UForm is a Multi-Modal Modal inference library designed to encode Multi-Lingual Texts, Images, and, soon, Audio, Video, and Documents, into a shared vector space! It comes with a family of homonymous pre-trained networks, so tiny and efficient you can run them anywhere from large servers to mobile phones... All available on HuggingFace 🤗
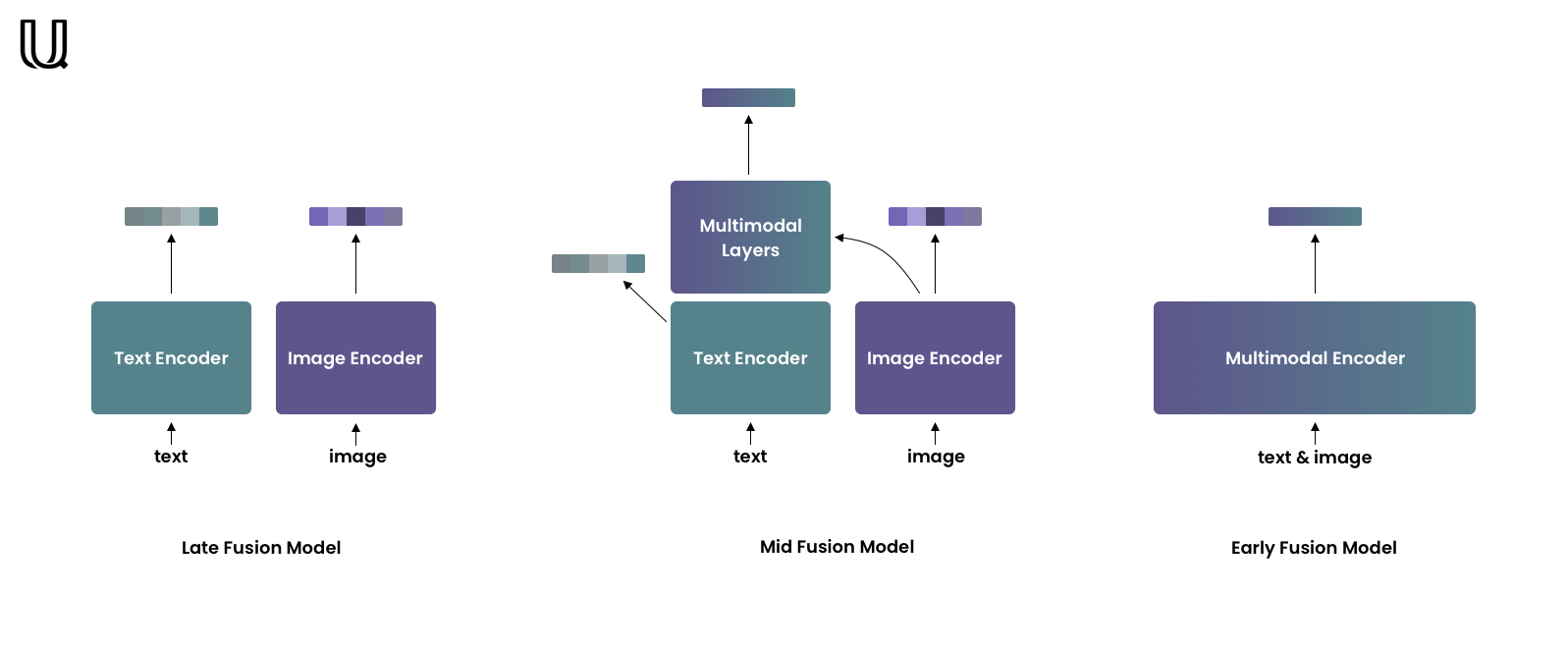
Late-fusion models encode each modality independently but into one shared vector space. Due to independent encoding, late-fusion models are good at capturing coarse-grained features but often neglect fine-grained ones. This type of model is well-suited for retrieval in extensive collections. The most famous example of such models is CLIP by OpenAI.
Early-fusion models encode both modalities jointly so they can take into account fine-grained features. Usually, these models are used for re-ranking relatively small retrieval results.
Mid-fusion models are the golden midpoint between the previous two types. Mid-fusion models consist of two parts – unimodal and multimodal. The unimodal part allows encoding each modality separately as late-fusion models do. The multimodal part takes unimodal features from the unimodal part as input and enhances them with a cross-attention mechanism.
