A binary expression tree is a kind of binary tree used to represent arithmetic expressions. Each node of a binary expression tree has either zero or two children. Leaf nodes (nodes with 0 children) correspond to operands (variables), and internal nodes (nodes with two children) correspond to the operators. In this problem, we only consider the '+' operator (i.e. addition).
You are given the roots of two binary expression trees, root1 and root2. Return true if the two binary expression trees are equivalent. Otherwise, return false.
Two binary expression trees are equivalent if they evaluate to the same value regardless of what the variables are set to.
Example 1:
Input: root1 = [x], root2 = [x] Output: true
Example 2:
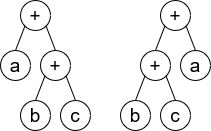
Input: root1 = [+,a,+,null,null,b,c], root2 = [+,+,a,b,c]
Output: true
Explaination: a + (b + c) == (b + c) + a
Example 3:
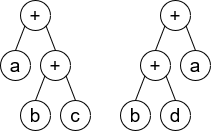
Input: root1 = [+,a,+,null,null,b,c], root2 = [+,+,a,b,d]
Output: false
Explaination: a + (b + c) != (b + d) + a
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in both trees are equal, odd and, in the range
[1, 4999]. Node.valis'+'or a lower-case English letter.- It's guaranteed that the tree given is a valid binary expression tree.
Follow up: What will you change in your solution if the tree also supports the '-' operator (i.e. subtraction)?
Companies: Google
Related Topics:
Tree, Depth-First Search, Binary Tree
Similar Questions:
- Build Binary Expression Tree From Infix Expression (Hard)
- Minimum Flips in Binary Tree to Get Result (Hard)
- Evaluate Boolean Binary Tree (Easy)
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/check-if-two-expression-trees-are-equivalent
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(H)
class Solution {
public:
bool checkEquivalence(Node* a, Node* b) {
int ca[26] = {}, cb[26] = {};
function<void(Node*, int[26])> dfs = [&](Node *root, int cnt[26]) {
if (!root) return;
if (root->val != '+') cnt[root->val - 'a']++;
dfs(root->left, cnt);
dfs(root->right, cnt);
};
dfs(a, ca);
dfs(b, cb);
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) {
if (ca[i] != cb[i]) return false;
}
return true;
}
};For the follow up question, we add a sign to the DFS calls.
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/check-if-two-expression-trees-are-equivalent
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(H)
class Solution {
public:
bool checkEquivalence(Node* a, Node* b) {
int ca[26] = {}, cb[26] = {};
function<void(Node*, int[26], int)> dfs = [&](Node *root, int cnt[26], int sign) {
if (!root) return;
if (root->val != '+' && root->val != '-') cnt[root->val - 'a'] += sign;
dfs(root->left, cnt, sign);
if (root->val == '-') sign *= -1;
dfs(root->right, cnt, sign);
};
dfs(a, ca, 1);
dfs(b, cb, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) {
if (ca[i] != cb[i]) return false;
}
return true;
}
};