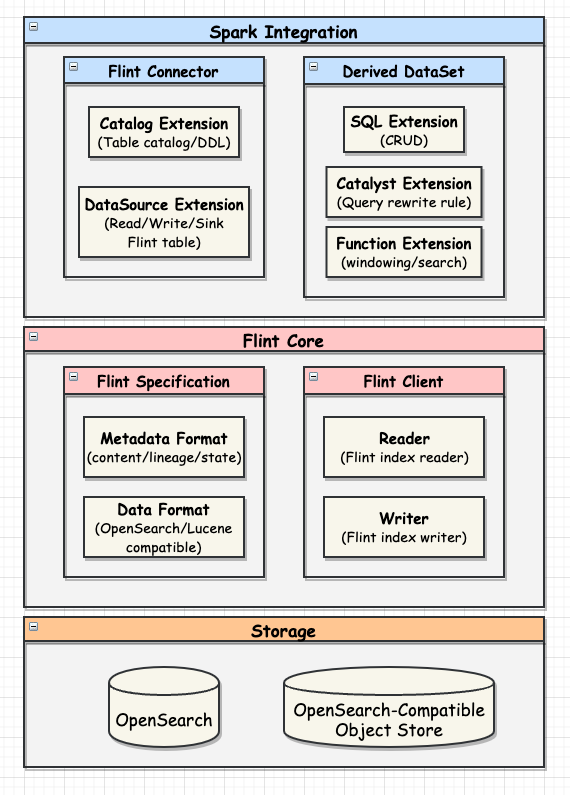
A Flint index is ...
- Skipping Index: accelerate data scan by maintaining compact aggregate data structure which includes
- Partition: skip data scan by maintaining and filtering partitioned column value per file.
- MinMax: skip data scan by maintaining lower and upper bound of the indexed column per file.
- ValueSet: skip data scan by building a unique value set of the indexed column per file.
- Covering Index: create index for selected columns within the source dataset to improve query performance
Please see the following example in which Index Building Logic and Query Rewrite Logic column shows the basic idea behind each skipping index implementation.
| Skipping Index | Create Index Statement | Index Building Logic | Query Rewrite Logic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Partition | CREATE SKIPPING INDEX ON alb_logs FOR COLUMNS ( year PARTITION, month PARTITION, day PARTITION, hour PARTITION ) |
INSERT INTO flint_alb_logs_skipping_index SELECT FIRST(year) AS year, FIRST(month) AS month, FIRST(day) AS day, FIRST(hour) AS hour, input_file_name() AS file_path FROM alb_logs GROUP BY input_file_name() |
SELECT * FROM alb_logs WHERE year = 2023 AND month = 4 => SELECT * FROM alb_logs (input_files = SELECT file_path FROM flint_alb_logs_skipping_index WHERE year = 2023 AND month = 4 ) WHERE year = 2023 AND month = 4 |
| ValueSet | CREATE SKIPPING INDEX ON alb_logs FOR COLUMNS ( elb_status_code VALUE_SET ) |
INSERT INTO flint_alb_logs_skipping_index SELECT COLLECT_SET(elb_status_code) AS elb_status_code, input_file_name() AS file_path FROM alb_logs GROUP BY input_file_name() |
SELECT * FROM alb_logs WHERE elb_status_code = 404 => SELECT * FROM alb_logs (input_files = SELECT file_path FROM flint_alb_logs_skipping_index WHERE ARRAY_CONTAINS(elb_status_code, 404) ) WHERE elb_status_code = 404 |
| MinMax | CREATE SKIPPING INDEX ON alb_logs FOR COLUMNS ( request_processing_time MIN_MAX ) |
INSERT INTO flint_alb_logs_skipping_index SELECT MIN(request_processing_time) AS request_processing_time_min, MAX(request_processing_time) AS request_processing_time_max, input_file_name() AS file_path FROM alb_logs GROUP BY input_file_name() |
SELECT * FROM alb_logs WHERE request_processing_time = 100 => SELECT * FROM alb_logs (input_files = SELECT file_path FROM flint_alb_logs_skipping_index WHERE request_processing_time_min <= 100 AND 100 <= request_processing_time_max ) WHERE request_processing_time = 100 |
Currently, Flint metadata is only static configuration without version control and write-ahead log.