This tiny package will help you deal with the last!
pip install uformUForm v0.3.0 and below depend on transformers and timm libraries.
All newer versions depend only on PyTorch and utility libraries.
For the best performance, PyTorch v2.0.0 and above is recommended.
To load the model:
import uform
model = uform.get_model('unum-cloud/uform-vl-english')
model = uform.get_model('unum-cloud/uform-vl-multilingual-v2')You can also load your own Mid-fusion model. Just upload it on HuggingFace and pass the model name to get_model.
To encode data:
from PIL import Image
text = 'a small red panda in a zoo'
image = Image.open('red_panda.jpg')
image_data = model.preprocess_image(image)
text_data = model.preprocess_text(text)
image_embedding = model.encode_image(image_data)
text_embedding = model.encode_text(text_data)
joint_embedding = model.encode_multimodal(image=image_data, text=text_data)Retrieving features is also trivial:
image_features, image_embedding = model.encode_image(image_data, return_features=True)
text_features, text_embedding = model.encode_text(text_data, return_features=True)These features can later be used to produce joint multimodal encodings faster, as the first layers of the transformer can be skipped:
joint_embedding = model.encode_multimodal(
image_features=image_features,
text_features=text_features,
attention_mask=text_data['attention_mask']
)You can also use our larger, faster, better proprietary models deployed in optimized cloud environments. For that, please, choose the cloud of liking, search the marketplace for "Unum UForm" and reinstall UForm with optional dependencies:
pip install uform[remote]The only thing that changes after that is calling get_client with the IP address of your instance instead of using get_model for local usage.
model = uform.get_client('0.0.0.0:7000')First, you will need to setup PopTorch for Graphcore IPUs. Follow the user guide.
import poptorch
from PIL import Image
options = poptorch.Options()
options.replicationFactor(1)
options.deviceIterations(4)
model = get_model_ipu('unum-cloud/uform-vl-english').parallelize()
model = poptorch.inferenceModel(model, options=options)
text = 'a small red panda in a zoo'
image = Image.open('red_panda.jpg')
image_data = model.preprocess_image(image)
text_data = model.preprocess_text(text)
image_data = image_data.repeat(4, 1, 1, 1)
text_data = {k: v.repeat(4, 1) for k,v in text_data.items()}
image_features, text_features = model(image_data, text_data)| Model | Language Tower | Image Tower | Multimodal Part | Languages | URL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
unum-cloud/uform-vl-english |
BERT, 2 layers | ViT-B/16 | 2 layers | 1 | weights.pt |
unum-cloud/uform-vl-multilingual |
BERT, 8 layers | ViT-B/16 | 4 layers | 12 | weights.pt |
unum-cloud/uform-vl-multilingual-v2 |
BERT, 8 layers | ViT-B/16 | 4 layers | 21 | weights.pt |
The multilingual were trained on a language-balanced dataset. For pre-training, we translated captions with NLLB.
Evaluating the unum-cloud/uform-vl-multilingual-v2 model, one can expect the following metrics for text-to-image search, compared against xlm-roberta-base-ViT-B-32 OpenCLIP model.
Check out the unum-cloud/coco-sm for details.
