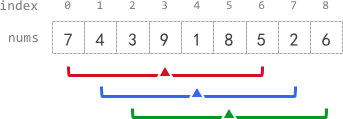
You are given a 0-indexed array nums of n integers, and an integer k.
The k-radius average for a subarray of nums centered at some index i with the radius k is the average of all elements in nums between the indices i - k and i + k (inclusive). If there are less than k elements before or after the index i, then the k-radius average is -1.
Build and return an array avgs of length n where avgs[i] is the k-radius average for the subarray centered at index i.
The average of x elements is the sum of the x elements divided by x, using integer division. The integer division truncates toward zero, which means losing its fractional part.
- For example, the average of four elements
2,3,1, and5is(2 + 3 + 1 + 5) / 4 = 11 / 4 = 3.75, which truncates to3.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [7,4,3,9,1,8,5,2,6], k = 3 Output: [-1,-1,-1,5,4,4,-1,-1,-1] Explanation: - avg[0], avg[1], and avg[2] are -1 because there are less than k elements before each index. - The sum of the subarray centered at index 3 with radius 3 is: 7 + 4 + 3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 = 37. Using integer division, avg[3] = 37 / 7 = 5. - For the subarray centered at index 4, avg[4] = (4 + 3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 + 2) / 7 = 4. - For the subarray centered at index 5, avg[5] = (3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 + 2 + 6) / 7 = 4. - avg[6], avg[7], and avg[8] are -1 because there are less than k elements after each index.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [100000], k = 0 Output: [100000] Explanation: - The sum of the subarray centered at index 0 with radius 0 is: 100000. avg[0] = 100000 / 1 = 100000.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [8], k = 100000 Output: [-1] Explanation: - avg[0] is -1 because there are less than k elements before and after index 0.
Constraints:
n == nums.length1 <= n <= 1050 <= nums[i], k <= 105
Similar Questions:
- Minimum Size Subarray Sum (Medium)
- Moving Average from Data Stream (Easy)
- Subarray Sum Equals K (Medium)
- Maximum Average Subarray I (Easy)
- Number of Sub-arrays of Size K and Average Greater than or Equal to Threshold (Medium)
Intuition: Keep a fixed-length sliding window of length 2k + 1. Slide it from left to right, and update the sum of the window on the fly.
Algorithm:
Let len = 2*k + 1.
If N < len, return all -1s directly because this array is too short to cover any window
Otherwise, loop i from 0 to N-1:
- Push
A[i]into the window.sum += A[i] - Pop
A[i-len]out of the window.sum -= A[i - len] - Assign the average value.
ans[i - k] = sum / len.
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/k-radius-subarray-averages/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(1) extra space
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getAverages(vector<int>& A, int k) {
long N = A.size(), len = 2 * k + 1, sum = 0; // `len` is the length of the window
vector<int> ans(N, -1);
if (N < len) return ans; // If the array is too short to cover a window, return all -1s
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
sum += A[i]; // push A[i] into the window
if (i - len >= 0) sum -= A[i - len]; // pop A[i-len], if any, out of window
if (i >= len - 1) ans[i - k] = sum / len; // the center of this window is at `i-k`
}
return ans;
}
};// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/k-radius-subarray-averages/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(N)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getAverages(vector<int>& A, int k) {
int N = A.size(), len = 2 * k + 1;
vector<int> ans(N, -1);
if (N < len) return ans; // If the array is too short to cover a window, return all -1s
vector<long> sum(N + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) sum[i + 1] = sum[i] + A[i];
for (int i = k; i + k < N; ++i) ans[i] = (sum[i + k + 1] - sum[i - k]) / len;
return ans;
}
};