-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 3
/
presentation.html
200 lines (148 loc) · 6.33 KB
/
presentation.html
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Tiger compiler presentation</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
@import url(https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Yanone+Kaffeesatz);
@import url(https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Droid+Serif:400,700,400italic);
@import url(https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Ubuntu+Mono:400,700,400italic);
body { font-family: 'Droid Serif'; }
h1, h2, h3 {
font-family: 'Yanone Kaffeesatz';
font-weight: normal;
}
.remark-code, .remark-inline-code { font-family: 'Ubuntu Mono'; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<textarea id="source">
class: center, middle
# Tiger compiler
By Aldana Ramirez, Lautaro Rinaldi and Martín Villagra
---
### includes
Include a file inside the let construction. Example:
```
let
include "other_definitions.tigd"
in
0
end
```
This feature was implemented by adding an extra stage just after parsing, where includes are replaced for the contents of the included files. Extra care was taken for detecting include loops. Implementation lives on `tigerinclude.sml`.
---
### extern
Added an `extern` keyword to declarate extern functions, this enables calling C functions from Tiger or to use any external library. Example:
```
let
type SDL_Window = {}
type SDL_Surface = {}
extern function SDL_GetWindowSurface(win:SDL_Window):SDL_Surface
in
SDL_GetWindowSurface(nil);
0
end
```
It was implemented by only editing the parser (`tigergrm.y`) as the compiler was already handling `extern` functions. Implementation:
```
| EXTERN FUNCTION id PI tyflds PD
{ ExternDec({name=$3, params=$5,
result=NONE}, P()) }
| EXTERN FUNCTION id PI tyflds PD DOSP id
{ ExternDec({name=$3, params=$5,
result=SOME $8}, P()) }
```
---
### gcc flags
All unrecognized flags are passed to gcc, which generates the executable code on the last stage. This enables passing parameters to the linking process, which is specially useful for projects requiring libraries. This is implemented in `tigermain.sml`.
Example:
```
./tiger ../juego/main.tig -lSDL2 -lSDL2_ttf -lSDL2_image -lSDL2_mixer ../juego/lib.c
```
---
### optimization 1: Representation of sets
During liveness analysis, following the suggestion from the book on page 216, we represent sets as ordered lists which drastically reduced the time of that step. This can be seen on `tigerliveness.sml`.
---
### optimization 2: Ordering the nodes
During liveness analysis, we implemented the optimization mentioned in the book on page 389. This greatly reduces compilation time by topological sorting the flow graph and use the order to process the nodes, thus reaching the fixed point much faster. Implemented on `tigerliveness.sml`.
---
### test automatization
We developed a simple script to run and maintain a test suite. Each test was added manually, it consists of a code and the expected output of the compiler and its execution. We do a small parsing of the first line of the code of the test in order to embed what parameters should be passed to the compiler (for example to print intermediate trees). This enables to create and maintain the test suite even when not all stages of the compiler are finished. It has saved us a lot of time by detecing bugs early and to avoid introducing new ones. The script is `tests/test` and is written in Bash.
We ended up with 164 tests for the tiger compiler.
---
Example test:
> liveness/hello.tig
```
/*TIGER_ARGS=-code -flow*/
(print ("Hello World");0)
```
> liveness/hello.out
```bien!
;;--FRAME--L0__tigermain_0:
LABEL: L3
MOVE: movq %'s0, %'d0 D:T2 S:rbx
MOVE: movq %'s0, %'d0 D:T3 S:r12
...
n22(LABEL: L2): n23
n23(OPER: D:[] S:[rax,rsp,rbp,rbx,r12,r13,r14,r15]):
;;-END-FLOW-:
yes!!
Hello World
Return code: 0
```
---
Screenshot:
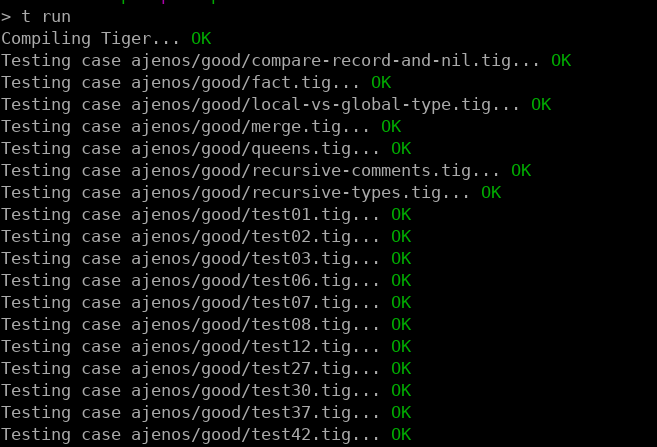
---
### sokoban game
By using some of the features implemented small game was programmed. It uses `SDL 2` C library and function wrappers in `juego/lib.c` has been written to call functions with strings (as C strings are diferent from Tiger strings). You can run it by:
Screenshot:

---
### compiler pipeline
We encapsulated each stage of the compiler in a function and by defining the operator `>>=` we are able to write the entire compiler as a series of steps in a very clear way:
```
fun perFragment fragment =
fragment >>= instructionSel >>= prntCode >>=
debugLivenessAnalysis
>>= coloreo
>>= prntColor
>>= procExit3
>>= formatter
source_filename >>= abreArchivo >>=
lexer >>= parser >>= (*de ASCII al arbol tigerabs.exp*)
expIncludes >>= (*etapa agregada para que funcionen los includes*)
escap >>= prntArbol >>=
seman >>= prntIr >>= (*chequeo de tipos y generacion de fragmentos*)
canonize >>= prntCanon >>=
(fn (stringList, frags) => (stringList, map perFragment frags)) >>=
serializer >>= prntAsm >>=
compileAsm >>=
prntOk (*si llega hasta aca esta todo ok*)
```
Implemented on `tigermain.sml`.
