checking-vpn-status
gcloud compute vpn-tunnels describe $GCP_VPN_TUNNEL \
--region $GCP_REGION \
--project $PROJECT \
--format='flattened(status,detailedStatus)'
detailedStatus: Tunnel is up and running.
status: ESTABLISHED
?. Console: NETWORKING, Hybrid Connectivity, VPN
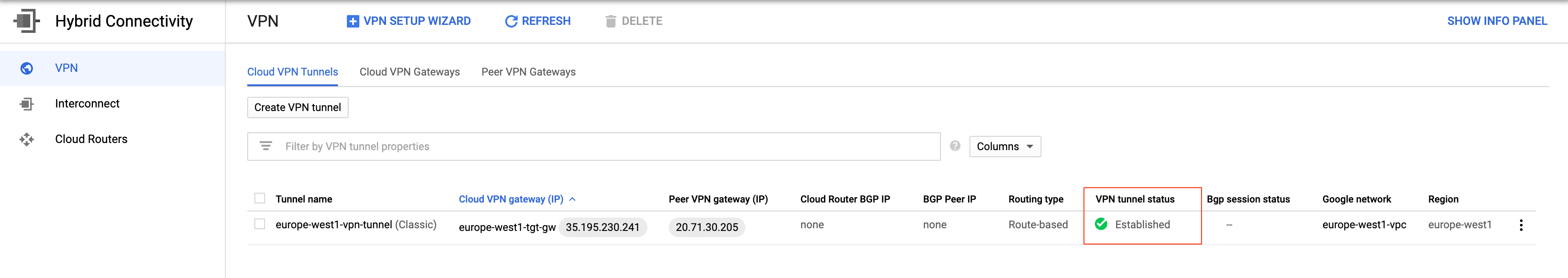
?. CLI: Azure VPN connection status
az network vpn-connection show --name VNetToVPC --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --query connectionStatus
"Connected"
?. Portal: All Services, Other, Virtual network gateways. Open $AZ_VNET_GW; Connections:
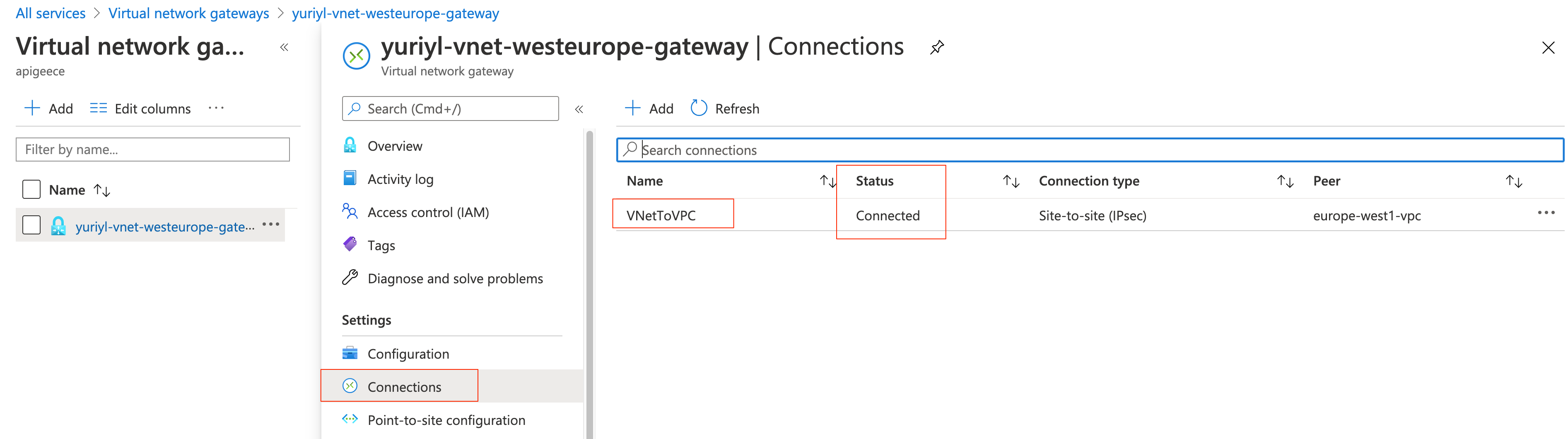
az vm create -n vm-az -g $RESOURCE_GROUP --location $AZ_REGION --vnet-name $AZ_VNET --subnet $AZ_VNET_SUBNET --image ubuntults --data-disk-sizes-gb 10 20 --size Standard_DS2_v2 --generate-ssh-keys
# --ssh-dest-key-path
# --ssh-key-values
...
"privateIpAddress": "10.4.0.4",
"publicIpAddress": "20.71.109.28",
...
gcloud compute instances create vm-gcp --zone=$GCP_ZONE --network $GCP_VPC --subnet $GCP_VPC_SUBNET
NAME ZONE MACHINE_TYPE PREEMPTIBLE INTERNAL_IP EXTERNAL_IP STATUS
vm-gcp europe-west1-b n1-standard-1 10.0.0.2 35.241.139.207 RUNNING
ssh 20.71.109.28 -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa
?. In the terminal,
ping 10.0.0.2
PING 10.0.0.2 (10.0.0.2) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.0.0.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=13.1 ms
64 bytes from 10.0.0.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=63 time=13.3 ms
64 bytes from 10.0.0.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=63 time=13.4 ms
^C
--- 10.0.0.2 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2002ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 13.186/13.335/13.497/0.184 ms
gcloud compute ssh vm-gcp --zone $GCP_ZONE
?. In the terminal,
ping 10.4.0.4
student-02-bc30a4a315fe@vm-gcp:~$ ping 10.4.0.4
PING 10.4.0.4 (10.4.0.4) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.4.0.4: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=13.7 ms
64 bytes from 10.4.0.4: icmp_seq=2 ttl=63 time=13.4 ms
64 bytes from 10.4.0.4: icmp_seq=3 ttl=63 time=14.2 ms
^C
--- 10.4.0.4 ping statistics ---
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 6ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 13.429/13.793/14.244/0.364 ms
For a convenince, we have all additional config files defined here. We instantiate them by running following cat commands.
The environment config files are related in a way to modularise/optimise settings location.
