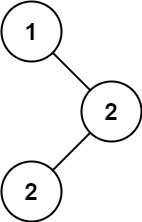
Given the root of a binary search tree (BST) with duplicates, return all the mode(s) (i.e., the most frequently occurred element) in it.
If the tree has more than one mode, return them in any order.
Assume a BST is defined as follows:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than or equal to the node's key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than or equal to the node's key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,null,2,2] Output: [2]
Example 2:
Input: root = [0] Output: [0]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. -105 <= Node.val <= 105
Follow up: Could you do that without using any extra space? (Assume that the implicit stack space incurred due to recursion does not count).
Related Topics:
Tree, Depth-First Search, Binary Search Tree, Binary Tree
Similar Questions:
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/find-mode-in-binary-search-tree/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(N)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findMode(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> ans;
unordered_map<int, int> m;
int maxFreq = 0;
function<void(TreeNode*)> dfs = [&](TreeNode *root) {
if (!root) return;
int f = ++m[root->val];
if (f > maxFreq) maxFreq = f, ans = {root->val};
else if (f == maxFreq) ans.push_back(root->val);
dfs(root->left);
dfs(root->right);
};
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
};If we traverse the tree in in-order, we see the numbers in ascending order.
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/find-mode-in-binary-search-tree
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(1) ignoring space taken by callstack
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findMode(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> ans;
int maxFreq = 0, curFreq = 0, cur = INT_MIN;
function<void(TreeNode *)> dfs = [&](TreeNode *node) {
if (!node) return;
dfs(node->left);
if (node->val != cur) {
cur = node->val;
curFreq = 0;
}
++curFreq;
if (curFreq > maxFreq) {
ans = {cur};
maxFreq = curFreq;
} else if (curFreq == maxFreq) {
ans.push_back(cur);
}
dfs(node->right);
};
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
};