| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Hard |
|
Given an m x n integers matrix, return the length of the longest increasing path in matrix.
From each cell, you can either move in four directions: left, right, up, or down. You may not move diagonally or move outside the boundary (i.e., wrap-around is not allowed).
Example 1:
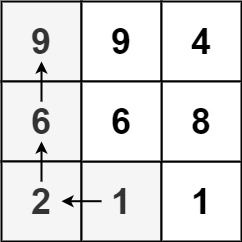
Input: matrix = [[9,9,4],[6,6,8],[2,1,1]]
Output: 4
Explanation: The longest increasing path is [1, 2, 6, 9].
Example 2:
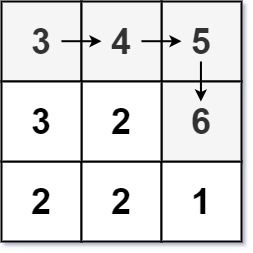
Input: matrix = [[3,4,5],[3,2,6],[2,2,1]]
Output: 4
Explanation: The longest increasing path is [3, 4, 5, 6]. Moving diagonally is not allowed.
Example 3:
Input: matrix = [[1]] Output: 1
Constraints:
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[i].length1 <= m, n <= 2000 <= matrix[i][j] <= 231 - 1
We design a function
The execution logic of the function
- If
$(i, j)$ has been visited, directly return$\textit{f}(i, j)$ ; - Otherwise, search
$(i, j)$ , search the coordinates$(x, y)$ in four directions. If$0 \le x < m, 0 \le y < n$ and$matrix[x][y] > matrix[i][j]$ , then search$(x, y)$ . After the search is over, update$\textit{f}(i, j)$ to$\textit{f}(i, j) = \max(\textit{f}(i, j), \textit{f}(x, y) + 1)$ . Finally, return$\textit{f}(i, j)$ .
The time complexity is
Similar problems:
class Solution:
def longestIncreasingPath(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> int:
@cache
def dfs(i: int, j: int) -> int:
ans = 0
for a, b in pairwise((-1, 0, 1, 0, -1)):
x, y = i + a, j + b
if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n and matrix[x][y] > matrix[i][j]:
ans = max(ans, dfs(x, y))
return ans + 1
m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
return max(dfs(i, j) for i in range(m) for j in range(n))class Solution {
private int m;
private int n;
private int[][] matrix;
private int[][] f;
public int longestIncreasingPath(int[][] matrix) {
m = matrix.length;
n = matrix[0].length;
f = new int[m][n];
this.matrix = matrix;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
ans = Math.max(ans, dfs(i, j));
}
}
return ans;
}
private int dfs(int i, int j) {
if (f[i][j] != 0) {
return f[i][j];
}
int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k];
int y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && matrix[x][y] > matrix[i][j]) {
f[i][j] = Math.max(f[i][j], dfs(x, y));
}
}
return ++f[i][j];
}
}class Solution {
public:
int longestIncreasingPath(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();
int f[m][n];
memset(f, 0, sizeof(f));
int ans = 0;
int dirs[5] = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
function<int(int, int)> dfs = [&](int i, int j) -> int {
if (f[i][j]) {
return f[i][j];
}
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && matrix[x][y] > matrix[i][j]) {
f[i][j] = max(f[i][j], dfs(x, y));
}
}
return ++f[i][j];
};
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
ans = max(ans, dfs(i, j));
}
}
return ans;
}
};func longestIncreasingPath(matrix [][]int) (ans int) {
m, n := len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
f := make([][]int, m)
for i := range f {
f[i] = make([]int, n)
}
dirs := [5]int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
var dfs func(i, j int) int
dfs = func(i, j int) int {
if f[i][j] != 0 {
return f[i][j]
}
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
x, y := i+dirs[k], j+dirs[k+1]
if 0 <= x && x < m && 0 <= y && y < n && matrix[x][y] > matrix[i][j] {
f[i][j] = max(f[i][j], dfs(x, y))
}
}
f[i][j]++
return f[i][j]
}
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
ans = max(ans, dfs(i, j))
}
}
return
}function longestIncreasingPath(matrix: number[][]): number {
const m = matrix.length;
const n = matrix[0].length;
const f: number[][] = Array(m)
.fill(0)
.map(() => Array(n).fill(0));
const dirs = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1];
const dfs = (i: number, j: number): number => {
if (f[i][j] > 0) {
return f[i][j];
}
for (let k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
const x = i + dirs[k];
const y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && matrix[x][y] > matrix[i][j]) {
f[i][j] = Math.max(f[i][j], dfs(x, y));
}
}
return ++f[i][j];
};
let ans = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
ans = Math.max(ans, dfs(i, j));
}
}
return ans;
}