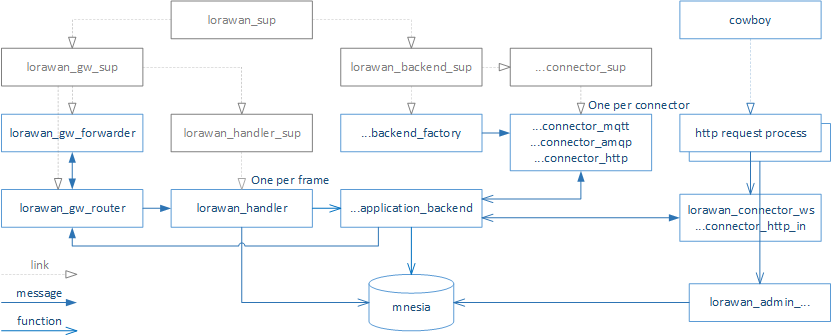
The following figure shows a process hierarchy of the lorawan-server:
The LoRaWAN communication is handled by the following modules:
- lorawan_gw_forwarder implements the packet_forwarder protocol
- lorawan_gw_router handles communication to multiple gateways. It performs uplink frame deduplication and downlink gateway selection.
- lorawan_handler is started for each uplink LoRaWAN frame
- invokes lorawan_mac to decode and decrypt the performs the frame
- invokes lorawan_mac_commands to handle the MAC commands, including ADR algorithms
- invokes the desired internal application or lorawan_application_backend
- lorawan_backend_factory starts and stops the individual backend connectors
- lorawan_application_backend extracts desired data fields from the uplink frame and forwards the fields to a pg2 process group corresponding to the handler name
- lorawan_connectors open and maintain connections to backend systems and transmits the data fields to/from them using a desired protocol. Each connector joins a given pg2 group
The Cowboy HTTP sever starts one process for each incoming each connection:
- lorawan_admin_... modules provide handlers for the REST API. They interact with the mnesia database only.
- lorawan_connector_ws provide handler for the WebSocket interface. One handler invoked for each incoming connection, to joins a given pg2 group as every connector and then filters the uplink frames based on given URI.
Using server logs is the most common technique to debug server functions. Please review the lager framework documentation for a comprehensive description.
For example, you can generate log messages by doing the following:
lager:warning("unexpected value: ~w", [Value])The lorawan-server is started as a cluster node lorawan@<hostname>, where
<hostname> is a short hostname of the machine hosting the server. For example,
if hostname --short returns debian, the server runs as a node lorawan@debian.
You can connect to a running lorawan-server by erl -sname test -remsh lorawan@<hostname>.
Once connected you can e.g. use the Mnesia functions
to directly access the server database.
Advanced users can also start the Observer and trace the lorawan-server processes and activities:
erl -smp -sname observer -hidden -setcookie MyCookie -run observerPlease note that nodes allowed to communicate with each other use the same
magic cookie. Make sure that $HOME/.erlang.cookie is the same, or
enter the cookie explicitly by the -setcookie MyCookie parameter.
To create a new release:
- update the version number in
rebar.config,src/lorawan_server.app.srcandscripts/buildroot/lorawan-server.mk - commit and push the change
- create a new signed tag, e.g.
git tag v0.6.5 master
git push origin v0.6.5