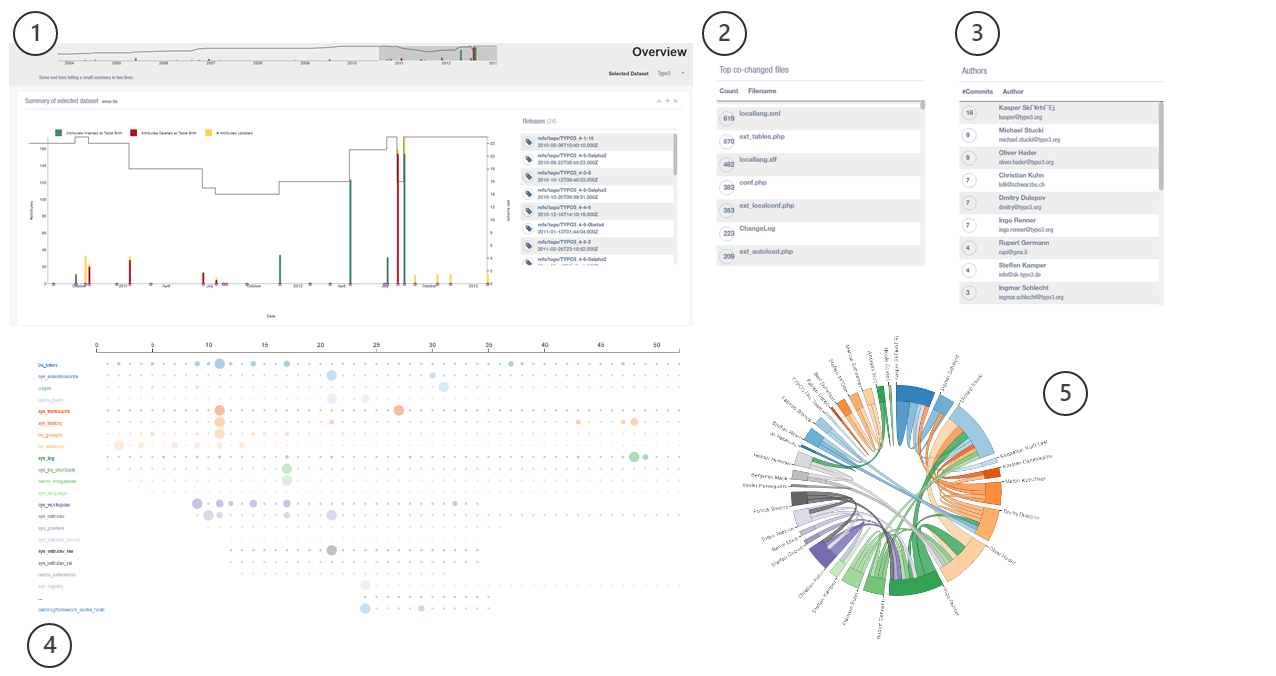
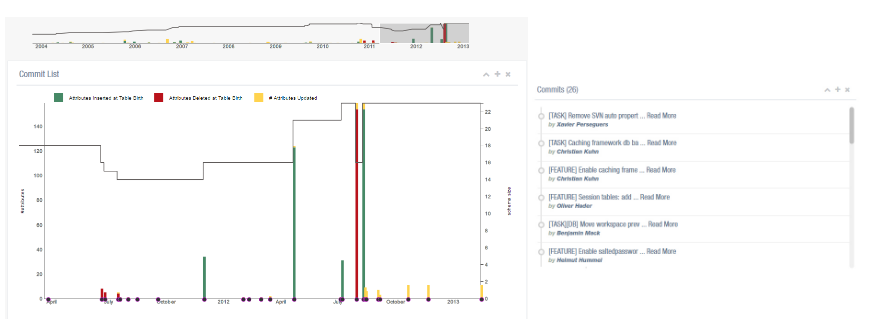
A web-based application that provides the user a variety of tools to explore the version histories of schemata
HTML, CSS and Typescript, Angular 4, NodeJs
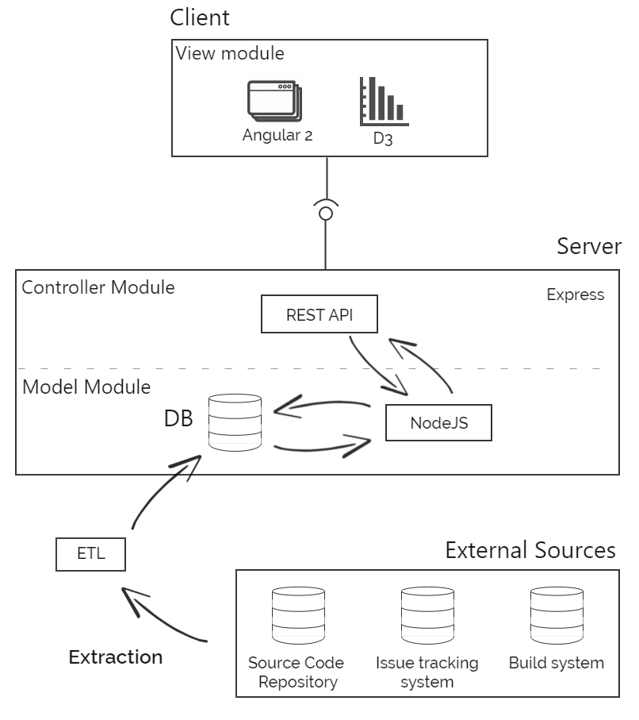
The whole application is built using the model-view-controller (MVC) architectural pattern. MVC architecture divides a given application into three interconnected parts in order to separate internal representation of the information allowing the efficient code reuse. Specifically, the project structure is separated into three large modules. The first module (models module) is responsible for implementing the concepts of the reference model, along with the database controllers that feed those concepts with data from the database. The second module (controllers module) is responsible for handling the HTTP requests making the resources of the application available to the client. Finally, the third module (views modules) is responsible for the interaction with the user.
The business logic of the application is implemented in this module. This module is composed of three individual parts: (a) databases and database handlers, (b) data structures that hold the meta-model and (c) data enrichment modules.
Databases and database handlers: In this part, the files holding the database of the system are located. The SQLite database of the system is loaded with the pre-processed data that was gathered with the method described in Chapter 3. Moreover, in this part of the system, a database controller is implemented for every concept of the meta-model. Every database handler is responsible for retrieving the data from the database, populate the data structures with the data and return the result.
Data structures implementing the meta-model: This part contains the concepts that are defined in each level of the meta-model as a data structures.
Data enrichment modules: This subpart of the system includes different modules that are used in order to enrich the raw data that was gathered with useful metrics and statistics. This sub-system, provides modules for automatic text generation based on the descriptive statistics. Moreover, in this part of the system, rule-based techniques are implemented.
This module is responsible for handling all the HTTP requests. Moreover, this module provides a RESTful web service using the HTTP protocol that provides access to application’s resources. REST stands for Representational State Transfer and it is a web-standards-based architecture. Therefore, this module is the intermediate that connects the back-end which holds all the available information with the front-end which presents the data to the user using an interactive way.
This module is responsible for handling the human and computer interaction. In fact, views module implements the front-end of the application that is built using AngularJS, Bootstrap and D3.js. It is responsible for (a) retrieving the necessary information using the RESTful API and (b) presenting the data to the user in an interactive way. The general representation of how the modules of the system are connected together and also how the system’s database is populated with the gathered data in Figure below.