| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
|
给出二叉 搜索 树的根节点,该树的节点值各不相同,请你将其转换为累加树(Greater Sum Tree),使每个节点 node 的新值等于原树中大于或等于 node.val 的值之和。
提醒一下,二叉搜索树满足下列约束条件:
- 节点的左子树仅包含键 小于 节点键的节点。
- 节点的右子树仅包含键 大于 节点键的节点。
- 左右子树也必须是二叉搜索树。
注意:本题和 1038: https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-search-tree-to-greater-sum-tree/ 相同
示例 1:
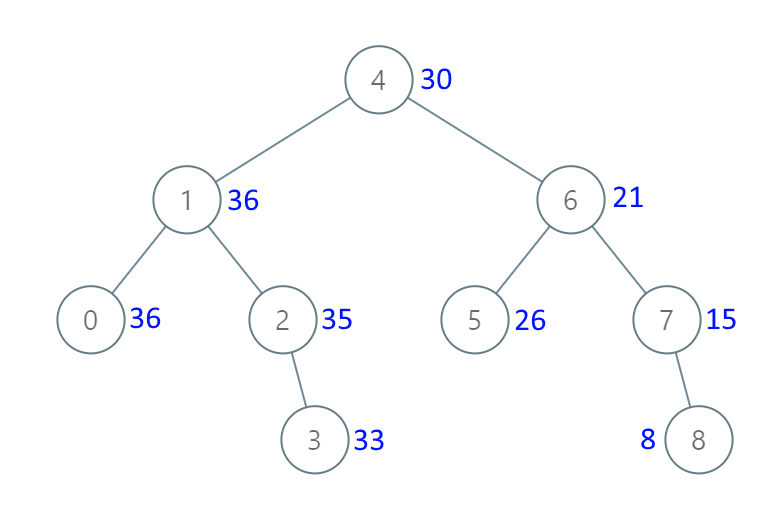
输入:[4,1,6,0,2,5,7,null,null,null,3,null,null,null,8] 输出:[30,36,21,36,35,26,15,null,null,null,33,null,null,null,8]
示例 2:
输入:root = [0,null,1] 输出:[1,null,1]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1,0,2] 输出:[3,3,2]
示例 4:
输入:root = [3,2,4,1] 输出:[7,9,4,10]
提示:
- 树中的节点数介于
0和104之间。 - 每个节点的值介于
-104和104之间。 - 树中的所有值 互不相同 。
- 给定的树为二叉搜索树。
按照“右根左”的顺序,递归遍历二叉搜索树,累加遍历到的所有节点值到 node 节点。
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def convertBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
def dfs(root):
nonlocal s
if root is None:
return
dfs(root.right)
s += root.val
root.val = s
dfs(root.left)
s = 0
dfs(root)
return root/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int s;
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return root;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
dfs(root.right);
s += root.val;
root.val = s;
dfs(root.left);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int s = 0;
TreeNode* convertBST(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
return root;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return;
dfs(root->right);
s += root->val;
root->val = s;
dfs(root->left);
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func convertBST(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
s := 0
var dfs func(*TreeNode)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode) {
if root == nil {
return
}
dfs(root.Right)
s += root.Val
root.Val = s
dfs(root.Left)
}
dfs(root)
return root
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var convertBST = function (root) {
let s = 0;
function dfs(root) {
if (!root) {
return;
}
dfs(root.right);
s += root.val;
root.val = s;
dfs(root.left);
}
dfs(root);
return root;
};Morris 遍历无需使用栈,时间复杂度
定义 s 表示二叉搜索树节点值累加和。遍历二叉树节点:
- 若当前节点 root 的右子树为空,将当前节点值添加至 s 中,更新当前节点值为 s,并将当前节点更新为
root.left。 - 若当前节点 root 的右子树不为空,找到右子树的最左节点 next(也即是 root 节点在中序遍历下的后继节点):
- 若后继节点 next 的左子树为空,将后继节点的左子树指向当前节点 root,并将当前节点更新为
root.right。 - 若后继节点 next 的左子树不为空,将当前节点值添加 s 中,更新当前节点值为 s,然后将后继节点左子树指向空(即解除 next 与 root 的指向关系),并将当前节点更新为
root.left。
- 若后继节点 next 的左子树为空,将后继节点的左子树指向当前节点 root,并将当前节点更新为
- 循环以上步骤,直至二叉树节点为空,遍历结束。
- 最后返回二叉搜索树根节点即可。
Morris 反序中序遍历跟 Morris 中序遍历思路一致,只是将中序遍历的“左根右”变为“右根左”。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def convertBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
s = 0
node = root
while root:
if root.right is None:
s += root.val
root.val = s
root = root.left
else:
next = root.right
while next.left and next.left != root:
next = next.left
if next.left is None:
next.left = root
root = root.right
else:
s += root.val
root.val = s
next.left = None
root = root.left
return node/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
int s = 0;
TreeNode node = root;
while (root != null) {
if (root.right == null) {
s += root.val;
root.val = s;
root = root.left;
} else {
TreeNode next = root.right;
while (next.left != null && next.left != root) {
next = next.left;
}
if (next.left == null) {
next.left = root;
root = root.right;
} else {
s += root.val;
root.val = s;
next.left = null;
root = root.left;
}
}
}
return node;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* convertBST(TreeNode* root) {
int s = 0;
TreeNode* node = root;
while (root) {
if (root->right == nullptr) {
s += root->val;
root->val = s;
root = root->left;
} else {
TreeNode* next = root->right;
while (next->left && next->left != root) {
next = next->left;
}
if (next->left == nullptr) {
next->left = root;
root = root->right;
} else {
s += root->val;
root->val = s;
next->left = nullptr;
root = root->left;
}
}
}
return node;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func convertBST(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
s := 0
node := root
for root != nil {
if root.Right == nil {
s += root.Val
root.Val = s
root = root.Left
} else {
next := root.Right
for next.Left != nil && next.Left != root {
next = next.Left
}
if next.Left == nil {
next.Left = root
root = root.Right
} else {
s += root.Val
root.Val = s
next.Left = nil
root = root.Left
}
}
}
return node
}