The goal of this training session is to go over the data submission process for the PacMAN decision support tool, and do a hands-on demonstration of every step in the process. Steps that you as a participant can try on your own computer are indicated with 👉.
The PacMAN decision support system integrates detections from various sources by connecting to the OBIS database. Data publishing to OBIS typically happens through an Integrated Publishing Toolkit (IPT) instance. This is also the case for the PacMAN monitoring campaigns. Before sequence data from eDNA sampling can be published to OBIS, it needs to be processed and formatted in the Darwin Core format. Processing involves quality controlling and trimming of sequences, ASV inference, and taxonomic annotation. These steps are taken care of by the PacMAN bioinformatics pipeline.
The PacMAN pipeline uses a number of taxonomic annotation algorithms. The main taxonomic assignment algorithm is a machine learning algorithm, which is used to populate the scientificName field in Darwin Core. The algorithm is a naïve Bayesian classifier called RDP Classifier. RDP Classifier calculates a probability for every possible taxonomic annotation using k-mer frequences, and then applies a bootstrapping procedure to obtain a confidence score for each taxonomic level.
The pipeline also includes a search algorithm called VSEARCH to find the closest matches in a reference database. VSEARCH also provides a similarity score for each matching sequence. The results from this alternative algorithm are included in the identificationRemarks Darwin Core field.
| Algorithm | Results | Darwin Core field |
|---|---|---|
| RDP Classifier | family X (confidence 1), genus Y (confidence 0.9), species B (confidence 0.3) | scientificName |
| VSEARCH | family X, genus Y, species A (identity 0.997) family X, genus Y, species B (identity 0.995) family X, genus Y, species B (identity 0.995) family X, genus Y, species A (identity 0.992) family X, genus Z, species C (identity 0.983) family X, genus Z, species C (identity 0.975) |
identificationRemarks |
The PacMAN decision support system uses taxonomic annotations from both algorithms to identify potential invasives.
The PacMAN bioinformatics pipeline is workflow based on commonly used bioinformatics tools and custom scripts. The pipeline is orchestrated using the Snakemake workflow management system. Snakemake takes care of installing the necessary dependencies in Conda environments, and running the different steps of the pipeline in the correct order.
In addition to installing Conda and Snakemake locally, it's also possible to run the pipeline using Docker. In this case, the pipeline is encapsulated in a Docker container, and the data and results folders are mounted as "volumes" so they can be shared between the Docker container and the host machine.
The following files are required to run the pipeline:
- Configuration file
- Manifest
- Sample metadata
- Raw sequences
- RDP reference database
- VSEARCH reference database
See the data preparation section in the pipeline README for example files and reference database downloads. Structure the files like this:
└── data
├── config_files
│ ├── config.yaml
│ ├── manifest.csv
│ └── sample_data.csv
├── raw_sequences
│ ├── USP-24-01-172_S172_L001_R1_001.fastq.gz
│ └── USP-24-01-172_S172_L001_R2_001.fastq.gz
└── reference_databases
├── COI_ncbi_1_50000_pcr_pga_taxon_derep_clean_sintax.fasta
└── COI_terrimporter
├── bergeyTrainingTree.xml
├── genus_wordConditionalProbList.txt
├── logWordPrior.txt
├── rRNAClassifier.properties
└── wordConditionalProbIndexArr.txt
Run the pipeline with Snakemake or Docker using either of the following commands:
snakemake --use-conda --configfile data/config_files/config.yaml --rerun-incomplete --printshellcmds
docker run --platform linux/amd64 \
-v $(pwd)/data:/pipeline/data \
-v $(pwd)/results:/pipeline/results \
-v $(pwd)/.snakemake:/pipeline/.snakemake \
pieterprovoost/pacman-pipeline👉 Sign into the OBIS JupyterHub with the provided credentials to explore an example pipeline result dataset. JupyterHub is an online computing environment that allows us to explore data data without the need to download any files or install any software locally.
👉 Navigate to the example dataset in shared/example_results and check the following files:
- The pipeline report in
results/PacMAN/runs/COI/06-report - The Darwin Core tables in
results/PacMAN/runs/COI/05-dwcaOccurrence_table.tsvDNA_extension_table.tsv
The pipeline results are also available as a phyloseq object, which makes it very convenient to analyse the dataset in R. To read more about this data format, continue to the phyloseq website.
👉 For example, to visualize the taxonomic composition of the dataset as a Krona plot, run the following code in an R notebook:
library(dplyr)
library(psadd)
library(phyloseq)
ps <- readRDS("shared/example_results/05-dwca/phyloseq_object.rds")
tax_table(ps) <- tax_table(ps) %>%
as.data.frame() %>%
select(phylum, class, order, family, genus, species) %>%
as.matrix(rownames.force = T)
plot_krona(ps, output = "krona_plot", variable = "eventID")Then open the resulting krona_plot.html file.