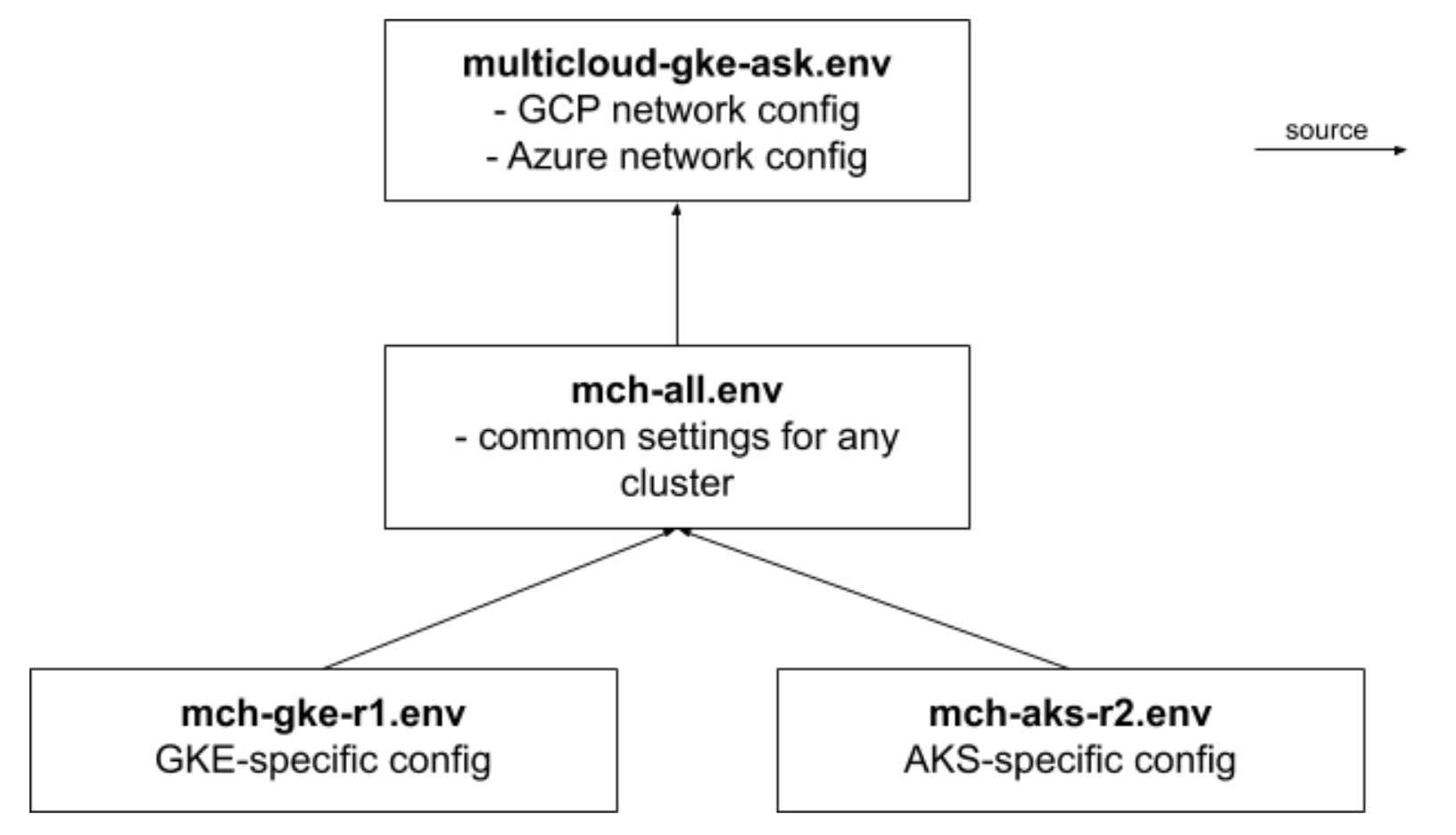
There is some redundancy in a variable definitions that benefit your workflow in a single or separate sessions.
For example, two variable R1_CLUSTER and R2_CLUSTER at the -all.env level define cluster names. At the same time, -gke-r1.env and -aks-r2.env files each contain $CLUSTER variable that use variables above. I.e., export CLUSTER=$R1_CLUSTER in -gke-r1.env.
When you source -gke-r1.env, you set up your session to contain CLUSTER as a current value for a Region 1. At the same time, you can use R1_CLUSTER as a kubectl --context value to be able to execute a command against a specific cluster.
Keep in mind that there is a single current context for an kubectl command across all your sessions. That means, if you use a $CLUSTER variable, you better make sure it works against intended cluser by invoking kubectl config use-cluster $CLUSTER command before invoking kubectl without a --context $CLUSTER option.
?. Create config files
cat <<"EOF" > $HYBRID_HOME/mch-all.env
# useful functions
source $AHR_HOME/bin/ahr-lib.sh # for get_platform_suffix
# common variables
source $HYBRID_HOME/multicloud-gke-aks.env
export PLATFORM=${PLATFORM:-linux}
export CERT_MANAGER_MANIFEST=https://github.com/jetstack/cert-manager/releases/download/v0.14.2/cert-manager.yaml
export ASM_PROFILE=asm-multicloud
export ASM_VERSION=${ASM_VERSION:-1.6.11-asm.1}
export ASM_TEMPLATE=$HYBRID_HOME/anthos-service-mesh-packages/asm/cluster/istio-operator.yaml
#
# GCP Project/Control Plane configuration
#
export REGION=$GCP_REGION
export ZONE=$GCP_ZONE
export AX_REGION=$REGION
#
# Hybrid release configuration
#
export HYBRID_VERSION=1.3.3
export HYBRID_TARBALL=apigeectl_$(get_platform_suffix apigeectl $PLATFORM)
#
# Runtime Cluster definition
#
export CLUSTER_TEMPLATE=$AHR_HOME/templates/cluster-single-zone-one-nodepool-template.json
export CLUSTER_VERSION=1.17
export R1_CLUSTER=cluster-gke
export R2_CLUSTER=cluster-az
#------------------------------------------------------------
#
# Runtime Hybrid configuration
#
export ORG=$PROJECT
export ENV=test
export ENV_GROUP=test-group
#export ENC_KEY_KMS=$(LC_ALL=C tr -dc "[:print:]" < /dev/urandom | head -c 32 | openssl base64)
#export ENC_KEY_KVM=$ENC_KEY_KMS
#export ENC_KEY_CACHE=$ENC_KEY_KMS
export SA_DIR=$HYBRID_HOME/service-accounts
export MART_ID=apigee-mart
export SYNCHRONIZER_ID=apigee-synchronizer
export SYNCHRONIZER_SA=$SA_DIR/$PROJECT-$SYNCHRONIZER_ID.json
export UDCA_SA=$SA_DIR/$PROJECT-apigee-udca.json
export MART_SA=$SA_DIR/$PROJECT-apigee-mart.json
export METRICS_SA=$SA_DIR/$PROJECT-apigee-metrics.json
export WATCHER_SA=$SA_DIR/$PROJECT-apigee-watcher.json
export MART_SA_ID=$MART_ID@$PROJECT.iam.gserviceaccount.com
export SYNCHRONIZER_SA_ID=$SYNCHRONIZER_ID@$PROJECT.iam.gserviceaccount.com
export RUNTIME_HOST_ALIAS=$ORG-$ENV.hybrid-apigee.net
export RUNTIME_SSL_CERT=$HYBRID_HOME/hybrid-cert.pem
export RUNTIME_SSL_KEY=$HYBRID_HOME/hybrid-key.pem
#------------------------------------------------------------
EOF
cat <<"EOF" > $HYBRID_HOME/mch-gke-r1.env
# region 1
BASEDIR="$( cd "$( dirname "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}" )" && pwd )"
. $BASEDIR/mch-all.env
## Region 1: GKE
#
# GCP Project:
#
export NETWORK=$GCP_VPC
export SUBNETWORK=$GCP_VPC_SUBNET
#
export MACHINE_TYPE_DATA=${MACHINE_TYPE_DATA:-e2-standard-8}
export MACHINE_TYPE_RUNTIME=${MACHINE_TYPE_RUNTIME:-e2-standard-4}
export CLUSTER_CONFIG=$HYBRID_HOME/cluster-sz-gke.json
export CLUSTER=$R1_CLUSTER
export CLUSTER_ZONE=${ZONE}
export CLUSTER_LOCATIONS='"'${ZONE:-europe-west1-b}'"'
export CONTEXT=$CLUSTER
#
export ASM_CONFIG=$HYBRID_HOME/istio-operator-gke.yaml
#--cluster-secondary-range-name= for pods
export GCP_VPC_SUBNET_PODS=$GCP_VPC-pods-secsubnet20
export GCP_VPC_SUBNET_PODS_CIDR=10.1.0.0/16
#--services-secondary-range-name= for services
export GCP_VPC_SUBNET_SERVICES=$GCP_VPC-services-secsubnet20
export GCP_VPC_SUBNET_SERVICES_CIDR=10.2.0.0/20
export RUNTIME_CONFIG=$HYBRID_HOME/runtime-sz-gke.yaml
export RUNTIME_IP=203.0.113.10
EOF
cat <<"EOF" > $HYBRID_HOME/mch-aks-r2.env
# region 2
BASEDIR="$( cd "$( dirname "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}" )" && pwd )"
. $BASEDIR/mch-all.env
# Azure
export RESOURCE_GROUP=yuriyl
export CLUSTER_CONFIG=$HYBRID_HOME/cluster-sz-az.json
export CLUSTER=$R2_CLUSTER
#
export ASM_CONFIG=$HYBRID_HOME/istio-operator-aks.yaml
#
export AKS_SERVICE_CIDR=10.5.0.0/16
export AKS_DNS_SERVICE_IP=10.5.0.10
export AKS_DOCKER_CIDR=172.17.0.2/16
export RUNTIME_CONFIG=$HYBRID_HOME/runtime-sz-aks.yaml
export RUNTIME_IP=203.0.113.10
EOF
?. Clone AHR repo
cd $HYBRID_HOME
git clone https://github.com/yuriylesyuk/ahr.git
export AHR_HOME=$HYBRID_HOME/ahr
export PATH=$AHR_HOME/bin:$PATH
?. Enable required GCP APIs
ahr-verify-ctl api-enable
Again, open two extra tabs in the Cloud Shell (two ssh sessions), 'nominate' them as "GCP Terminal" and "Azure Terminal" and switch between them, when executing following commands.
