There is an undirected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1 and n - 1 edges.
You are given a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1 where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree. You are also given an integer array restricted which represents restricted nodes.
Return the maximum number of nodes you can reach from node 0 without visiting a restricted node.
Note that node 0 will not be a restricted node.
Example 1:
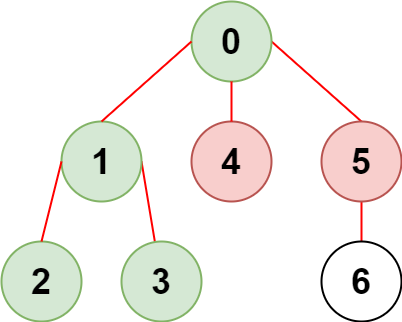
Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[3,1],[4,0],[0,5],[5,6]], restricted = [4,5] Output: 4 Explanation: The diagram above shows the tree. We have that [0,1,2,3] are the only nodes that can be reached from node 0 without visiting a restricted node.
Example 2:
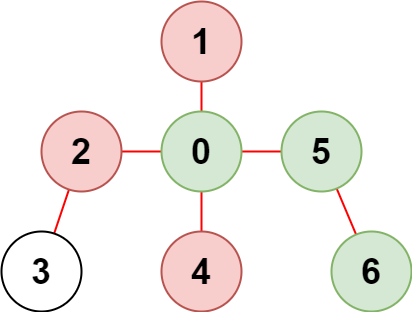
Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,5],[0,4],[3,2],[6,5]], restricted = [4,2,1] Output: 3 Explanation: The diagram above shows the tree. We have that [0,5,6] are the only nodes that can be reached from node 0 without visiting a restricted node.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 105edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < nai != biedgesrepresents a valid tree.1 <= restricted.length < n1 <= restricted[i] < n- All the values of
restrictedare unique.
Companies: MakeMyTrip
Related Topics:
Array, Hash Table, Tree, Depth-First Search, Breadth-First Search, Graph
Similar Questions:
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/reachable-nodes-with-restrictions
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N + E)
// Space: O(N + E)
class Solution {
public:
int reachableNodes(int n, vector<vector<int>>& E, vector<int>& R) {
vector<vector<int>> G(n);
unordered_set<int> r(begin(R), end(R));
for (auto &e : E) {
int u = e[0], v = e[1];
G[u].push_back(v);
G[v].push_back(u);
}
int ans = 0;
function<void(int, int)> dfs = [&](int u, int prev) {
++ans;
for (int v : G[u]) {
if (v == prev || r.count(v)) continue;
dfs(v, u);
}
};
dfs(0, -1);
return ans;
}
};