Given the root of a binary tree where every node has a unique value and a target integer k, return the value of the nearest leaf node to the target k in the tree.
Nearest to a leaf means the least number of edges traveled on the binary tree to reach any leaf of the tree. Also, a node is called a leaf if it has no children.
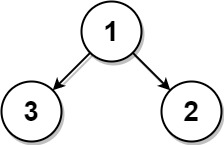
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,3,2], k = 1 Output: 2 Explanation: Either 2 or 3 is the nearest leaf node to the target of 1.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1], k = 1 Output: 1 Explanation: The nearest leaf node is the root node itself.
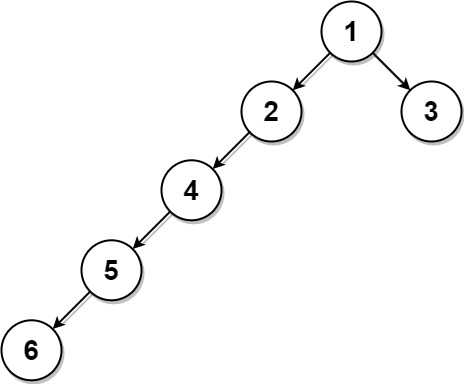
Example 3:
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,null,null,null,5,null,6], k = 2 Output: 3 Explanation: The leaf node with value 3 (and not the leaf node with value 6) is nearest to the node with value 2.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 1000]. 1 <= Node.val <= 1000- All the values of the tree are unique.
- There exist some node in the tree where
Node.val == k.
Companies: Facebook, Databricks, Amazon
Related Topics:
Tree, Depth-First Search, Breadth-First Search, Binary Tree
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/closest-leaf-in-a-binary-tree
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(H)
class Solution {
public:
int findClosestLeaf(TreeNode* root, int k) {
int Inf = 1e9, minDist = Inf, ans = -1;
function<array<int, 3>(TreeNode*)> dfs = [&](TreeNode *root) -> array<int, 3> { // dist to target node, the depth and id of the node on the other subtree with the minimum depth
if (!root) return {Inf, Inf, -1};
if (!root->left && !root->right) {
if (root->val == k) {
minDist = 0;
ans = k;
return {0, 0, root->val};
}
return {Inf, 0, root->val};
}
auto [a, b, c] = dfs(root->left);
auto [d, e, f] = dfs(root->right);
int dist = b + 1, id = c;
if (e < b) dist = e + 1, id = f;
if (root->val == k) {
minDist = dist;
ans = id;
return {0, dist, id};
}
if (a >= Inf && d >= Inf) return {Inf, dist, id};
if (d < Inf) swap(a, d), swap(b, e), swap(c, f);
int sum = a + 1 + e;
if (sum < minDist) {
minDist = sum;
ans = f;
}
return {a + 1, e + 1, f};
};
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
};// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/closest-leaf-in-a-binary-tree
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(N)
class Solution {
public:
int findClosestLeaf(TreeNode* root, int k) {
unordered_map<int, vector<int>> G;
unordered_set<int> leaf, seen;
function<void(TreeNode*, TreeNode*)> convertGraph = [&](TreeNode *root, TreeNode *parent) {
if (!root) return;
if (parent) {
G[parent->val].push_back(root->val);
G[root->val].push_back(parent->val);
}
if (!root->left && !root->right) leaf.insert(root->val);
convertGraph(root->left, root);
convertGraph(root->right, root);
};
convertGraph(root, nullptr);
queue<int> q{{k}};
seen.insert(k);
while (q.size()) {
int cnt = q.front();
while (cnt--) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
if (leaf.count(u)) return u;
for (int v : G[u]) {
if (seen.count(v)) continue;
seen.insert(v);
q.push(v);
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};- Get the path from root to the target node.
- For each node in this path, find the
r.nodewith the minimumdistFromTarget + r.dist. HeredistFromTargetis the distance from the target node to the current node.r.nodeis the closest leaf node to the current node, andr.distis the corresponding distance between these two nodes.
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/closest-leaf-in-a-binary-tree
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(N)
public:
int findClosestLeaf(TreeNode* root, int k) {
vector<TreeNode*> path;
unordered_map<TreeNode*, LeafResult> annotation;
function<bool(TreeNode*)> getPath = [&](TreeNode *root) {
if (!root) return false;
path.push_back(root);
if (root->val == k) return true;
if (getPath(root->left) || getPath(root->right)) return true;
path.pop_back();
return false;
};
getPath(root);
function<LeafResult(TreeNode *root)> closestLeaf = [&](TreeNode *root) {
if (!root) return LeafResult(nullptr, INT_MAX);
if (!root->left && !root->right) return LeafResult(root, 0);
if (annotation.count(root)) return annotation[root];
auto L = closestLeaf(root->left);
auto R = closestLeaf(root->right);
return annotation[root] = LeafResult(L.dist < R.dist ? L.node : R.node, min(L.dist, R.dist) + 1);
};
int distFromTarget = path.size() - 1, dist = INT_MAX, ans = -1;
for (auto n : path) {
auto r = closestLeaf(n);
if (r.dist + distFromTarget < dist) {
dist = r.dist + distFromTarget;
ans = r.node->val;
}
distFromTarget--;
}
return ans;
}
};