TIP: Configure a new session. For any new shell you open, this set of commands configures your environment
?. Use this command snippet to initialise your session state in each new terminal
export PROJECT=$(gcloud projects list --filter='project_id~qwiklabs-gcp' --format=value'(project_id)')
gcloud config set project $PROJECT
export HYBRID_HOME=~/mch-hybrid-install
export AHR_HOME=$HYBRID_HOME/ahr
export PATH=$AHR_HOME/bin:$PATH
export APIGEECTL_HOME=$HYBRID_HOME/$(tar tf $HYBRID_HOME/$HYBRID_TARBALL | grep VERSION.txt | cut -d "/" -f 1)
export PATH=$APIGEECTL_HOME:$PATH
?. GCP: source GKE cluster environment
source $HYBRID_HOME/mch-gke-r1.env
?. Create secondary ranges for pods and services
gcloud compute networks subnets update $GCP_VPC_SUBNET \
--region=$GCP_REGION \
--add-secondary-ranges=$GCP_VPC_SUBNET_PODS=$GCP_VPC_SUBNET_PODS_CIDR,$GCP_VPC_SUBNET_SERVICES=$GCP_VPC_SUBNET_SERVICES_CIDR
?. Define cluster configuration file using provided small topology cluster template
ahr-cluster-ctl template $CLUSTER_TEMPLATE > $CLUSTER_CONFIG
?. Explicitly configure pods and services CIDRs
export CLUSTER_IP_ALLOCATION_POLICY=$( cat << EOT
{
"useIpAliases": true,
"clusterSecondaryRangeName": "$GCP_VPC_SUBNET_PODS",
"servicesSecondaryRangeName": "$GCP_VPC_SUBNET_SERVICES"
}
EOT
)
cat <<< "$(jq .cluster.ipAllocationPolicy="$CLUSTER_IP_ALLOCATION_POLICY" < $CLUSTER_CONFIG)" > $CLUSTER_CONFIG
?. Inspect the cluster that we are creating
vi $CLUSTER_CONFIG
?. Create the cluster
ahr-cluster-ctl create
?. Being native GKE cluster, we can straight away administrate and manage it.
Console: COMPUTE, Kubernetes Engine, Clusters
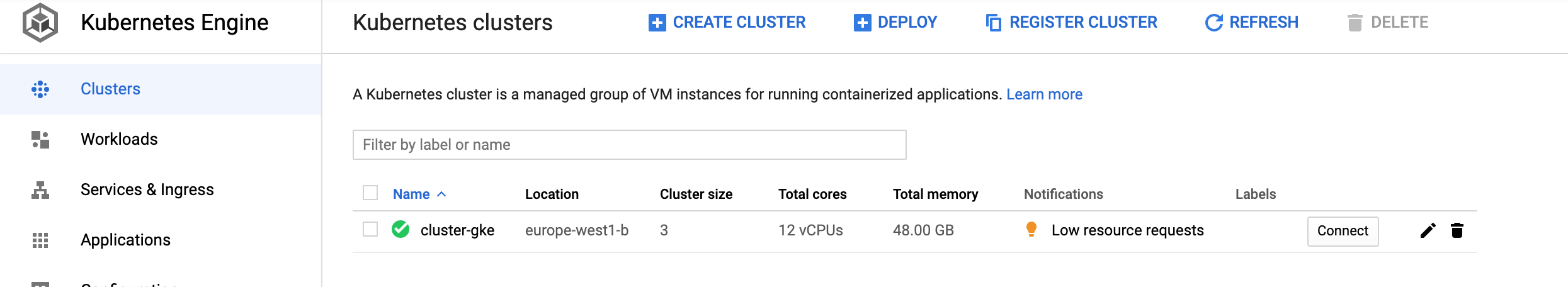
?. Source the session environment
source $HYBRID_HOME/mch-aks-r2.env
?. Get AZ_VNET_SUBNET id
export AZ_VNET_SUBNET_ID=$(
az network vnet subnet show \
--resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP \
--vnet-name $AZ_VNET \
--name $AZ_VNET_SUBNET \
--query id \
--output tsv )
?. Create AKS cluster
az aks create \
--resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP \
--name $CLUSTER \
--location $AZ_REGION \
--kubernetes-version 1.17.11 \
--nodepool-name hybridpool \
--node-vm-size Standard_DS3_v2 \
--node-count 4 \
--network-plugin azure \
--vnet-subnet-id $AZ_VNET_SUBNET_ID \
--service-cidr $AKS_SERVICE_CIDR \
--dns-service-ip $AKS_DNS_SERVICE_IP \
--docker-bridge-address $AKS_DOCKER_CIDR \
--generate-ssh-keys \
--output table
?. Get cluster credentials
az aks get-credentials --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --name $CLUSTER
?. AKS Cluster membership (see ahr/aks single region for detailed information).
gcloud iam service-accounts create anthos-hub --project=$PROJECT
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $PROJECT \
--member="serviceAccount:anthos-hub@$PROJECT.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role="roles/gkehub.connect"
gcloud iam service-accounts keys create $HYBRID_HOME/anthos-hub-$PROJECT.json \
--iam-account=anthos-hub@$PROJECT.iam.gserviceaccount.com --project=$PROJECT
gcloud container hub memberships register $CLUSTER \
--context=$CLUSTER \
--kubeconfig=~/.kube/config \
--service-account-key-file=$HYBRID_HOME/anthos-hub-$PROJECT.json
?. Kubectl: Create kubernetes service account
kubectl create serviceaccount anthos-user
kubectl create clusterrolebinding aksadminbinding --clusterrole view --serviceaccount default:anthos-user
kubectl create clusterrolebinding aksadminnodereader --clusterrole node-reader --serviceaccount default:anthos-user
kubectl create clusterrolebinding aksclusteradminbinding --clusterrole cluster-admin --serviceaccount default:anthos-user
?. Kubectl: Get the token for the service account
export CLUSTER_SECRET=$(kubectl get serviceaccount anthos-user -o jsonpath='{$.secrets[0].name}')
kubectl get secret ${CLUSTER_SECRET} -o jsonpath='{$.data.token}' | base64 --decode
?. GCP Console: Log into Cluster via the token form the previous step.
