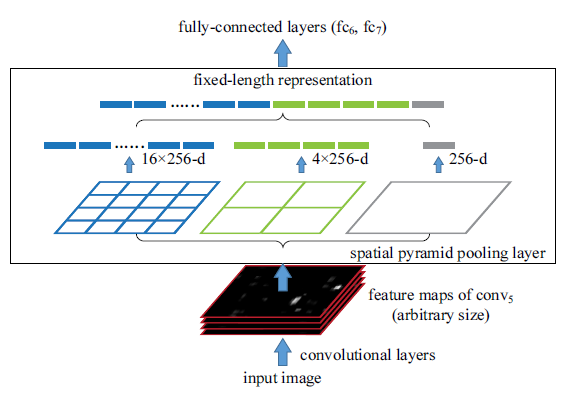
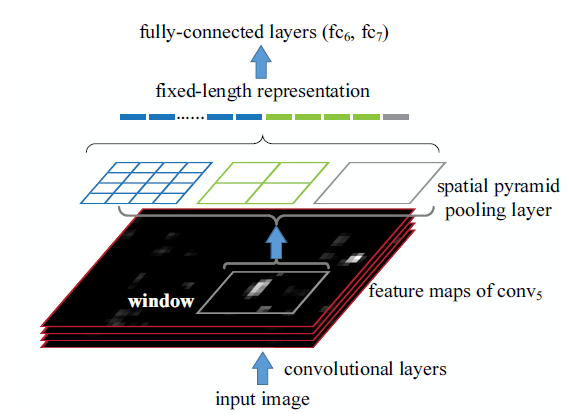
This paper mainly proposes the Spatial Pyramid Pooling operation which can be utilized to:
- Allow images of different size input to the neural network without warping or clipping
- Avoid repeatly caculating feature maps of regions in detection
- Improve classification accuracy by training the network on images with different scales
- Speed up detection
-
Spatial Pyramid Pooling
As shown on the above figure, Spatial Pyramid Pooling layer divides a feature map into n*n (n = 1,2,4) grid and do pooling at each cell, yeilding a n*n vector for different n. Then it concatenates pooling results from different n, yeilding a fixed-length feature vector.
-
Training Algorithm
Theoretically, SPP Net can be trained directly by the BP algorithm, but in order to use existing deep learning frameworks such as Caffe, the author proposes another training strategy. They train the network with inputs of different sizes on each epoch. This method can also be viewed as training several networks with different input size with shared parameters.
-
Object Detection Algorithm
The object detection algorithm is almost the same with RCNN, except they use SPP layer to allow extracting image feature only once and pooling features for different regions directly from the image feature maps.
- Spatial Pyramid Pooling looks interesting but a little complicated, I think people find that the depth of network helps more, so they don't use SPP anymore.
- Scales are important to neural networks, networks trained with different image scales tend to perform better, but I think people now achieve variant scaling by concatenating feature maps from different layers rather than using different sized images as inputs.
Despite SPP layer avoids repeatly extracting features for different regions, the whole detection pipeline still has three stages: Region Proposal -> CNN Feature Extraction -> SVM Classification, especially the Region Proposal method not only depends on low level image features but also is slow.
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Spatial Pyramid Pooling in Deep Convolutional Networks for Visual Recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2015, 8691(1):1904-1916.