-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 18
Hydraulic network
The hydraulic network allows the user to simulate flow propagation in a network. The network is composed of nodes and links between nodes.
Lekan supports the following nodes for simulation:
- junction nodes: nodes with one or more upstream links and one downstream link.
- watershed nodes: nodes associated with a watershed from the watershed module. This type of node can also have upstream links and one downstream link.
The links supported are routing links, which are elements that transform input hydrograph to output hydrograph for simulating flow propagation.
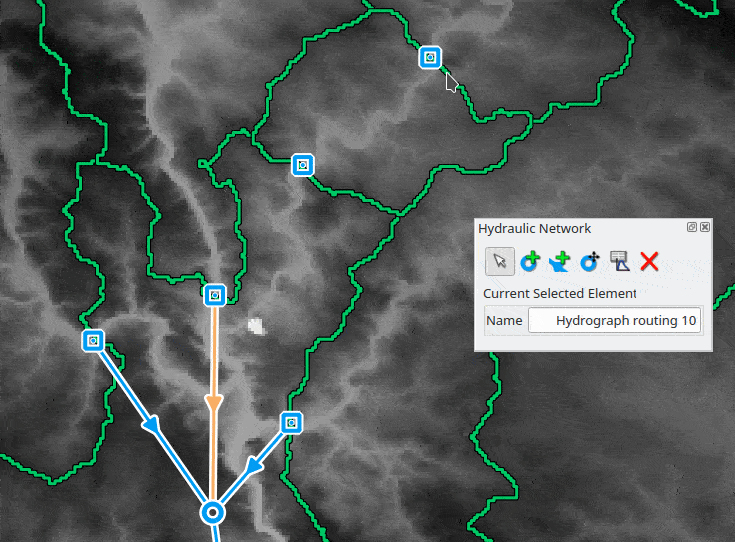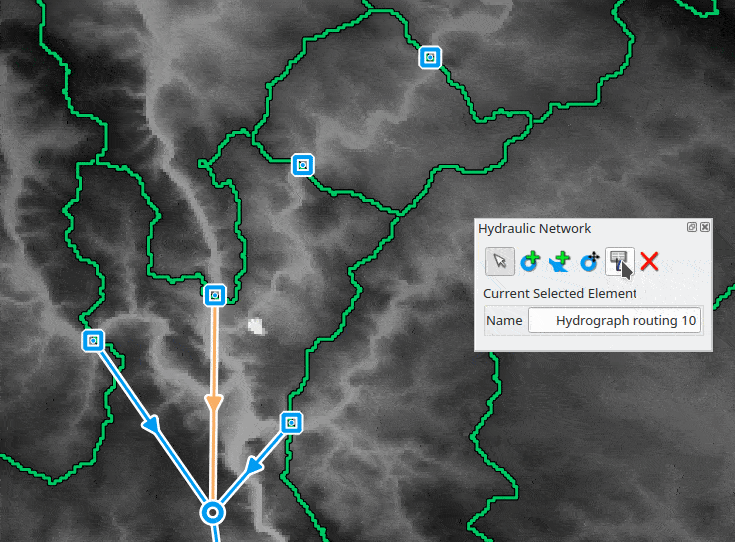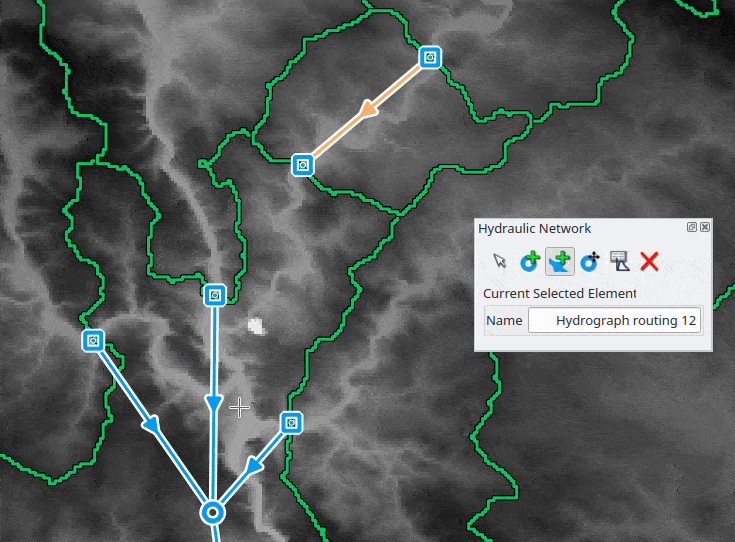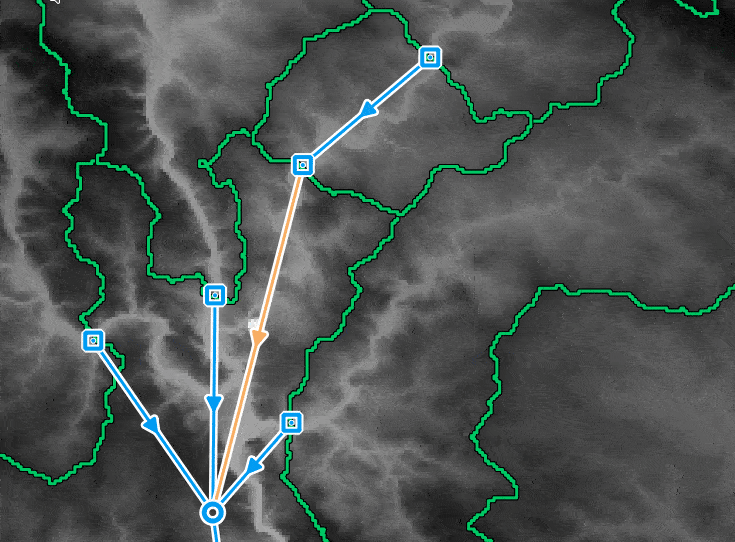
To build a network, the user can add new junction nodes on the map with the dedicated map tool 
Links are added by activating the dedicated map tool 
Adding/removing a watershed node is done with the button at the bottom of the watershed tree.
It is possible to remove all types of selected nodes with the "Remove Hydraulic Element" button 
Once junction nodes are created, the user can move them with the "Move Hydrograph Junction" button 
Selecting elements (node or link) on the map after activating the "Select hydraulic Element" map tool 
Once an element is selected, the user can also open the properties widget of this element by clicking on the "Hydraulic Element Properties" button