?. At this point, both clusters should be accessible from our GCP Console
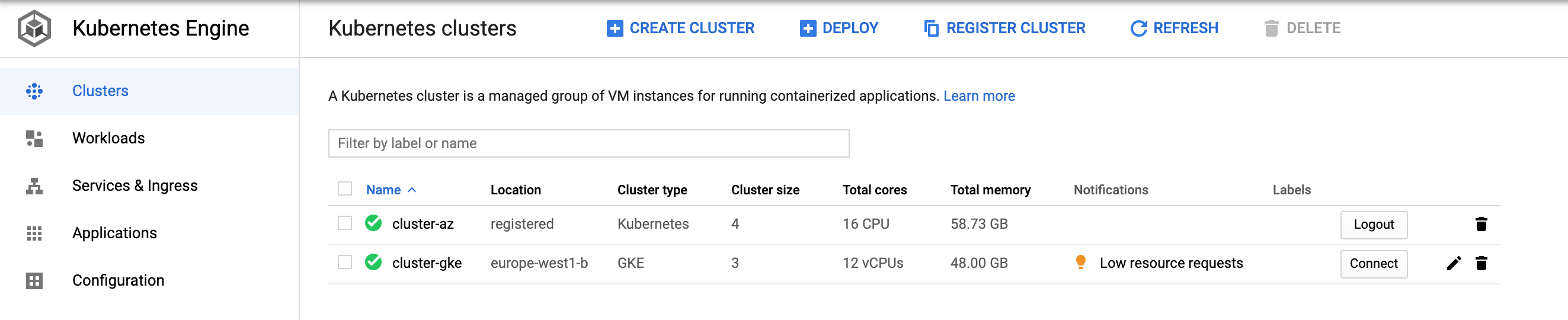
?. Configure a firewall rule for Cassandra inter node communication (tcp ports 7000, 7001)
gcloud compute firewall-rules create fr-$GCP_VPC-cs-internode --network $GCP_VPC --allow tcp:7000,tcp:7001
?. In a 'gke' terminal session
kubectl --context $R1_CLUSTER run -i --tty busybox --image=busybox --restart=Never -- sh
?. In an 'aks' terminal session
kubectl --context $R2_CLUSTER run -i --tty busybox --image=busybox --restart=Never -- sh
?. In a 'control' session, source env variables
source $HYBRID_HOME/mch-all.env
?. Get IP addreses of busybox pods
kubectl --context $R1_CLUSTER describe pod busybox | grep ^IP:
kubectl --context $R2_CLUSTER describe pod busybox | grep ^IP:
Example output:
$ kubectl --context $R1_CLUSTER describe pod busybox | grep ^IP:
IP: 10.96.1.4
$ kubectl --context $R2_CLUSTER describe pod busybox | grep ^IP:
IP: 10.4.0.76
?. gke:
hostname -i
10.96.1.4
?. az:
hostname -i
10.4.0.76
?. gke ping az
ping 10.4.0.76
?. az ping gke
ping 10.96.1.4
?. start nc in a listening mode
nc -l 0.0.0.0 -p 7000 -v
?. gke nc az
nc -v 10.4.0.76 7000
?. Probe in an opposing direction
nc -v 10.4.0.111 7000
?. You can delete busybox containers now
kubectl --context $R1_CLUSTER delete pod busybox
kubectl --context $R2_CLUSTER delete pod busybox
?. Install Certificate Manager
kubectl --context $CLUSTER apply --validate=false -f $CERT_MANAGER_MANIFEST
?. Feel free to use GCP Console Kuberenetes Engine/Workloads page to watch pods and their statuses
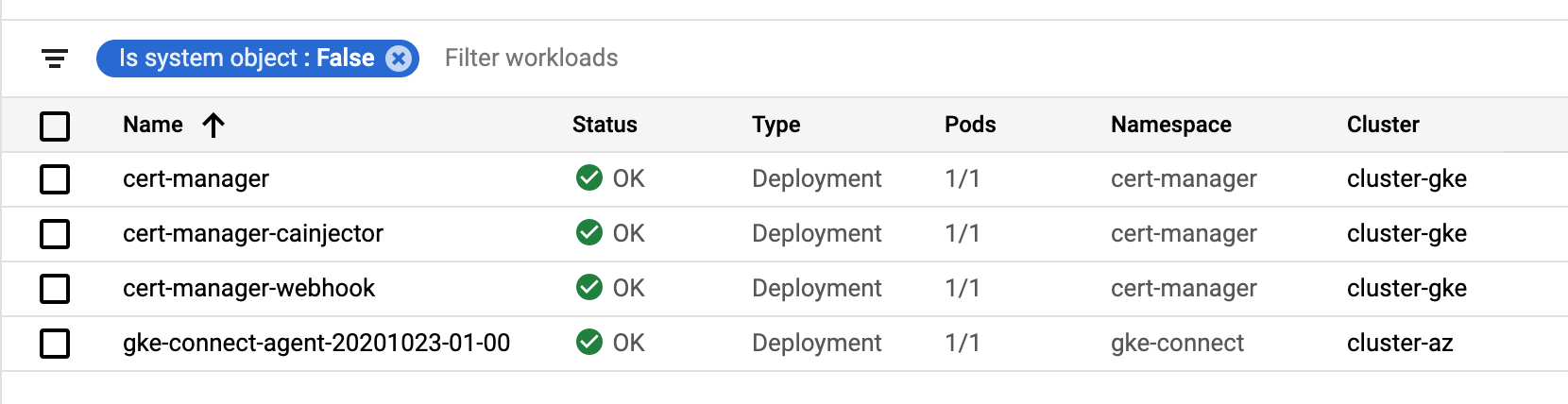
?. Create a regional load balancer we will use for istio ingress gateway configuration.
gcloud compute addresses create runtime-ip --region $REGION
?. Get the value of the IP address
export RUNTIME_IP=$(gcloud compute addresses describe runtime-ip --region $REGION --format='value(address)')
?. Replace RUNTIME_IP value in gke environment file
sed -i -E "s/^(export RUNTIME_IP=).*/\1$RUNTIME_IP/g" $HYBRID_HOME/mch-gke-r1.env
?. The $mch-gke-r1.evn file now has a value of RUNTIME_IP address set to just provisioned static IP address.
vi $HYBRID_HOME/mch-gke-r1.env
?. Make sure $ASM_PROFILE is asm-multicloud
echo $ASM_PROFILE
?. configure IstioOperator manifest.
export PROJECT_NUMBER=$(gcloud projects describe ${PROJECT} --format="value(projectNumber)")
export ref=\$ref
export ASM_RELEASE=$(echo "$ASM_VERSION"|awk '{sub(/\.[0-9]+-asm\.[0-9]+/,"");print}')
?. Process provided template file suitable for on-prem ASM installation
ahr-cluster-ctl template $AHR_HOME/templates/istio-operator-$ASM_RELEASE-$ASM_PROFILE.yaml > $ASM_CONFIG
?. Get ASM installation files
ahr-cluster-ctl asm-get $ASM_VERSION
?. Define ASM_HOME and add ASM bin directory to the path by copying and pasting provided export statements from the previous command output.