| Language | OpenCLIP @ 1 | UForm @ 1 | OpenCLIP @ 5 | UForm @ 5 | OpenCLIP @ 10 | UForm @ 10 | Speakers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arabic 🇸🇦 | 22.7 | 31.7 | 44.9 | 57.8 | 55.8 | 69.2 | 274 M |
| Armenian 🇦🇲 | 5.6 | 22.0 | 14.3 | 44.7 | 20.2 | 56.0 | 4 M |
| Chinese 🇨🇳 | 27.3 | 32.2 | 51.3 | 59.0 | 62.1 | 70.5 | 1'118 M |
| English 🇺🇸 | 37.8 | 37.7 | 63.5 | 65.0 | 73.5 | 75.9 | 1'452 M |
| French 🇫🇷 | 31.3 | 35.4 | 56.5 | 62.6 | 67.4 | 73.3 | 274 M |
| German 🇩🇪 | 31.7 | 35.1 | 56.9 | 62.2 | 67.4 | 73.3 | 134 M |
| Hebrew 🇮🇱 | 23.7 | 26.7 | 46.3 | 51.8 | 57.0 | 63.5 | 9 M |
| Hindi 🇮🇳 | 20.7 | 31.3 | 42.5 | 57.9 | 53.7 | 69.6 | 602 M |
| Indonesian 🇮🇩 | 26.9 | 30.7 | 51.4 | 57.0 | 62.7 | 68.6 | 199 M |
| Italian 🇮🇹 | 31.3 | 34.9 | 56.7 | 62.1 | 67.1 | 73.1 | 67 M |
| Japanese 🇯🇵 | 27.4 | 32.6 | 51.5 | 59.2 | 62.6 | 70.6 | 125 M |
| Korean 🇰🇷 | 24.4 | 31.5 | 48.1 | 57.8 | 59.2 | 69.2 | 81 M |
| Persian 🇮🇷 | 24.0 | 28.8 | 47.0 | 54.6 | 57.8 | 66.2 | 77 M |
| Polish 🇵🇱 | 29.2 | 33.6 | 53.9 | 60.1 | 64.7 | 71.3 | 41 M |
| Portuguese 🇵🇹 | 31.6 | 32.7 | 57.1 | 59.6 | 67.9 | 71.0 | 257 M |
| Russian 🇷🇺 | 29.9 | 33.9 | 54.8 | 60.9 | 65.8 | 72.0 | 258 M |
| Spanish 🇪🇸 | 32.6 | 35.6 | 58.0 | 62.8 | 68.8 | 73.7 | 548 M |
| Thai 🇹🇭 | 21.5 | 28.7 | 43.0 | 54.6 | 53.7 | 66.0 | 61 M |
| Turkish 🇹🇷 | 25.5 | 33.0 | 49.1 | 59.6 | 60.3 | 70.8 | 88 M |
| Ukranian 🇺🇦 | 26.0 | 30.6 | 49.9 | 56.7 | 60.9 | 68.1 | 41 M |
| Vietnamese 🇻🇳 | 25.4 | 28.3 | 49.2 | 53.9 | 60.3 | 65.5 | 85 M |
| Mean | 26.5±6.4 | 31.8±3.5 | 49.8±9.8 | 58.1±4.5 | 60.4±10.6 | 69.4±4.3 | - |
| Google Translate | 27.4±6.3 | 31.5±3.5 | 51.1±9.5 | 57.8±4.4 | 61.7±10.3 | 69.1±4.3 | - |
| Microsoft Translator | 27.2±6.4 | 31.4±3.6 | 50.8±9.8 | 57.7±4.7 | 61.4±10.6 | 68.9±4.6 | - |
| Meta NLLB | 24.9±6.7 | 32.4±3.5 | 47.5±10.3 | 58.9±4.5 | 58.2±11.2 | 70.2±4.3 | - |
On RTX 3090, the following performance is expected from uform on text encoding.
| Model | Multilingual | Sequences per Second | Speedup |
|---|---|---|---|
bert-base-uncased |
No | 1'612 | |
distilbert-base-uncased |
No | 3'174 | x 1.96 |
sentence-transformers/MiniLM-L12 |
Yes | 3'604 | x 2.24 |
sentence-transformers/MiniLM-L6 |
No | 6'107 | x 3.79 |
unum-cloud/uform-vl-multilingual |
Yes | 6'809 | x 4.22 |
There are two options to calculate semantic compatibility between an image and a text: Cosine Similarity and Matching Score.
import torch.nn.functional as F
similarity = F.cosine_similarity(image_embedding, text_embedding)The similarity will belong to the [-1, 1] range, 1 meaning the absolute match.
Pros:
- Computationally cheap.
- Only unimodal embeddings are required. Unimodal encoding is faster than joint encoding.
- Suitable for retrieval in large collections.
Cons:
- Takes into account only coarse-grained features.
Unlike cosine similarity, unimodal embedding is not enough.
Joint embedding will be needed, and the resulting score will belong to the [0, 1] range, 1 meaning the absolute match.
score = model.get_matching_scores(joint_embedding)Pros:
- Joint embedding captures fine-grained features.
- Suitable for re-ranking - sorting retrieval result.
Cons:
- Resource-intensive.
- Not suitable for retrieval in large collections.