Because it's free, open-source, and requires only 1% CPU utilization to collect thousands of metrics every second, Netdata is a superb single-node monitoring tool.
In this quickstart guide, you'll learn how to access your single node's metrics through dashboards, configure your node to your liking, and make sure the Netdata Agent is collecting metrics from the applications or containers you're running on your node.
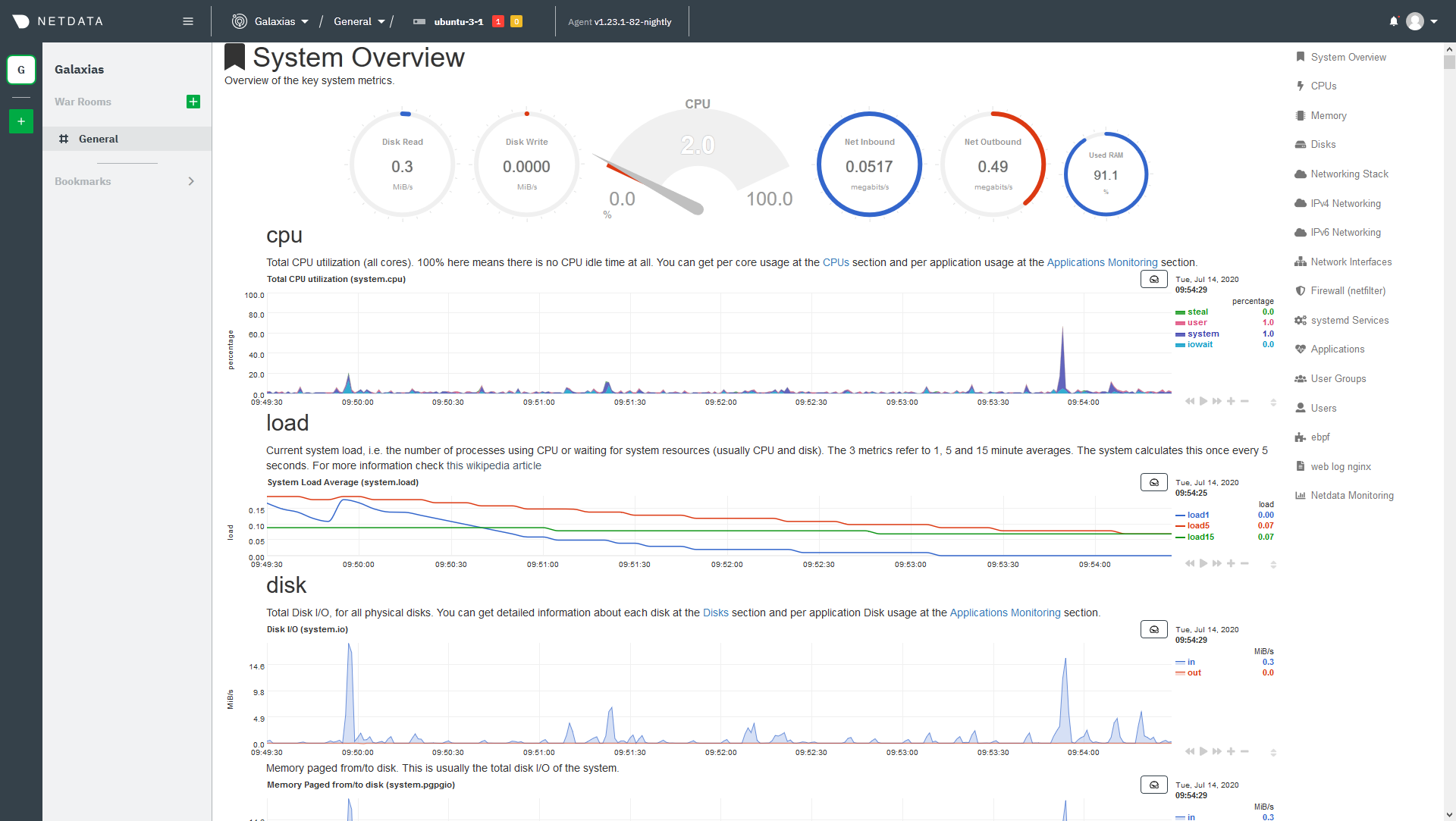
To see your node's real-time metrics, you need to access its dashboard. You can either view the local dashboard, which runs on the node itself, or see the dashboard through Netdata Cloud. Both methods feature real-time, interactive, and synchronized charts, with the same metrics, and use the same UI.
The primary difference is that Netdata Cloud also has a few extra features, like creating new dashboards using a drag-and-drop editor, that enhance your monitoring and troubleshooting experience.
To see your node's local dashboard, open up your web browser of choice and navigate to http://NODE:19999, replacing
NODE with the IP address or hostname of your Agent. Hit Enter.
To see a node's dashboard in Netdata Cloud, sign in. From the Nodes view in your General War Room, click on the hostname of your node to access its dashboard through Netdata Cloud.
Once you've decided which dashboard you prefer, learn about interacting with dashboards and charts to get the most from Netdata's real-time metrics.
The Netdata Agent is highly configurable so that you can match its behavior to your node. You will find most
configuration options in the netdata.conf file, which is typically at /etc/netdata/netdata.conf. The best way to
edit this file is using the edit-config script, which ensures updates to the Netdata Agent do not overwrite your
changes. For example:
cd /etc/netdata
sudo ./edit-config netdata.confOur configuration basics doc contains more information about netdata.conf, edit-config,
along with simple examples to get you familiar with editing your node's configuration.
After you've learned the basics, you should secure your node using one of our recommended methods. These security best practices ensure no untrusted parties gain access to your dashboard or its metrics.
Netdata has 300+ pre-installed collectors that gather thousands of metrics with zero configuration. Collectors search your node in default locations and ports to find running applications and gather as many metrics as possible without you having to configure them individually.
These metrics enrich both the local and Netdata Cloud dashboards.
Most collectors work without configuration, but you should read up on how collectors work and how to enable/configure them.
In addition, find detailed information about which system, container, and application metrics you can collect from across your infrastructure with Netdata.
Netdata has many features that help you monitor the health of your node and troubleshoot complex performance problems. Once you understand configuration, and are certain Netdata is collecting all the important metrics from your node, try out some of Netdata's other visualization and health monitoring features:
- Build new dashboards to put disparate but relevant metrics onto a single interface.
- Create new alarms, or tweak some of the pre-configured alarms, to stay on top of anomalies.
- Enable notifications to Slack, PagerDuty, email, and 30+ other services.
- Change how long your node stores metrics based on how many metrics it collects, your preferred retention period, and the resources you want to dedicate toward long-term metrics retention.
- Export metrics to an external time-series database to use Netdata alongside other monitoring and troubleshooting tools.