---
### compiler diagram
A diagram was created showing the main stages of the compiler.
Original document:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/0ByI9GfoY63_aTDFaUjVLRjVwM1k/view?usp=sharing
Image preview:
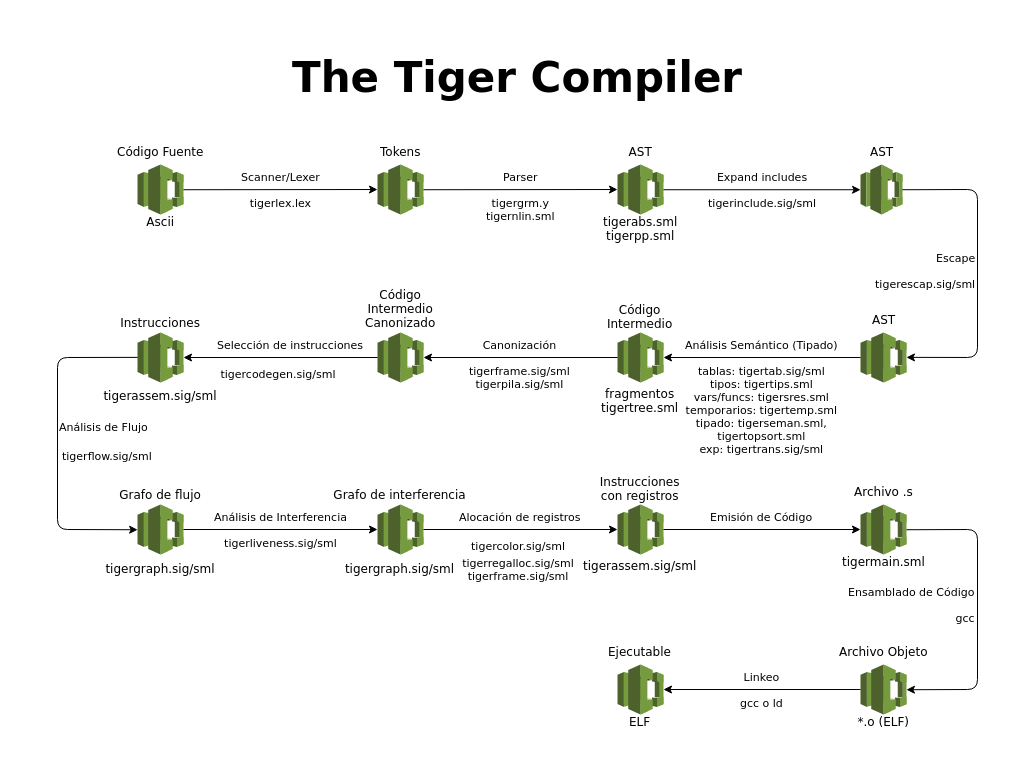
---
### open source
Full code of the compiler, tests, game, class notes and presentation are available at:
https://github.com/vmartinv/tiger-compiler
---
### file opener
All source files start with `tiger` and there are many files with the same name but different extensions (some come from compilation subproducts). For this reason we found ourselves spending a lot of time looking for the specific files we wanted to open. For this reason we made a small script to list and open the sources files easily. Implementation is in `src/e` and is written in Bash.
Screenshot:
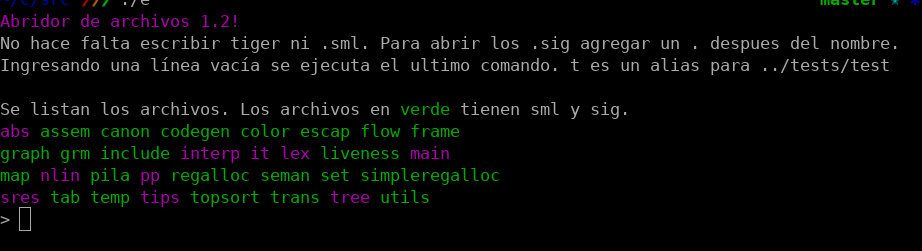
</textarea>
<script src="https://remarkjs.com/downloads/remark-latest.min.js">
</script>
<script>
var slideshow = remark.create();
</script>
</body>
</html>