export ASM_HOME=$HYBRID_HOME/istio-$ASM_VERSION
export PATH=$ASM_HOME/bin:$PATH
?. Install ASM into our cluster
istioctl --context $CLUSTER install -f $ASM_CONFIG
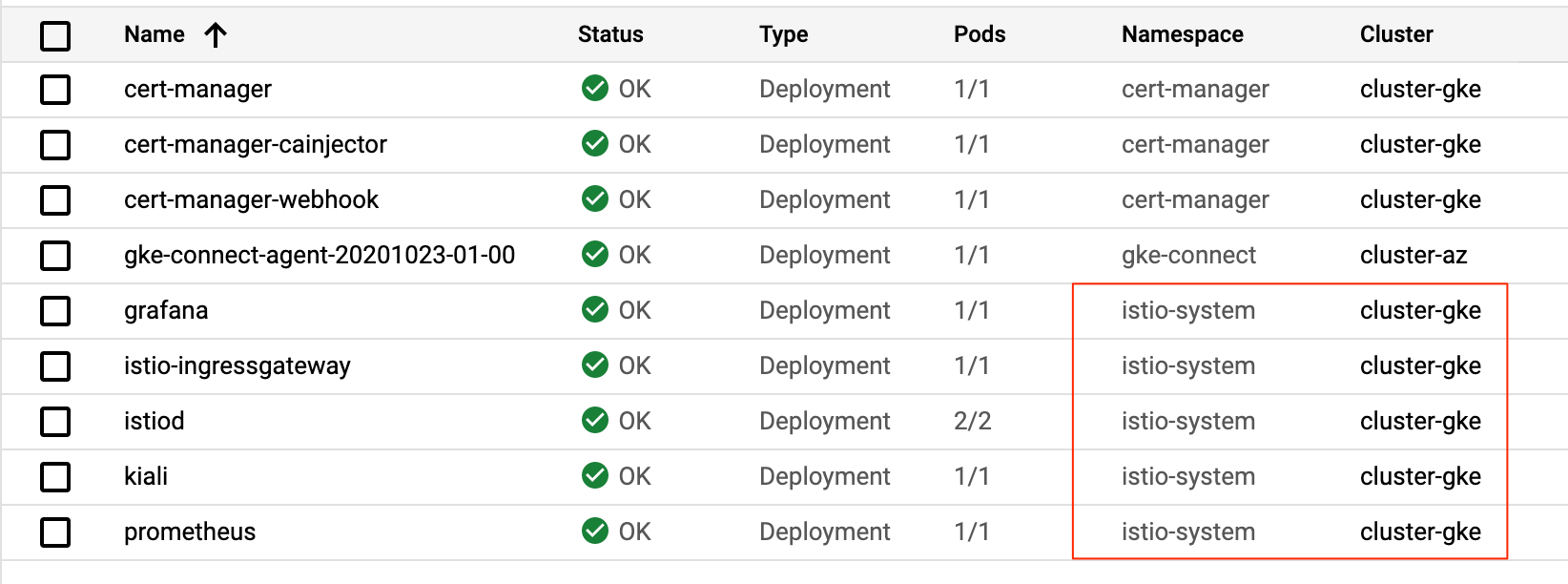
? Create a hybrid organization, environment, and environment group.
ahr-runtime-ctl org-create $ORG --ax-region $AX_REGION
ahr-runtime-ctl env-create $ENV
ahr-runtime-ctl env-group-create $ENV_GROUP $RUNTIME_HOST_ALIAS
ahr-runtime-ctl env-group-assign $ORG $ENV_GROUP $ENV
?. SAs and their Keys
ahr-sa-ctl create-sa all
ahr-sa-ctl create-key all
?. Set up synchronizer Service Account identifier (email)
ahr-runtime-ctl setsync $SYNCHRONIZER_SA_ID
?. Configure self-signed certificate for Ingress Gateway
ahr-verify-ctl cert-create-ssc $RUNTIME_SSL_CERT $RUNTIME_SSL_KEY $RUNTIME_HOST_ALIAS
?. Get apigeectl and hybrid distribution
ahr-runtime-ctl get
?. Amend PATH
export APIGEECTL_HOME=$HYBRID_HOME/$(tar tf $HYBRID_HOME/$HYBRID_TARBALL | grep VERSION.txt | cut -d "/" -f 1)
export PATH=$APIGEECTL_HOME:$PATH
?. Generate Runtime Configuration yaml file
ahr-runtime-ctl template $AHR_HOME/templates/overrides-small-13-template.yaml > $RUNTIME_CONFIG
?. Deploy Init and runtime Hybrid Components
kubectl config use-context $CLUSTER
ahr-runtime-ctl apigeectl init -f $RUNTIME_CONFIG
ahr-runtime-ctl apigeectl wait-for-ready -f $RUNTIME_CONFIG
ahr-runtime-ctl apigeectl apply -f $RUNTIME_CONFIG
ahr-runtime-ctl apigeectl wait-for-ready -f $RUNTIME_CONFIG
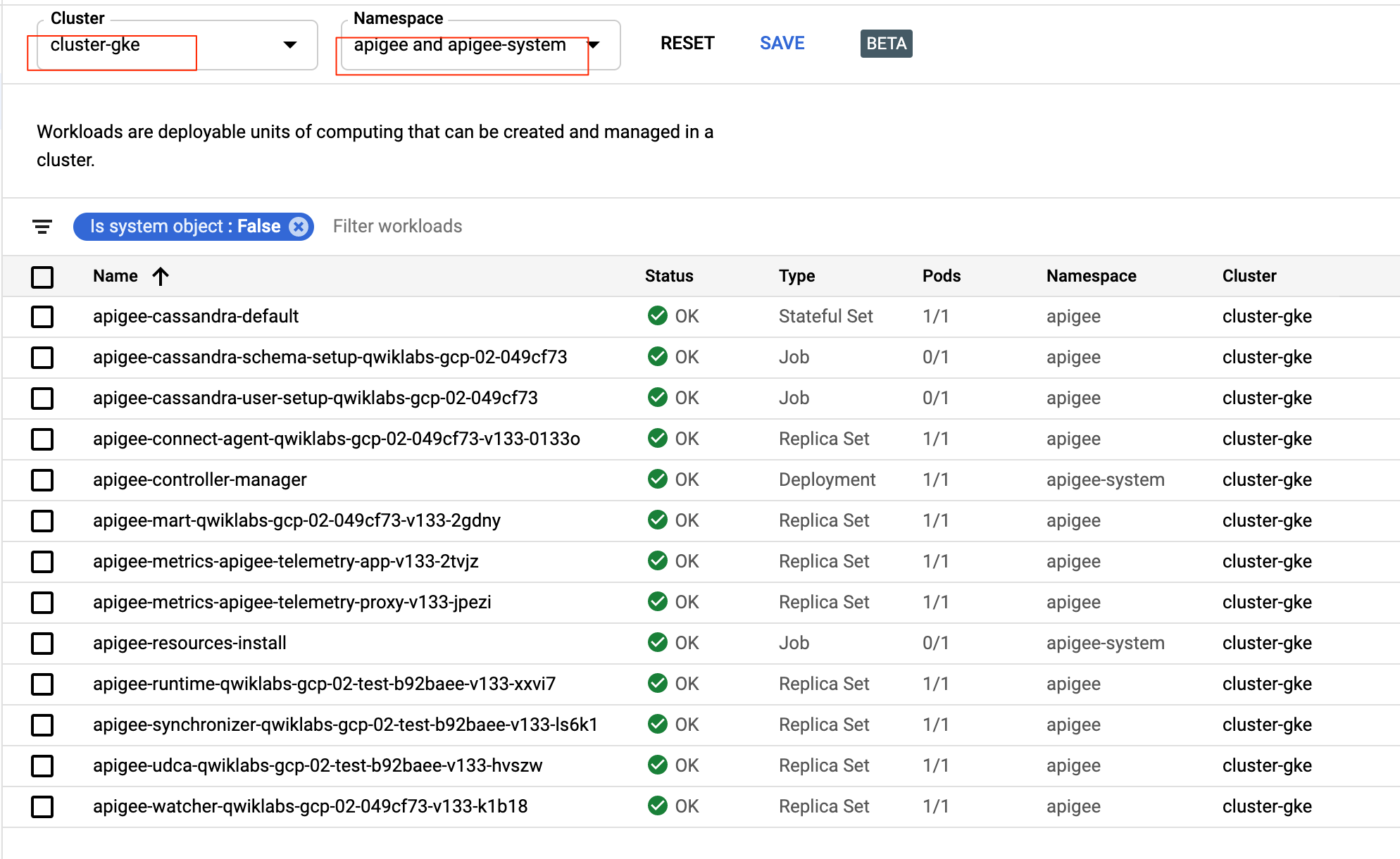
?. Deploy provided ping proxy
$AHR_HOME/proxies/deploy.sh
Deploying Proxy: ping Revision: 1...