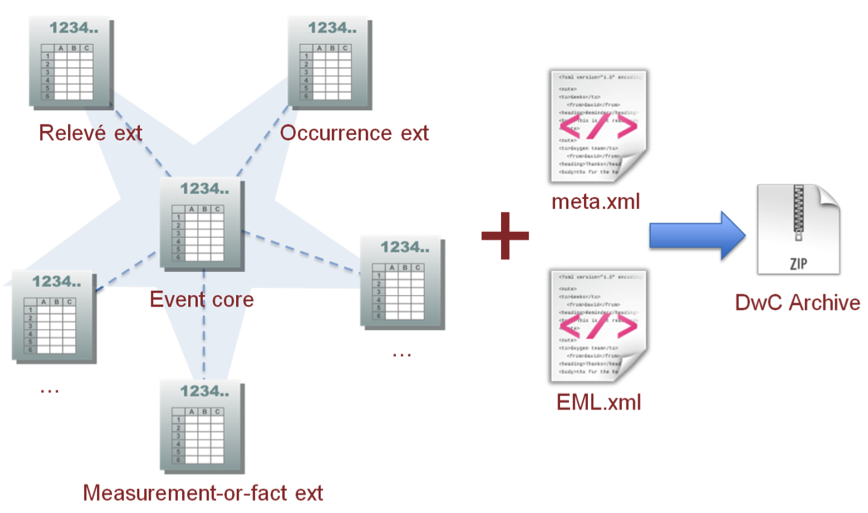
After conversion to Darwin Core tables, our dataset can be published to OBIS trough a Integrated Publishing Toolkit (IPT) instance. IPT allows us to enter metadata through a form, and map the columns in our tables to Darwin Core fields. The result will be a Darwin Core Archive file which can be ingested by platforms such as OBIS and GBIF. This archive contains our data tables, a metadata document, and a document describing the structure of our dataset (tables and fields).
👉 For this training we will work on the OBIS training IPT. Go to https://ipt.iobis.org/training and sign in with the provided credentials.
👉 Before proceeding, download the occurrence and DNA tables from the example dataset in JupyterHub (find both files in results/PacMAN/runs/COI/05-dwca).
👉 To create a new dataset in IPT, navigate to the Manage Resources tab and click Create new.
👉 Scroll to the Metadata section and click Edit. Minimal metadata needs to be completed to be able to publish the dataset, such as a title, license, description, and contacts. After completing the form, click Save at the top.
👉 Go back to the dataset overview and scroll to the Source Data section. Click Add on the right. Upload the Ocurrence and DNADerivedData files, but make sure to check if the number of columns detected is correct. If not, adjust the field delimiter (should be \t), and click Options > Analyze at the top to update the number of columns.
👉 Now go to Darwin Core Mappings and click Add. First select Darwin Core Occurrence and pick the appropriate source file. Click Save to continue.
As the files are using Darwin Core terms, the mapping is done automatically and we can confirm with Save. Also add a mapping for the DNA table.
👉 We are now ready to publish. First set visibility to public the Visibility section, then go to the Publishing section, and click Publish on the right. If we were working on a production IPT instance, the dataset would now be ingested by OBIS and be available for the decision support system.
To see how records are made available by the OBIS system, run this API call which fetches occurrence data from the Suva area.
Go to the PacMAN decision support portal at https://portal.pacman.obis.org/. The portal home page shows all detections (most recent first) regardless of their identification confidence score or assessed risk level. To read more about confidence scores and risk levels, navigate to the About page.
Apply filters to only see detections with higher confidence levels or risk score. For example, this only shows detections with medium confidence or above and medium risk or above. For molecular observations, medium confidence means sufficient reads, high percent identity with a reference sequence, and few alternative identifications. Medium risk or above means that the species is a known introduced species in the region. If the species is known to have impacts, this will result in a high risk score.
A few examples:
- Detection of Phaeostachys spinifera
Lowconfidence score because there are just 8 reads, and 5 possible identifications.Lowrisk score because it is not a known introduced species in the area, there are no records of impact anywhere, and it has been detected outside the species' thermal range.
- Detection of Perna viridis
Lowconfidence score because there are just 7 reads.Highrisk score because the species is on a priority list for the area. In addition, it is detected in its introduced range and is known to have impacts.
- Detection of Eualetes tulipa
Mediumconfidence score due to sufficient reads and 100% identity with reference sequence.Mediumrisk score because the occurrence is within the thermal range of the species, and impacts have been recorded for other areas.
- Detection of Musculus viridulus
Highconfidence score because it is a morphological identification.Lowrisk score because it is not recorded within the introduced range, and the species is not recorded as invasive anywhere (at least according to WRiMS).
Use the taxon filter on the right to show the detections for a single species, for example: Didemnum perlucidum. This is an interesting example as it includes detections with low, medium, and high confidence scores.
This page allows quickly scanning pipeline results before submitting data to OBIS. Taxonomic identifiers are extracted from the data, and a list of matching risk analyses is shown.
👉 Test this by submitting the occurrence file you downloaded earlier.
Administrators of the system can:
- Change the status of a detection
- Change the pest status of a species for an area
- Add notes about species (example: Eualetes tulipa)
- Add notes about a specific species in an area (example: Didemnum vexillum)
- OBIS SG 12 training: training materials on R, JupyterHub, git, and DNADerivedData.
- First PacMAN training: training materials on data management, R, the PacMAN bioinformatics pipeline.
- PacMAN pipeline: the PacMAN bioinformatics pipeline.