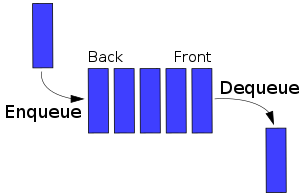
A queue is a data structure that operates on a first in first out basis, similar to a line for a movie. The two operations that define a queue are enqueue and dequeue. Enqueue adds an item to the back of the queue, dequeue removes an item from the back of the queue.
Software queues are used in a lot of cases like real life queues -- they give service to the task that asked for it first. A printer, for example, usually prints the first job given to it and then queues up the others until it is their turn. Queues are also used for breadth-first searches where each vertex is traversed.
Some implementations use arrays or array lists, which mean that the operations have similar complexities to those of an array. Others use nodes and pointers or doubly linked lists and therefore would have similar complexities to those structures.
class Queue:
def __init__(self):
self.data = []
def enqueue(self, item):
self.data.insert(0, item)
def dequeue(self):
return self.data.pop()
def peek(self):
return self.data[-1]In this implementation utilizing a Python list the Big-O complexity looks like this:
| Operation | Complexity |
|---|---|
| Access | O(n) |
| Search | O(n) |
| Insert | O(n) |
| Delete | O(1) |
Either the insert or delete functionality will be O(n) since the insertion or deletion will occur at the beginning of the list, a procedure that isn't optimized in Python like push and pop are.
class Node:
def __init__(self, data, next=None, prev=None):
self.data = data
self.next = next
self.prev = prev
class Queue:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.tail = None
self.length = 0
def enqueue(self, data):
new_node = Node(data, None, self.head)
if not self.head:
self.head = new_node
else:
self.tail.next = new_node
new_node.prev = self.tail
self.tail = new_node
self.length += 1
def dequeue(self):
data = self.head.data
self.head = self.head.next
self.length -= 1
return dataIn this implementation utilizing a doubly linked list the Big-O complexity looks like this:
| Operation | Complexity |
|---|---|
| Access | O(n) |
| Search | O(n) |
| Insert | O(1) |
| Delete | O(1) |
Insertion and deletion in this example is more efficient, though there is more data being stored (i.e. the pointers to next and prev).