Given a binary tree, find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree.
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes p and q as the lowest node in T that has both p and q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).”
Given the following binary tree: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]
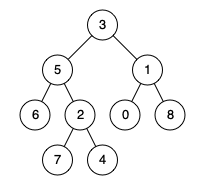
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
Output: 3
Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 1 is 3.
Example 2:
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4
Output: 5
Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 4 is 5, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
Note:
- All of the nodes' values will be unique.
- p and q are different and both values will exist in the binary tree.
从 root 开始遍历树,使用类似于前序遍历的方法,找到 p 、 q 节点,同时记录遍历的路径,得到公共祖先
public class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
List<TreeNode> path1 = new ArrayList<>();
List<TreeNode> path2 = new ArrayList<>();
findPath(root, p, new ArrayList<TreeNode>(), path1);
findPath(root, q, new ArrayList<TreeNode>(), path2);
TreeNode lca = root;
int n = Math.min(path1.size(), path2.size());
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (path1.get(i).val == path2.get(i).val) {
lca = path1.get(i);
} else {
break;
}
}
return lca;
}
/**
* 找到从root到target的路径
* 注意:这里一定需要curPath和path分别记录root到当前节点的路径和root到target的路径
* 因为findPath并不会在找到target时结束递归调用,会继续递归,curPath会更新
*
* @param cur
* @param target
* @param curPath 从root节点当当前节点的路径
* @param path 找到target节点时的curPath值
*/
private void findPath(TreeNode cur, TreeNode target, List<TreeNode> curPath, List<TreeNode> path) {
if (cur == null) {
return;
}
if (cur.val == target.val) {
curPath.add(cur);
path.addAll(curPath);
return;
}
curPath.add(cur);
findPath(cur.left, target, curPath, path);
findPath(cur.right, target, curPath, path);
curPath.remove(curPath.size() - 1);
}
}上述的遍历方法在遍历过程中记录遍历经过的节点,backTrack函数并没有返回值,如果我们每层返回是否找到target节点的信息,就可以快速确定公共节点。
Example:
p、q分别是LCA左右子树。以题图中的树为例,p=6,q=4,LCA = 5。从root开始遍历,遍历到6时返回true表示找到了p节点,然后回到上层5时也返回true表示我找到了p,以此类推。同样,在遍历到4时也返回我找到了q的信息,一层层返回,直到返回到5节点,5现在直到了我的左子树找到了p,我的右子树找到了q,那我就是LCA。p、q中一个是LCA。以题图中的树为例,p=5,q=4,LCA = 5。53会得到在左子树找到p的信息,4253都会返回找到q的信息。因此5收到q找到的信息,同时判断自己就是p,可以确定该节点是LCA。
class Solution {
private TreeNode ans;
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
recurseTree(root, p, q);
return ans;
}
private boolean recurseTree(TreeNode curNode, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (curNode == null) {
return false;
}
int left = recurseTree(curNode.left, p, q) ? 1 : 0;
int right = recurseTree(curNode.right, p, q) ? 1 : 0;
int self = (curNode == p || curNode == q) ? 1 : 0;
// 如果左子树,右子树,当前节点中有2个节点返回找到了p和q,就认为当前节点是LCA
// 需要注意的是题目有限定每个节点是unique的,并且要找的节点一定存在,否则不能这样写
if (left + right + self >= 2) {
this.ans = curNode;
}
return (left + right + self > 0);
}
}https://leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/solution/