-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 626
涉及到的一些Java 8的知识
项目中BuyerProductController.java中有这么一段代码。
//1.查询所有的上架的商品
List<ProductInfo> productInfoList=productService.findUpAll();
//2.查询在架商品所属类目(一次性查询)
// List<Integer> categoryTypeList=new ArrayList<>();
// //传统方法
// for(ProductInfo productInfo: productInfoList){
// categoryTypeList.add(productInfo.getCategoryType());
// }
//精简方法lamba表达式
List<Integer> categoryTypeList=productInfoList.stream()
.map(e->e.getCategoryType()).collect(Collectors.toList());
//或者像下面这样使用方法引用来简化lambda表达式
// List<Integer> categoryTypeList=productInfoList.stream()
// .map(ProductInfo::getCategoryType).collect(Collectors.toList());上面代码中涉及了一些java8的知识:
- Stream(流)
- lambda表达式
- 使用方法引用来简化lambda表达式
- 使用Stream操作集合
在学习lambda表达式之前,要先了解函数式接口。
函数式接口是只含有一个抽象方法的接口,比如下面就是一个函数式接口:
@FunctionalInterface
interface MyFunInterface {
int test(String s);
}我们还可以使用@FunctionalInterface注解函数式接口,使用该注解后,该接口就只能定义一个抽象方法。
我们可以使用lambda表达式来实现一个函数式接口,如下:
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyFunInterface lengthCal = s -> s.length();
int len=lengthCal.test("hello");
System.out.println(len);
}
}lambda表达式还是比较常用,很简洁。不过还有比lambda表达式更简洁的写法,那就是方法引用,先上代码:
//1.上面个lambda可以用:引用类方法简化
MyFunInterface lengthCal1=String::length;
int len1=lengthCal.test("hello");以上是使用方法引用来简化lambda表达式。如果lambda表达式的方法体只有一个方法调用,可以使用方法引用来简化lambda表达式。
下面对几种方法引用的方式总结:
| 种类 | 使用方式 |
|---|---|
| 引用类方法 | 类名::类方法 |
| 引用类的实例方法 | 类名::实例方法 |
| 引用特定对象的实例方法 | 特定对象::实例方法 |
| 引用构造器 | 类名::new |
下面一段代码用例子说明了上面四种情况:
/**
* Created by SqMax on 2018/6/12.
*/
@FunctionalInterface
interface MyFunInterface {
int test(String s);
}
@FunctionalInterface
interface MyFunInterface1 {
String subStr(String s,int begin,int end);
}
@FunctionalInterface
interface MyFunInterface2{
JFrame win(String title);
}
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//下面是对4中方式的举例
MyFunInterface intValConvertor=from->Integer.valueOf(from);
int intVal = intValConvertor.test("2018");
//1.上面个lambda可以用:引用类方法简化
MyFunInterface intValConvertor1=Integer::valueOf;
intVal=intValConvertor1.test("2018");
System.out.println(intVal);
MyFunInterface1 subStrUtil=(a, b, c)->a.substring(b,c);
String sub=subStrUtil.subStr("hello world",2,4);
//2.上面lambda可以用:引用类的实例方法简化
MyFunInterface1 subStrUtil1=String::substring;
String sub1=subStrUtil1.subStr("hello world",2,4);
System.out.println(sub);
MyFunInterface begIdxCal= s->"hello world".indexOf(s);
int begIdx=begIdxCal.test("lo");
//3.上面lambda可以用:引用特定对象的实例方法简化
MyFunInterface begIdxCal1="hello world"::indexOf;
int begIdx1=begIdxCal1.test("lo");
System.out.println(begIdx1);
MyFunInterface2 jFrame=a->new JFrame(a);
JFrame jf=jFrame.win("我的窗口");
//4.上面的lambda可以用:引用构造器简化
MyFunInterface2 jFrame2=JFrame::new;
JFrame jf2=jFrame2.win("我的窗口");
System.out.println(jf2);
}
}现在主要讲解流中和集合操作相关的的操作。
本文的开头productInfoList.stream()返回一个Stream对象,下面挑选stream中一个典型的方法分析一下使用方式。
- 下面是map方法。
/**
* Returns a stream consisting of the results of applying the given
* function to the elements of this stream.
*
* <p>This is an <a href="package-summary.html#StreamOps">intermediate
* operation</a>.
