Given an m x n integers matrix, return the length of the longest increasing path in matrix.
From each cell, you can either move in four directions: left, right, up, or down. You may not move diagonally or move outside the boundary (i.e., wrap-around is not allowed).
Example 1:
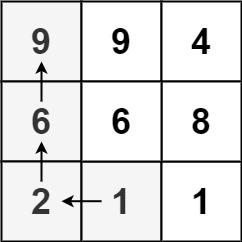
Input: matrix = [[9,9,4],[6,6,8],[2,1,1]]
Output: 4
Explanation: The longest increasing path is [1, 2, 6, 9].
Example 2:
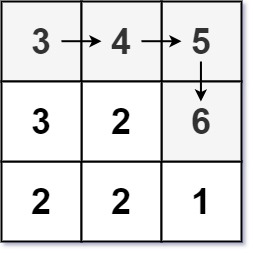
Input: matrix = [[3,4,5],[3,2,6],[2,2,1]]
Output: 4
Explanation: The longest increasing path is [3, 4, 5, 6]. Moving diagonally is not allowed.
Example 3:
Input: matrix = [[1]] Output: 1
Constraints:
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[i].length1 <= m, n <= 2000 <= matrix[i][j] <= 231 - 1
Related Topics:
Depth-first Search, Topological Sort, Memoization
A DFS version topoligical sort is Post-order Traversal + Memo.
Use a vector<vector<int>> cnt, where cnt[i][j] is the length of longest increasing path starting from matrix[i][j]. Initially values in cnt are all zeroes.
For each position matrix[x][y],
- if
cnt[x][y]is not zero, which means it's already visited, returncnt[x][y]right away. - otherwise, probe the 4 directions,
cnt[x][y]is one greater than its largest neightbor.
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-increasing-path-in-a-matrix/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(MN)
// Space: O(MN)
class Solution {
vector<vector<int>> cnt;
int ans = 0, M, N, dirs[4][2] = {{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0}};
int dfs(vector<vector<int>> &A, int x, int y) {
if (cnt[x][y]) return cnt[x][y];
cnt[x][y] = 1;
for (auto &dir : dirs) {
int a = x + dir[0], b = y + dir[1];
if (a < 0 || b < 0 || a >= M || b >= N || A[a][b] <= A[x][y]) continue;
cnt[x][y] = max(cnt[x][y], 1 + dfs(A, a, b));
}
return cnt[x][y];
}
public:
int longestIncreasingPath(vector<vector<int>>& A) {
if (A.empty() || A[0].empty()) return 0;
M = A.size(), N = A[0].size();
cnt.assign(M, vector<int>(N));
for (int i = 0; i < M; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j)
ans = max(ans, dfs(A, i, j));
return ans;
}
};// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-increasing-path-in-a-matrix/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(MN)
// Space: O(MN)
class Solution {
public:
int longestIncreasingPath(vector<vector<int>>& A) {
int M = A.size(), N = A[0].size(), dirs[4][2] = {{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0}}, ans = 0;
vector<vector<int>> indegree(M, vector<int>(N));
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
for (int i = 0; i < M; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j) {
for (auto &[dx, dy] : dirs) {
int a = i + dx, b = j + dy;
if (a < 0 || b < 0 || a >= M || b >= N || A[a][b] >= A[i][j]) continue;
indegree[i][j]++;
}
if (indegree[i][j] == 0) q.push({ i, j });
}
}
while (q.size()) {
int cnt = q.size();
++ans;
while (cnt--) {
auto [x, y] = q.front();
q.pop();
for (auto &[dx, dy] : dirs) {
int a = x + dx, b = y + dy;
if (a < 0 || b < 0 || a >= M || b >= N || A[a][b] <= A[x][y]) continue;
if (--indegree[a][b] == 0) q.push({ a, b });
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};