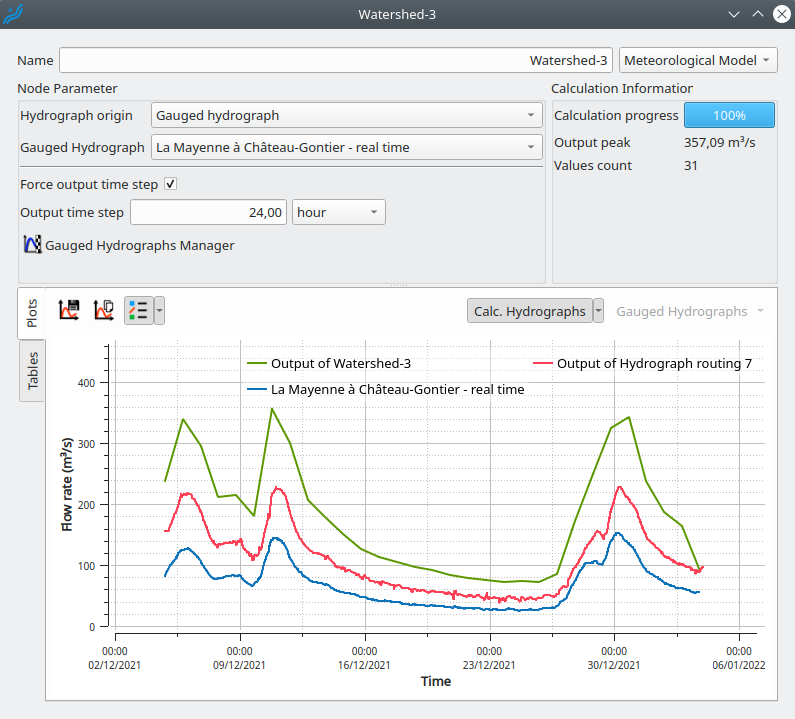
The node parameters can be set in the "Node Parameter" group box.
For the simple junction node, the user can inject a hydrograph from one of the gauged hydrographs associated with this node (see how to associate gauge hydrograph below).
If the check box "Inject Gauged Hydrograph" is checked, the user must choose one of the available hydrographs in the drop-down menu. Then this hydrograph will be summed to the hydrograph coming from upstream links if any. If there is no upstream link, the output of this node will be simply the injected hydrograph, a convenient way to inject any hydrograph into a network.
For the watershed nodes, the parameters are also set in the "Node Parameter" group box. Here, the user has to choose either a runoff hydrograph (coming from the runoff hydrograph calculation see Watershed section) or one of the gauged hydrographs associated with the watershed (associated here, see below) or from watershed gauged hydrograph windows).
Watershed nodes and junction nodes have common properties defined in their windows.
The first option is the "Force output time step option", which can be activated by checking the associated check box.

Once this option is activated, the node's output will have a forced constant time step defined below the check box. The downstream hydrograph will be calculated with this constant time step. That can be convenient to smooth hydrograph or when a downstream method needs a specific time step. For example, the Muskingum routing method validity depends on the input hydrograph time step.
Note that this option is different from "Display constant time step" proposed under the result tables. With this option, only the table has the constant time step, convenient to export by copy/paste results. But here, hydrographs keep their proper time step internally and downstream.
The second common option is access to the gauged hydrograph associated with the node by the following button:
For watershed nodes, this button leads to the same hydrographs defined by the watershed gauged hydrograph windows.
Link represents a hydraulic element that transfers flow from a node to another. During this transfer, the hydrograph can be transformed. For now, Lekan provides the following method for transformation:
- The Muskingum routing method: the well now method to take account of lag and attenuation of hydrograph in a reach, with parameter K and x.
- The lag routing method: simply an offset time of the output hydrograph compared to the input hydrograph
- No transformation: no transformation.

The hydraulic network flow propagation results are available on each element in the properties windows. One result form is plots of each input/output hydrograph. In addition, gauged hydrograph not concerned by the calculation can also be displayed for nodes to compare with results.
The other result form is tables of numerical values of all input/output hydrographs that can be copied/pasted by right-clicking on the table.
This is a side bar