*
* @param <R> The element type of the new stream
* @param mapper a <a href="package-summary.html#NonInterference">non-interfering</a>,
* <a href="package-summary.html#Statelessness">stateless</a>
* function to apply to each element
* @return the new stream
*/
<R> Stream<R> map(Function<? super T, ? extends R> mapper);上面注释就是说该方法返回一个流,该流是一个中间操作,它包含通过mapper函数运算后结果。
比如productInfoList.stream().map(e->e.getCategoryType())就是将集合中商品的种类映射为一个Stream,它是一个中间流,再看后面一部分collect(Collectors.toList()),它表示把这个中间流变成一个List。
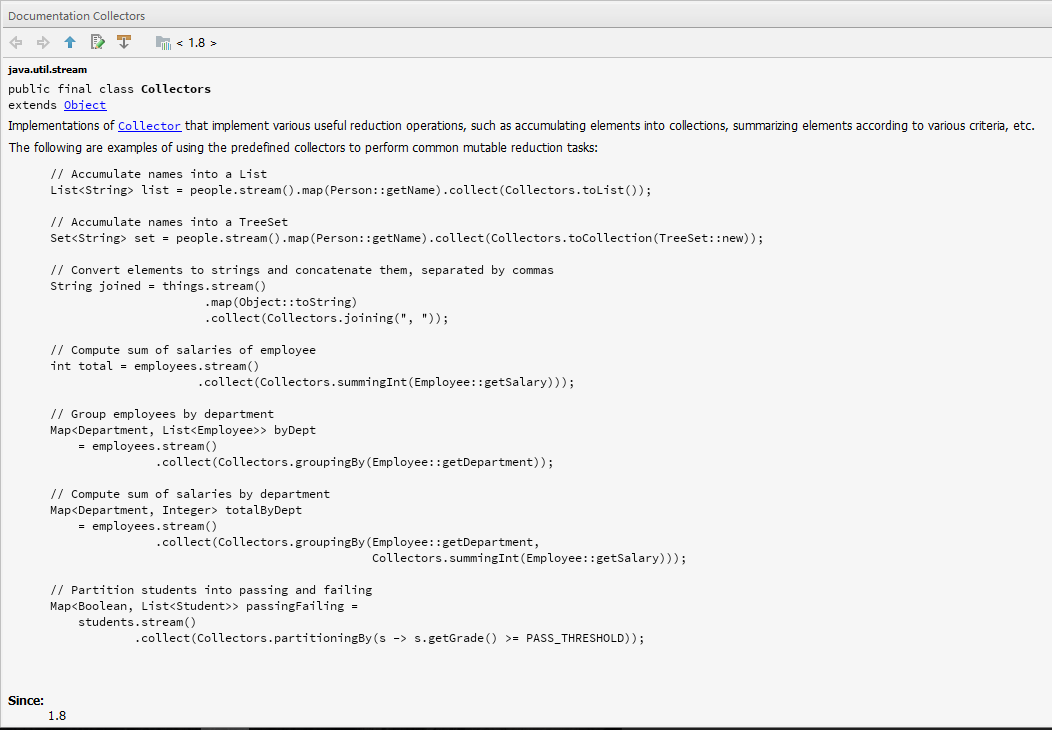
下面我们对Collectors这个类进行探究。
下面是Collectors类注释的截图:
使用方式说的很明白,详情参见:Collectors的API文档
下面用一个例子对上面的文档进行详细说明,建议在在IDEA里debug模式下运行,查看个变量的内容。
/**
* Created by SqMax on 2018/6/13.
*/
public class MyTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<People> peopleList=new ArrayList<>();
peopleList.add(new People("sun","male",23,8000.0));
peopleList.add(new People("li","female",21,7600.1));
peopleList.add(new People("wang", "male", 32, 9000));
peopleList.add(new People("fan","female",18,5000));
//将姓名收集到一个list
List<String> nameList = peopleList.stream().map(People::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());
//将姓名收集到一个set
Set<String> nameSet=peopleList.stream().map(People::getName).collect(Collectors.toSet());
//将姓名以逗号为分隔符连接
String nameJoined = peopleList.stream().map(People::getName).collect(Collectors.joining(", "));
//计算总年龄
int totalAge=peopleList.stream().collect(Collectors.summingInt(People::getAge));
//以性别对人员分组
Map<String, List<People>> bySex = peopleList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(People::getSex));
//计算各性别的总薪水
Map<String,Double> totalBySex=peopleList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(People::getSex,
Collectors.summingDouble(People::getSalary)));
//以6000薪水分割线对人员分组
Map<Boolean, List<People>> pass6000 = peopleList.stream().collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(people -> people.getSalary() > 6000));
}
}
class People{
private String name;
private String sex;
private int age;
private double salary;
public People(String name, String sex, int age, double salary) {
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
this.salary = salary;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
}目录