{
"version": "0.1",
"indexConfig": {
"kind": "skipping",
"properties": {
"indexedColumns": [{
"kind": "...",
"columnName": "...",
"columnType": "..."
}]
}
},
"source": "alb_logs",
"state": "active",
"enabled": true
}For now, Flint Index doesn't define its own data type and uses OpenSearch field type instead.
| FlintDataType |
|---|
| boolean |
| long |
| integer |
| short |
| byte |
| double |
| float |
| date |
| keyword |
| text |
| object |
Please see Index Store section for more details.
FlintClient provides low-level Flint index management and data access API.
Index management API example:
// Initialized Flint client for a specific storage
FlintClient flintClient = new FlintOpenSearchClient("localhost", 9200);
FlintMetadata metadata = new FlintMetadata(...)
flintClient.createIndex("alb_logs_skipping_index", metadata)
flintClient.getIndexMetadata("alb_logs_skipping_index")Index data read and write example:
FlintClient flintClient = new FlintOpenSearchClient("localhost", 9200);
// read example
FlintReader reader = flintClient.createReader("indexName", null)\
while(reader.hasNext) {
reader.next()
}
reader.close()
// write example
FlintWriter writer = flintClient.createWriter("indexName")
writer.write("{\"create\":{}}")
writer.write("\n")
writer.write("{\"aInt\":1}")
writer.write("\n")
writer.flush()
writer.close()High level API is dependent on query engine implementation. Please see Query Engine Integration section for details.
CREATE SKIPPING INDEX [IF NOT EXISTS]
ON <object>
( column <index_type> [, ...] )
WHERE <filter_predicate>
WITH ( options )
REFRESH SKIPPING INDEX ON <object>
[DESC|DESCRIBE] SKIPPING INDEX ON <object>
DROP SKIPPING INDEX ON <object>
<object> ::= [db_name].[schema_name].table_nameSkipping index type:
<index_type> ::= { PARTITION, VALUE_SET, MIN_MAX }Example:
CREATE SKIPPING INDEX ON alb_logs
(
elb_status_code VALUE_SET
)
WHERE time > '2023-04-01 00:00:00'
REFRESH SKIPPING INDEX ON alb_logs
DESCRIBE SKIPPING INDEX ON alb_logs
DROP SKIPPING INDEX ON alb_logsCREATE INDEX [IF NOT EXISTS] name ON <object>
( column [, ...] )
WHERE <filter_predicate>
WITH ( options )
REFRESH INDEX name ON <object>
SHOW [INDEX|INDEXES] ON <object>
[DESC|DESCRIBE] INDEX name ON <object>
DROP INDEX name ON <object>Example:
CREATE INDEX elb_and_requestUri
ON alb_logs ( elb, requestUri )
REFRESH INDEX elb_and_requestUri ON alb_logs
SHOW INDEX ON alb_logs
DESCRIBE INDEX elb_and_requestUri ON alb_logs
DROP INDEX elb_and_requestUri ON alb_logsUser can provide the following options in WITH clause of create statement:
auto_refresh: triggers Incremental Refresh immediately after index create complete if true. Otherwise, user has to trigger Full Refresh byREFRESHstatement manually.refresh_interval: a string as the time interval for incremental refresh, e.g. 1 minute, 10 seconds. This is only applicable when auto refresh enabled. Please checkorg.apache.spark.unsafe.types.CalendarIntervalfor valid duration identifiers. By default, next micro batch will be generated as soon as the previous one complete processing.checkpoint_location: a string as the location path for incremental refresh job checkpoint. The location has to be a path in an HDFS compatible file system and only applicable when auto refresh enabled. If unspecified, temporary checkpoint directory will be used and may result in checkpoint data lost upon restart.