{
"environment": "test",
"apiProxy": "ping",
"revision": "1",
"deployStartTime": "1604519878830"
}
Checking Deployment Status........
Proxy ping is deployed.
?. GCP: Execute a test request
curl --cacert $RUNTIME_SSL_CERT https://$RUNTIME_HOST_ALIAS/ping -v --resolve "$RUNTIME_HOST_ALIAS:443:$RUNTIME_IP" --http1.1
...
* Hostname qwiklabs-gcp-02-a95097ba358c-test.hybrid-apigee.net was found in DNS cache
* Trying 35.195.154.10...
...
* CAfile: /home/student_02_1e227e9add01/mch-hybrid-install/hybrid-cert.pem
CApath: /etc/ssl/certs
...
* Server certificate:
* subject: CN=api.exco.com
* start date: Nov 4 19:50:12 2020 GMT
* expire date: Dec 4 19:50:12 2020 GMT
...
> GET /ping HTTP/1.1
> Host: qwiklabs-gcp-02-a95097ba358c-test.hybrid-apigee.net
> User-Agent: curl/7.64.0
> Accept: */*
>
...
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< host: qwiklabs-gcp-02-a95097ba358c-test.hybrid-apigee.net
...
?. Copy and paste the apigee-ca secret from R1 to R2
kubectl config use-context $CLUSTER
kubectl create namespace cert-manager
kubectl --context=$R1_CLUSTER get secret apigee-ca --namespace=cert-manager -o yaml | kubectl --context=$R2_CLUSTER apply --namespace=cert-manager -f -
kubectl --context $CLUSTER apply --validate=false -f $CERT_MANAGER_MANIFEST
?. Create public IP
az network public-ip create --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --name $CLUSTER-public-ip --location $AZ_REGION --sku Standard --allocation-method static --query publicIp.ipAddress -o tsv
?. Assign delegated permissions to the resource group for our Service Principal.
export SP_PRINCIPAL_ID=$(az aks show --name $CLUSTER --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --query servicePrincipalProfile.clientId -o tsv)
export SUBSCRIPTION_ID=$(az account show --query id -o tsv)
az role assignment create --assignee $SP_PRINCIPAL_ID --role "Network Contributor" --scope /subscriptions/$SUBSCRIPTION_ID/resourcegroups/$RESOURCE_GROUP
?. Get the IP address value
export RUNTIME_IP=$(az network public-ip show --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --name $CLUSTER-public-ip --query ipAddress --output tsv)
?. Replace IP in the environment file
sed -i -E "s/^(export RUNTIME_IP=).*/\1$RUNTIME_IP/g" $HYBRID_HOME/mch-aks-r2.env
?. Prepare session variables to create an IstioOperator manifest file.
export PROJECT_NUMBER=$(gcloud projects describe ${PROJECT} --format="value(projectNumber)")
export ref=\$ref
export ASM_RELEASE=$(echo "$ASM_VERSION"|awk '{sub(/\.[0-9]+-asm\.[0-9]+/,"");print}')
?. Clone provided IstioOperator template for on-prem/multi-cloud installation.
cp $AHR_HOME/templates/istio-operator-$ASM_RELEASE-$ASM_PROFILE.yaml $HYBRID_HOME/istio-operator-aks-template.yaml
?. Edit $HYBRID_HOME/istio-operator-aks-template.yaml to add necessary service annotation at the following location: spec.components.ingressGateways[name=istio-ingressgateway].k8s.serviceAnnotations
vi $HYBRID_HOME/istio-operator-aks-template.yaml
serviceAnnotations:
service.beta.kubernetes.io/azure-load-balancer-resource-group: $RESOURCE_GROUP
The result should look something like:
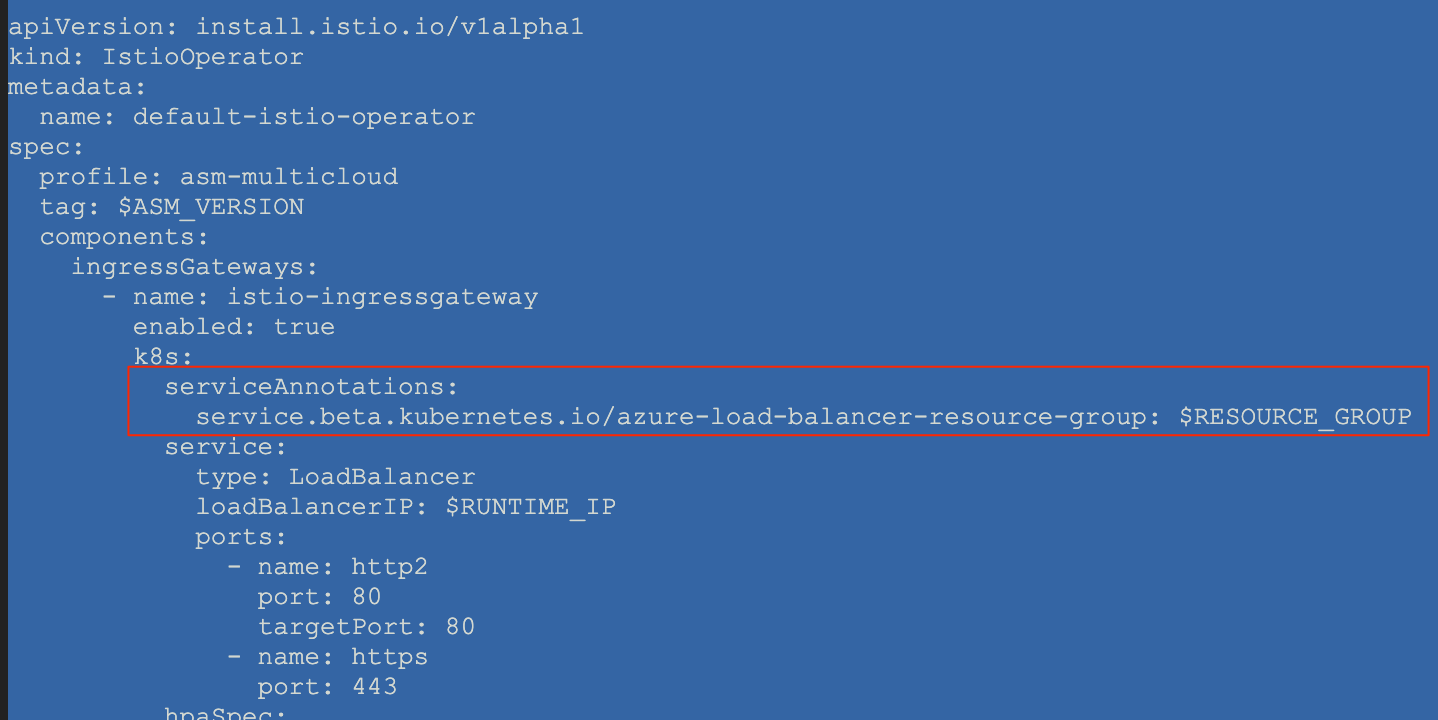
