You are given the root of a binary tree with n nodes. Each node is assigned a unique value from 1 to n. You are also given an array queries of size m.
You have to perform m independent queries on the tree where in the ith query you do the following:
- Remove the subtree rooted at the node with the value
queries[i]from the tree. It is guaranteed thatqueries[i]will not be equal to the value of the root.
Return an array answer of size m where answer[i] is the height of the tree after performing the ith query.
Note:
- The queries are independent, so the tree returns to its initial state after each query.
- The height of a tree is the number of edges in the longest simple path from the root to some node in the tree.
Example 1:
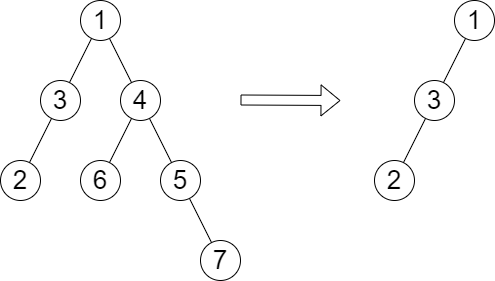
Input: root = [1,3,4,2,null,6,5,null,null,null,null,null,7], queries = [4] Output: [2] Explanation: The diagram above shows the tree after removing the subtree rooted at node with value 4. The height of the tree is 2 (The path 1 -> 3 -> 2).
Example 2:
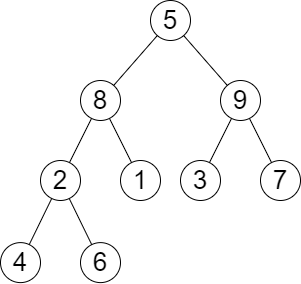
Input: root = [5,8,9,2,1,3,7,4,6], queries = [3,2,4,8] Output: [3,2,3,2] Explanation: We have the following queries: - Removing the subtree rooted at node with value 3. The height of the tree becomes 3 (The path 5 -> 8 -> 2 -> 4). - Removing the subtree rooted at node with value 2. The height of the tree becomes 2 (The path 5 -> 8 -> 1). - Removing the subtree rooted at node with value 4. The height of the tree becomes 3 (The path 5 -> 8 -> 2 -> 6). - Removing the subtree rooted at node with value 8. The height of the tree becomes 2 (The path 5 -> 9 -> 3).
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is
n. 2 <= n <= 1051 <= Node.val <= n- All the values in the tree are unique.
m == queries.length1 <= m <= min(n, 104)1 <= queries[i] <= nqueries[i] != root.val
Companies: Google
Related Topics:
Array, Tree, Depth-First Search, Breadth-First Search, Binary Tree
Similar Questions:
Hints:
- Try pre-computing the answer for each node from 1 to n, and answer each query in O(1).
- The answers can be precomputed in a single tree traversal after computing the height of each subtree.
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N + Q)
// Space: O(N)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& Q) {
vector<vector<int>> nodes;
unordered_map<int, int> height, subTreeHeight, result;
function<void(TreeNode*, int)> fillHeights = [&](TreeNode *n, int h) {
height[n->val] = h;
if (n->left) fillHeights(n->left, h + 1);
if (n->right) fillHeights(n->right, h + 1);
};
fillHeights(root, 0); // height[nodeValue] is the depth of the node from root. Root's depth is 0.
function<int(TreeNode*)> fillSubTreeHeights = [&](TreeNode *n) {
if (!n) return 0;
return subTreeHeight[n->val] = max({height[n->val], fillSubTreeHeights(n->left), fillSubTreeHeights(n->right) });
};
fillSubTreeHeights(root); // subTreeHeight[nodeValue] is the maximum height value of the subtree rooted at the node with nodeValue.
function<void(TreeNode *)> fillNodes = [&](TreeNode *r) {
int lv = 0;
queue<TreeNode*> q{{r}};
while (q.size()) {
int cnt = q.size();
nodes.emplace_back();
while (cnt--) {
auto n = q.front();
q.pop();
nodes.back().push_back(n->val);
if (n->left) q.push(n->left);
if (n->right) q.push(n->right);
}
}
};
fillNodes(root); // Level-order traversal to store the node values layer by layer.
for (int i = nodes.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) { // for each layer
stack<int> s; // we use monostack to track the maximum subTreeHeight of the nodes to the right
int leftMax = 0; // leftMax tracks the maximum subTreeHeight of the nodes to the left
for (int j = nodes[i].size() - 1; j >= 0; --j) {
if (s.empty() || subTreeHeight[nodes[i][j]] >= subTreeHeight[s.top()]) s.push(nodes[i][j]);
}
for (int j = 0; j < nodes[i].size(); ++j) {
if (s.size() && s.top() == nodes[i][j]) s.pop();
result[nodes[i][j]] = max({leftMax, height[nodes[i][j]] - 1, s.size() ? subTreeHeight[s.top()] : 0}); // the result corresponding to the current node value is max of leftMax, height[nodeValue] - 1 and rightMax, where rightMax = subTreeHeight[s.top()]
leftMax = max(leftMax, subTreeHeight[nodes[i][j]]);
}
}
vector<int> ans(Q.size());
for (int i = 0; i < Q.size(); ++i) ans[i] = result[Q[i]];
return ans;
}
};Or
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/height-of-binary-tree-after-subtree-removal-queries
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N + Q)
// Space: O(N)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> treeQueries(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& Q) {
unordered_map<TreeNode*, int> depth, height;
unordered_map<int, int> m;
function<int(TreeNode*, int)> dfs = [&](TreeNode *root, int d) {
if (!root) return d - 1;
depth[root] = d;
return height[root] = max(dfs(root->left, d + 1), dfs(root->right, d + 1));
};
dfs(root, 0);
deque<TreeNode*> q{root};
while (q.size()) {
int cnt = q.size(), maxLeft = -1;
stack<TreeNode*> s;
while (cnt--) {
auto n = q.back();
q.pop_back();
q.push_front(n);
if (s.empty() || height[s.top()] < height[n]) s.push(n);
}
cnt = q.size();
while (cnt--) {
auto n = q.front();
q.pop_front();
if (s.size() && s.top() == n) s.pop();
int maxRight = s.size() ? height[s.top()] : -1;
m[n->val] = max(maxLeft, maxRight);
if (m[n->val] == -1) m[n->val] = depth[n] - 1;
maxLeft = max(maxLeft, height[n]);
if (n->left) q.push_back(n->left);
if (n->right) q.push_back(n->right);
}
}
vector<int> ans;
for (int q : Q) ans.push_back(m[q]);
return ans;
}
};