WITH (
auto_refresh = [true|false],
refresh_interval = 'time interval expression',
checkpoint_location = 'checkpoint directory path'
)Example:
CREATE INDEX elb_and_requestUri
ON alb_logs ( elb, requestUri )
WITH (
auto_refresh = true,
refresh_interval = '1 minute',
checkpoint_location = 's3://test/'
)OpenSearch stores the Flint index in an OpenSearch index of the given name.
In the index mapping, the _meta and propertiesfield stores meta and schema info of a Flint index.
{
"_meta": {
"version": "0.1",
"indexConfig": {
"kind": "skipping",
"properties": {
"indexedColumns": [
{
"kind": "Partition",
"columnName": "year",
"columnType": "int"
},
{
"kind": "ValuesSet",
"columnName": "elb_status_code",
"columnType": "int"
}
]
}
},
"source": "alb_logs"
},
"properties": {
"year": {
"type": "integer"
},
"elb_status_code": {
"type": "integer"
},
"file_path": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}spark.datasource.flint.host: default is localhost.spark.datasource.flint.port: default is 9200.spark.datasource.flint.scheme: default is http. valid values [http, https]spark.datasource.flint.auth: default is false. valid values [false, sigv4]spark.datasource.flint.region: default is us-west-2. only been used when auth=sigv4spark.datasource.flint.customAWSCredentialsProvider: default is empty.spark.datasource.flint.write.id_name: no default value.spark.datasource.flint.ignore.id_column: default value is true.spark.datasource.flint.write.batch_size: default value is 1000.spark.datasource.flint.write.refresh_policy: default value is false. valid values [NONE(false), IMMEDIATE(true), WAIT_UNTIL(wait_for)]spark.datasource.flint.read.scroll_size: default value is 100.spark.flint.optimizer.enabled: default is true.spark.flint.index.hybridscan.enabled: default is false.
The following table define the data type mapping between Flint data type and Spark data type.
| FlintDataType | SparkDataType |
|---|---|
| boolean | BooleanType |
| long | LongType |
| integer | IntegerType |
| short | ShortType |
| byte | ByteType |
| double | DoubleType |
| float | FloatType |
| date(Timestamp) | DateType |
| date(Date) | TimestampType |
| keyword | StringType, VarcharType, CharType |
| text | StringType(meta(osType)=text) |
| object | StructType |
- Currently, Flint data type only support date. it is mapped to Spark Data Type based on the format:
- Map to DateType if format = strict_date, (we also support format = date, may change in future)
- Map to TimestampType if format = strict_date_optional_time_nanos, (we also support format = strict_date_optional_time | epoch_millis, may change in future)
- Spark data types VarcharType(length) and CharType(length) are both currently mapped to Flint data type keyword, dropping their length property. On the other hand, Flint data type keyword only maps to StringType.
Unsupported Spark data types:
- DecimalType
- BinaryType
- YearMonthIntervalType
- DayTimeIntervalType
- ArrayType
- MapType
Here is an example for Flint Spark integration:
val flint = new FlintSpark(spark)
// Skipping index
flint.skippingIndex()
.onTable("alb_logs")
.filterBy("time > 2023-04-01 00:00:00")
.addPartitions("year", "month", "day")
.addValueSet("elb_status_code")
.addMinMax("request_processing_time")
.create()
flint.refresh("flint_alb_logs_skipping_index", FULL)
// Covering index
flint.coveringIndex()
.name("elb_and_requestUri")
.onTable("alb_logs")
.addIndexColumns("elb", "requestUri")
.create()
flint.refresh("flint_alb_logs_elb_and_requestUri_index")trait FlintSparkSkippingStrategy {
TODO: outputSchema, getAggregators, rewritePredicate
}Here is an example for read index data from AWS OpenSearch domain.