?. Process the template to obtain $ASM_CONFIG file suitable for on-prem ASM installation
ahr-cluster-ctl template $HYBRID_HOME/istio-operator-aks-template.yaml > $ASM_CONFIG
?. As we obtained ASM installation in a GCP session, in this session we just need to correct the PATH variable
export ASM_HOME=$HYBRID_HOME/istio-$ASM_VERSION
export PATH=$ASM_HOME/bin:$PATH
?. Install ASM into our cluster
istioctl install -f $ASM_CONFIG
?. Generate Runtime Configuration yaml file
ahr-runtime-ctl template $AHR_HOME/templates/overrides-small-13-template.yaml > $RUNTIME_CONFIG
?. Install yq
mkdir -p ~/bin
source ~/.profile
curl -L https://github.com/mikefarah/yq/releases/download/3.2.1/yq_linux_amd64 -o ~/bin/yq
chmod +x ~/bin/yq
?. Display Cassandra ring status
kubectl --context $R1_CLUSTER -n apigee exec -it apigee-cassandra-default-0 -- nodetool status
Datacenter: dc-1
================
Status=Up/Down
|/ State=Normal/Leaving/Joining/Moving
-- Address Load Tokens Owns (effective) Host ID Rack
UN 10.1.1.35 405.91 KiB 256 100.0% bbf099ab-cf9a-477d-857a-f97e7de9e9ff ra-1
?. Identify a seed host address for Cassandra in the current region. Not a brainer for our single node. In case of multiples nodes, picks any.
10.1.1.35
?. Define it in a convenience variable:
export DC1_CS_SEED_NODE=10.1.1.35
?. Patch the RUNTIME_CONFIG file with the Cassandra seed node information
yq m -i $RUNTIME_CONFIG - <<EOF
cassandra:
multiRegionSeedHost: $DC1_CS_SEED_NODE
datacenter: "dc-2"
rack: "ra-1"
EOF
?. Amend PATH with apigeectl binary location
export APIGEECTL_HOME=$HYBRID_HOME/$(tar tf $HYBRID_HOME/$HYBRID_TARBALL | grep VERSION.txt | cut -d "/" -f 1)
export PATH=$APIGEECTL_HOME:$PATH
?. Deploy Init and runtime Hybrid Components
kubectl config use-context $CLUSTER
ahr-runtime-ctl apigeectl init -f $RUNTIME_CONFIG
ahr-runtime-ctl apigeectl wait-for-ready -f $RUNTIME_CONFIG
ahr-runtime-ctl apigeectl apply -f $RUNTIME_CONFIG
ahr-runtime-ctl apigeectl wait-for-ready -f $RUNTIME_CONFIG
?. Check ring status
kubectl --context $R2_CLUSTER -n apigee exec -it apigee-cassandra-default-0 -- nodetool status
Datacenter: dc-1
================
Status=Up/Down
|/ State=Normal/Leaving/Joining/Moving
-- Address Load Tokens Owns (effective) Host ID Rack
UN 10.1.1.35 405.91 KiB 256 100.0% bbf099ab-cf9a-477d-857a-f97e7de9e9ff ra-1
Datacenter: dc-2
================
Status=Up/Down
|/ State=Normal/Leaving/Joining/Moving
-- Address Load Tokens Owns (effective) Host ID Rack
UN 10.4.0.35 113.08 KiB 256 100.0% 3ccb9924-f895-45a2-8ce3-32cd39405f73 ra-1
?. Validate spaces configuration. Deploy cassandra client container that has cqlsh utility
kubectl --context $R2_CLUSTER run -i --tty --restart=Never --rm --image google/apigee-hybrid-cassandra-client:1.0.0 cqlsh
?. In the cassandra client container, start cqlsh; Enter password in the next line on a Password: prompt
cqlsh apigee-cassandra-default-0.apigee-cassandra-default.apigee.svc.cluster.local -u ddl_user --ssl
# Password: iloveapis123
SELECT * from system_schema.keyspaces;
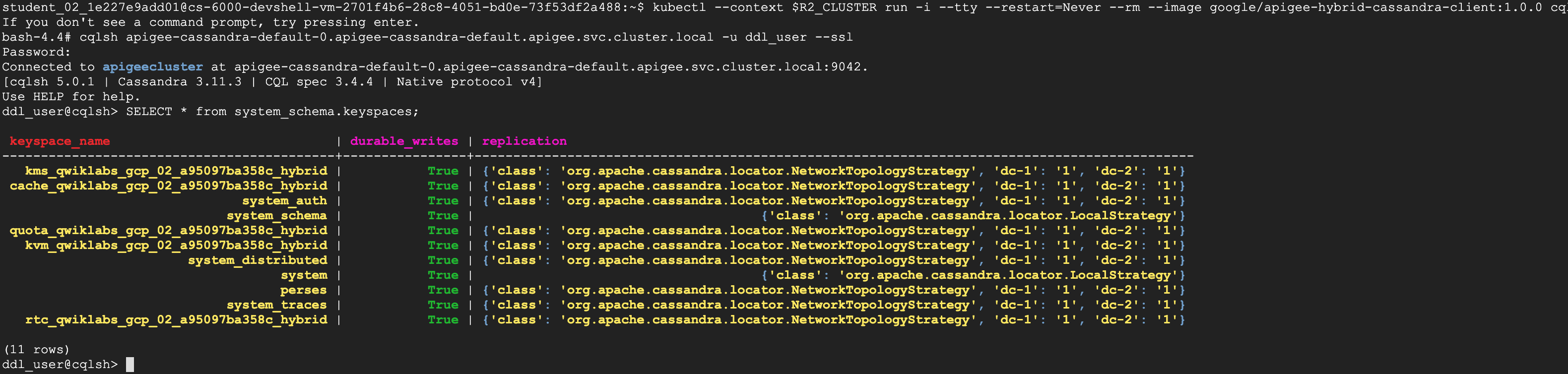
?. Exit from the cqlsh and from the cassandra client container.
