| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
简单 |
1462 |
第 131 场周赛 Q2 |
|
给出一棵二叉树,其上每个结点的值都是 0 或 1 。每一条从根到叶的路径都代表一个从最高有效位开始的二进制数。
- 例如,如果路径为
0 -> 1 -> 1 -> 0 -> 1,那么它表示二进制数01101,也就是13。
对树上的每一片叶子,我们都要找出从根到该叶子的路径所表示的数字。
返回这些数字之和。题目数据保证答案是一个 32 位 整数。
示例 1:
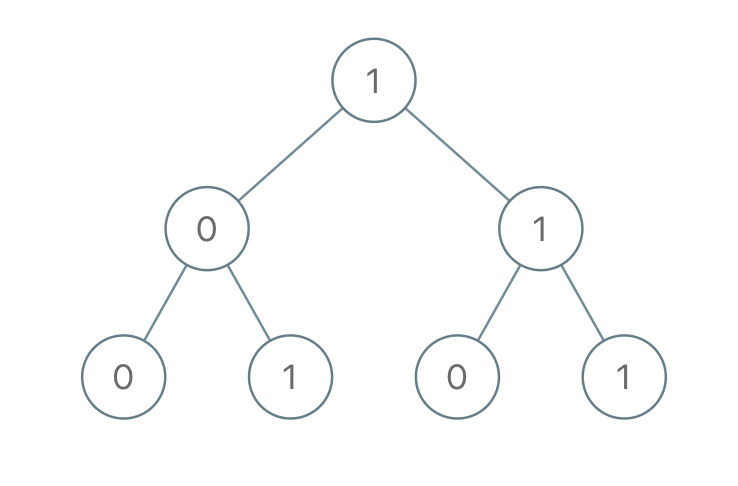
输入:root = [1,0,1,0,1,0,1] 输出:22 解释:(100) + (101) + (110) + (111) = 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 = 22
示例 2:
输入:root = [0] 输出:0
提示:
- 树中的节点数在
[1, 1000]范围内 Node.val仅为0或1
我们设计一个递归函数 dfs(root, t),它接收两个参数:当前节点 root 和当前节点的父节点对应的二进制数 t。函数的返回值是从当前节点到叶子节点的路径所表示的二进制数之和。答案即为 dfs(root, 0)。
递归函数的逻辑如下:
- 如果当前节点
root为空,则返回0,否则计算当前节点对应的二进制数t,即t = t << 1 | root.val。 - 如果当前节点是叶子节点,则返回
t,否则返回dfs(root.left, t)和dfs(root.right, t)的和。
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def sumRootToLeaf(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
def dfs(root, t):
if root is None:
return 0
t = (t << 1) | root.val
if root.left is None and root.right is None:
return t
return dfs(root.left, t) + dfs(root.right, t)
return dfs(root, 0)/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int sumRootToLeaf(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root, 0);
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root, int t) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
t = (t << 1) | root.val;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return t;
}
return dfs(root.left, t) + dfs(root.right, t);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int sumRootToLeaf(TreeNode* root) {
return dfs(root, 0);
}
int dfs(TreeNode* root, int t) {
if (!root) return 0;
t = (t << 1) | root->val;
if (!root->left && !root->right) return t;
return dfs(root->left, t) + dfs(root->right, t);
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func sumRootToLeaf(root *TreeNode) int {
var dfs func(root *TreeNode, t int) int
dfs = func(root *TreeNode, t int) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
t = (t << 1) | root.Val
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
return t
}
return dfs(root.Left, t) + dfs(root.Right, t)
}
return dfs(root, 0)
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function sumRootToLeaf(root: TreeNode | null): number {
const dfs = (root: TreeNode | null, num: number) => {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
const { val, left, right } = root;
num = (num << 1) | val;
if (left == null && right == null) {
return num;
}
return dfs(left, num) + dfs(right, num);
};
return dfs(root, 0);
}// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::rc::Rc;
impl Solution {
fn dfs(root: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, mut num: i32) -> i32 {
if root.is_none() {
return 0;
}
let root = root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow();
num = (num << 1) | root.val;
if root.left.is_none() && root.right.is_none() {
return num;
}
Self::dfs(&root.left, num) + Self::dfs(&root.right, num)
}
pub fn sum_root_to_leaf(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
Self::dfs(&root, 0)
}
}