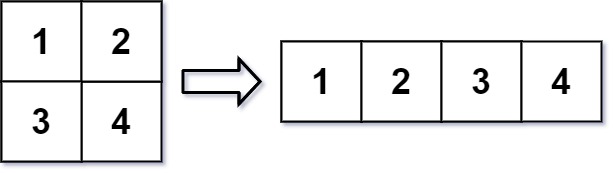
In MATLAB, there is a handy function called reshape which can reshape an m x n matrix into a new one with a different size r x c keeping its original data.
You are given an m x n matrix mat and two integers r and c representing the row number and column number of the wanted reshaped matrix.
The reshaped matrix should be filled with all the elements of the original matrix in the same row-traversing order as they were.
If the reshape operation with given parameters is possible and legal, output the new reshaped matrix; Otherwise, output the original matrix.
Example 1:
Input: mat = [[1,2],[3,4]], r = 1, c = 4 Output: [[1,2,3,4]]
Example 2:
Input: mat = [[1,2],[3,4]], r = 2, c = 4 Output: [[1,2],[3,4]]
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 100-1000 <= mat[i][j] <= 10001 <= r, c <= 300
Companies:
Mathworks
Related Topics:
Array, Matrix, Simulation
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/reshape-the-matrix/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(MN)
// Space: O(1)
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> matrixReshape(vector<vector<int>>& nums, int r, int c) {
int M = nums.size(), N = nums[0].size();
if (M * N != r * c) return nums;
vector<vector<int>> ans;
for (int i = 0; i < r; ++i) {
vector<int> row;
for (int j = 0; j < c; ++j) {
int index = i * c + j;
row.push_back(nums[index / N][index % N]);
}
ans.push_back(row);
}
return ans;
}
};Or
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/reshape-the-matrix/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(MN)
// Space: O(1)
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> matrixReshape(vector<vector<int>>& A, int r, int c) {
int M = A.size(), N = A[0].size(), a = 0, b = 0;
if (M == r || r * c != M * N) return A;
vector<vector<int>> ans(r, vector<int>(c));
for (int i = 0; i < M; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j) {
ans[a][b] = A[i][j];
if (++b == c) {
b = 0;
++a;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};