exit
exit
?. Rebuild new node(s) in Region 2 using dc-1 as a source
kubectl --context $R2_CLUSTER exec apigee-cassandra-default-0 -n apigee -- nodetool rebuild -- dc-1
?. Verify rebuild operation status via cassandra log
kubectl --context $R2_CLUSTER logs apigee-cassandra-default-0 -n apigee
INFO [RMI TCP Connection(80)-10.4.0.25] 2020-11-04 20:41:33,351 StorageService.java:1179 - rebuild from dc: dc-1, (All keyspaces), (All tokens)
INFO [RMI TCP Connection(80)-10.4.0.25] 2020-11-04 20:41:33,502 StreamResultFuture.java:90 - [Stream #200280a0-1ede-11eb-8b6f-a7a4108aa8d1] Executing streaming plan for Rebuild
INFO [StreamConnectionEstablisher:1] 2020-11-04 20:41:33,504 StreamSession.java:266 - [Stream #200280a0-1ede-11eb-8b6f-a7a4108aa8d1] Starting streaming to /10.1.2.18
INFO [StreamConnectionEstablisher:1] 2020-11-04 20:41:33,995 StreamCoordinator.java:264 - [Stream #200280a0-1ede-11eb-8b6f-a7a4108aa8d1, ID#0] Beginning stream session with /10.1.2.18
INFO [STREAM-IN-/10.1.2.18:7001] 2020-11-04 20:41:34,227 StreamResultFuture.java:173 - [Stream #200280a0-1ede-11eb-8b6f-a7a4108aa8d1 ID#0] Prepare completed. Receiving 5 files(4.852KiB), sending 0 files(0.000KiB)
INFO [StreamReceiveTask:1] 2020-11-04 20:41:34,488 StreamResultFuture.java:187 - [Stream #200280a0-1ede-11eb-8b6f-a7a4108aa8d1] Session with /10.1.2.18 is complete
INFO [StreamReceiveTask:1] 2020-11-04 20:41:34,508 StreamResultFuture.java:219 - [Stream #200280a0-1ede-11eb-8b6f-a7a4108aa8d1] All sessions completed
?. Azure: Execute a test request
curl --cacert $RUNTIME_SSL_CERT https://$RUNTIME_HOST_ALIAS/ping -v --resolve "$RUNTIME_HOST_ALIAS:443:$RUNTIME_IP" --http1.1
* Trying 51.124.60.15...
...
> GET /ping HTTP/1.1
> Host: qwiklabs-gcp-02-a95097ba358c-test.hybrid-apigee.net
> User-Agent: curl/7.64.0
> Accept: */*
...
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
?. Remove Seed Host key from the AKS $RUNTIME_CONFIG yaml file to replace remote node source to a local one.
yq d -i $RUNTIME_CONFIG cassandra.multiRegionSeedHost
?. Update datastore containters
ahr-runtime-ctl apigeectl apply --datastore -f $RUNTIME_CONFIG
NOTE: if you need to start hybrid installation from scratch, you can remove all components using following command:
ahr-runtime-ctl apigeectl delete --all -f $RUNTIME_CONFIGIf you need to delete an apigee-ca secret:
kubectl --context=$R2_CLUSTER delete secret apigee-ca --namespace=cert-manager
TODO: use apigee.google.com to create a developer
?. Go to apigee.google.com in your browser.
?. In the left-hand menu pane, open Publish/Developers item
?. User +Developer button to create a new developer. For example:
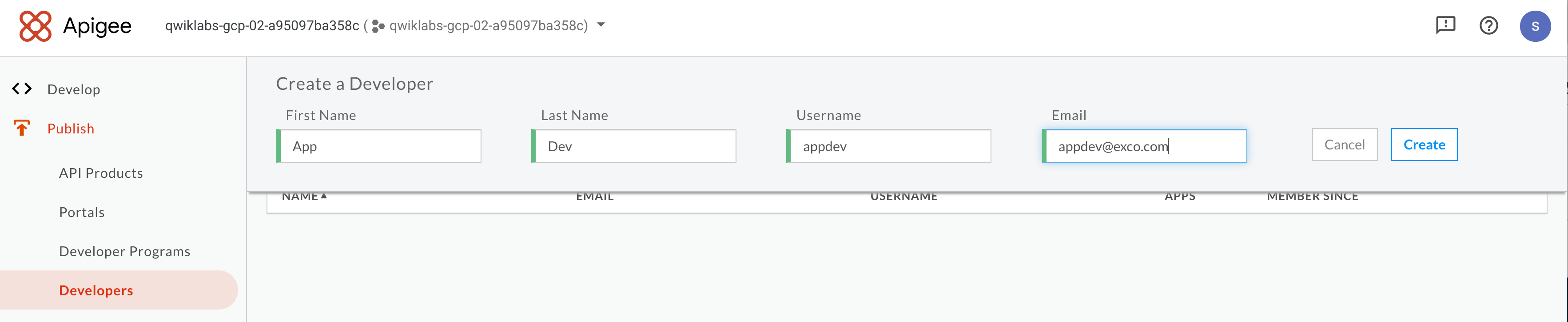
?. Press Create button.
Let's again use two terminals to prove that data replication is working correctly.
?. In GKE terminal, log into a cassandra client container, as we still have it running
kubectl --context $R1_CLUSTER exec -it cqlsh -- sh
?. Log into csqlsh utility
cqlsh apigee-cassandra-default-0.apigee-cassandra-default.apigee.svc.cluster.local -u ddl_user --ssl
?. Identify keyspace name that contains your org name and the developer table
describe tables;
...
Keyspace kms_qwiklabs_gcp_02_a95097ba358c_hybrid
------------------------------------------------
...
developer
...
?. Select data from developer table in the kms_$ORG_hybrid keyspace
WARNING: Replace my organization name with your organization name!!
select * from kms_qwiklabs_gcp_02_a95097ba358c_hybrid.developer;
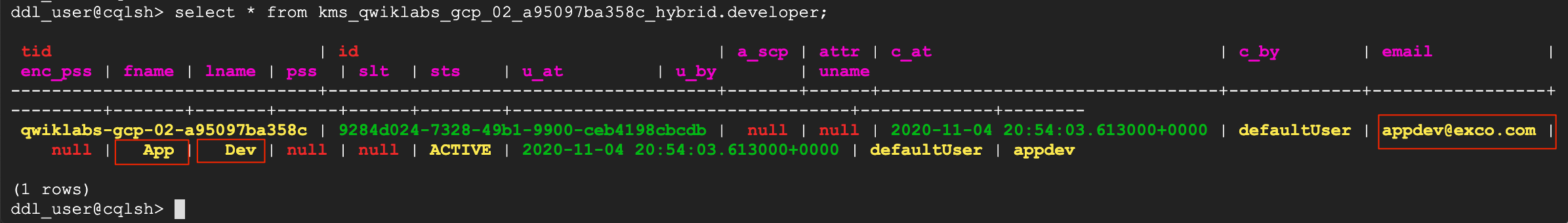
?. Now, query same table by contacting Cassandra client and cassandra node in Region 2
kubectl --context $R2_CLUSTER run -i --tty --restart=Never --rm --image google/apigee-hybrid-cassandra-client:1.0.0 cqlsh
Observe the developer record, create in a one region then replicated into another one.
TODO: add
# vm-gke
gcloud compute instances delete vm-gcp --zone=$GCP_ZONE
## network
# ip address
gcloud compute addresses delete $xxx \
--region $GCP_REGION \
--project $PROJECT
...
# vm at azure
az vm delete -n vm-az -g $RESOURCE_GROUP
#vm: nic
# vm publicIP
# vm: nsg
az network nsg list
# vm: disks
TODO:
az disk list
#
az network vpn-connection delete --name VNetToVPC --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP
# vnet gateway
az network vnet-gateway delete --name $AZ_VNET_GW --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP
# dep on vnet-gateway
az network public-ip delete \
--name $AZ_VNET_GW_IP_NAME \
--resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP
# local network gateway
az network local-gateway delete --name $GCP_VPC --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP
az network vnet delete \
--name $AZ_VNET \
--resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP
 AHR-*-CTL
AHR-*-CTL 