spark.conf.set("spark.datasource.flint.host", "yourdomain.us-west-2.es.amazonaws.com")
spark.conf.set("spark.datasource.flint.port", "-1")
spark.conf.set("spark.datasource.flint.scheme", "https")
spark.conf.set("spark.datasource.flint.auth", "sigv4")
spark.conf.set("spark.datasource.flint.region", "us-west-2")
spark.conf.set("spark.datasource.flint.refresh_policy", "wait_for")
val df = spark.range(15).toDF("aInt")
val re = df.coalesce(1)
.write
.format("flint")
.mode("overwrite")
.save("t001")
val df = new SQLContext(sc).read
.format("flint")
.load("t001")
TODO
For now, only single or conjunct conditions (conditions connected by AND) in WHERE clause can be optimized by skipping index.
Manual refreshing a table which already has skipping index being auto-refreshed, will be prevented. However, this assumption relies on the condition that the incremental refresh job is actively running in the same Spark cluster, which can be identified when performing the check.
Flint use DefaultAWSCredentialsProviderChain. When running in EMR Spark, Flint use executionRole credentials
--conf spark.jars.packages=org.opensearch:opensearch-spark-standalone_2.12:0.1.0-SNAPSHOT \
--conf spark.jars.repositories=https://aws.oss.sonatype.org/content/repositories/snapshots \
--conf spark.emr-serverless.driverEnv.JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-17-amazon-corretto.x86_64 \
--conf spark.executorEnv.JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-17-amazon-corretto.x86_64 \
--conf spark.datasource.flint.host=opensearch-domain.us-west-2.es.amazonaws.com \
--conf spark.datasource.flint.port=-1 \
--conf spark.datasource.flint.scheme=https \
--conf spark.datasource.flint.auth=sigv4 \
--conf spark.datasource.flint.region=us-west-2 \
- In AccountB, add trust relationship to arn:aws:iam::AccountB:role/CrossAccountRoleB
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::AccountA:role/JobExecutionRoleA"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}
- In AccountA, add STS assume role permission to arn:aws:iam::AccountA:role/JobExecutionRoleA
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Resource": "arn:aws:iam::AccountB:role/CrossAccountRoleB"
}
]
}
- Set the spark.datasource.flint.customAWSCredentialsProvider property with value as com.amazonaws.emr.AssumeRoleAWSCredentialsProvider. Set the environment variable ASSUME_ROLE_CREDENTIALS_ROLE_ARN with the ARN value of CrossAccountRoleB.
--conf spark.jars.packages=org.opensearch:opensearch-spark-standalone_2.12:0.1.0-SNAPSHOT \
--conf spark.jars.repositories=https://aws.oss.sonatype.org/content/repositories/snapshots \
--conf spark.emr-serverless.driverEnv.JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-17-amazon-corretto.x86_64 \
--conf spark.executorEnv.JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-17-amazon-corretto.x86_64 \
--conf spark.datasource.flint.host=opensearch-domain.us-west-2.es.amazonaws.com \
--conf spark.datasource.flint.port=-1 \
--conf spark.datasource.flint.scheme=https \
--conf spark.datasource.flint.auth=sigv4 \
--conf spark.datasource.flint.region=us-west-2 \
--conf spark.datasource.flint.customAWSCredentialsProvider=com.amazonaws.emr.AssumeRoleAWSCredentialsProvider \
--conf spark.emr-serverless.driverEnv.ASSUME_ROLE_CREDENTIALS_ROLE_ARN=arn:aws:iam::AccountB:role/CrossAccountRoleB \
--conf spark.executorEnv.ASSUME_ROLE_CREDENTIALS_ROLE_ARN=arn:aws:iam::AccountBB:role/CrossAccountRoleB