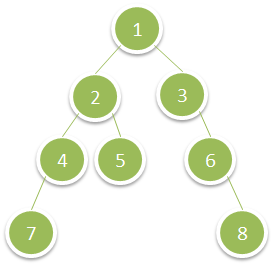
Given a binary tree, return the sum of values of its deepest leaves.
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,6,7,null,null,null,null,8] Output: 15
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is between
1and10^4. - The value of nodes is between
1and100.
Related Topics:
Tree, Depth-first Search
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/deepest-leaves-sum/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(H)
class Solution {
int getDepth(TreeNode *root) {
return root ? 1 + max(getDepth(root->left), getDepth(root->right)) : 0;
}
int getSumAtDepth(TreeNode *root, int d, int depth) {
if (!root) return 0;
if (d == depth) return root->val;
return getSumAtDepth(root->left, d + 1, depth) + getSumAtDepth(root->right, d + 1, depth);
}
public:
int deepestLeavesSum(TreeNode* root) {
int depth = getDepth(root);
return getSumAtDepth(root, 1, depth);
}
};// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/deepest-leaves-sum/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(N)
class Solution {
public:
int deepestLeavesSum(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 0;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
int ans;
q.push(root);
while (q.size()) {
int cnt = q.size();
ans = 0;
while (cnt--) {
auto node = q.front();
q.pop();
ans += node->val;
if (node->left) q.push(node->left);
if (node->right) q.push(node->right);
}
}
return ans;
}
};