-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 5
MARTE NFP Types Reference
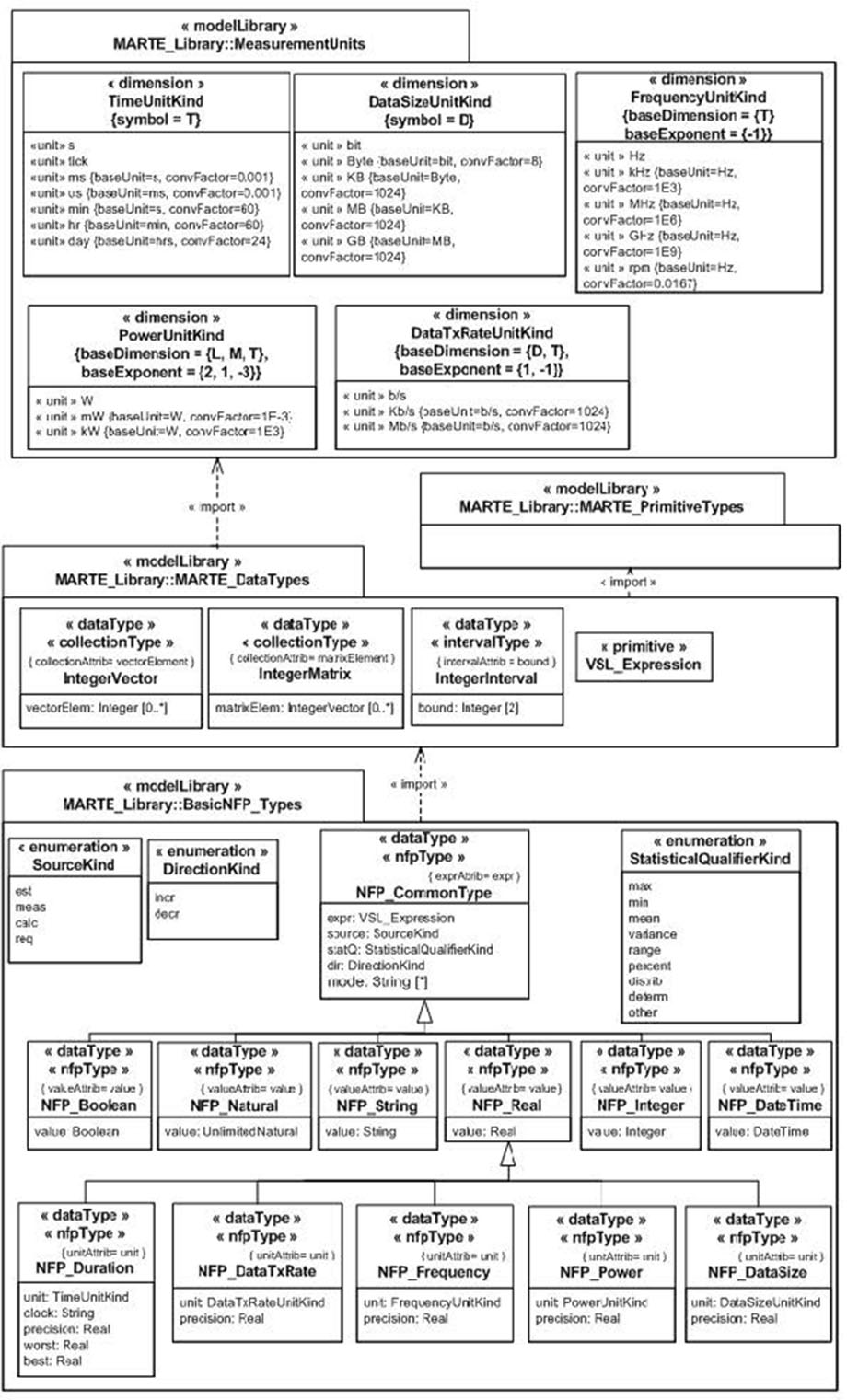
Here we describe the NFP Types of the MARTE standard that are of common use in the DICE Simulation Tool.
Parts of this text may describe usages that are more restricted than the normative specification. Specifically, parts striked out describe normative usages specified in the MARTE standard that are not implemented or are not guaranteed to work properly.
We highlight these unimplemented parts of the standard since their use may lead to unexpected behavior of the DICE transformations.
Literals: est (estimated), req (required), meas (measured), calc (calculated).
Literals: max (maximum), min (minimum), mean (mean), variance (variance), range (range), percent (percentile), distrib (distribution), determ (deterministic), other (other).
Literals: tick (ticks), s (seconds), ms (miliseconds), us (microseconds), min (minutes), hr (hours), day (days).
Literals: Hz, kHz, MHz, GHz, rpm
-
expr: VSL_Expression [0..1] A VSL expression.- Only arithmetic expressions involving basic types and variables are supported.
- Expressions must be evaluatable to a basic type (e.g., Integer, Real, etc.).
-
source: SourceKind [0..1]-
empty (
null): The value (either the value of theexprexpression or thevalueof a subtype) should be treated as an input value for the simulation (e.g.est). -
est: The value (either the value of theexprexpression or thevalueof a subtype) should be treated as an input value for the simulation. -
req: The property is a requirement and should be calculated as an output parameter. The obtained value must be compared with the value specified in the model (either thevalueor theexprexpression). -
meas: The value, that has been obtained from a measure of a real execution of the system, should be treated as an input value for the simulation. -
calc: The property should be calculated and considered as an output parameter
-
empty (
-
statQ: StatisticalQualifierKind [0..1]-
empty (
null): The value of the property is the mean value. -
mean: The value of the property is the mean value. max,min,mean,variance,range,percent,distrib,determ,other
-
empty (
dir: DirectionKind [0..1]mode: String[*]
-
value: Integer [0..1]- If
valueis empty, anexprexpression must be defined. - If
valueis not empty,exprmust be empty.
- If
-
value: Real [0..1]- If
valueis empty, anexprexpression must be defined. - If
valueis not empty,exprmust be empty.
- If
-
unit: TimeUnitKind [0..1] Attribute representing the measurement unit.-
empty (
null): The value (either thevalueor the value of theexpr) is expressed ins(seconds). -
s: The property is expressed in seconds. -
tick,ms,us,min,hr,day
-
empty (
clock: String [0..1]precision: Real [0..1]worst: Real [0..1]best: Real [0..1]
-
unit: FrequencyUnitKind [0..1] Attribute representing the frequency unit.-
empty (
null): The value (either thevalueor the value of theexpr) is expressed inHz. -
Hz: The property is expressed in Hertz (number of cycles -i.e. processed jobs- per unit time -seconds-). -
kHz,MHz,GHz,rpm
-
empty (
precision: Real [0..1]
-
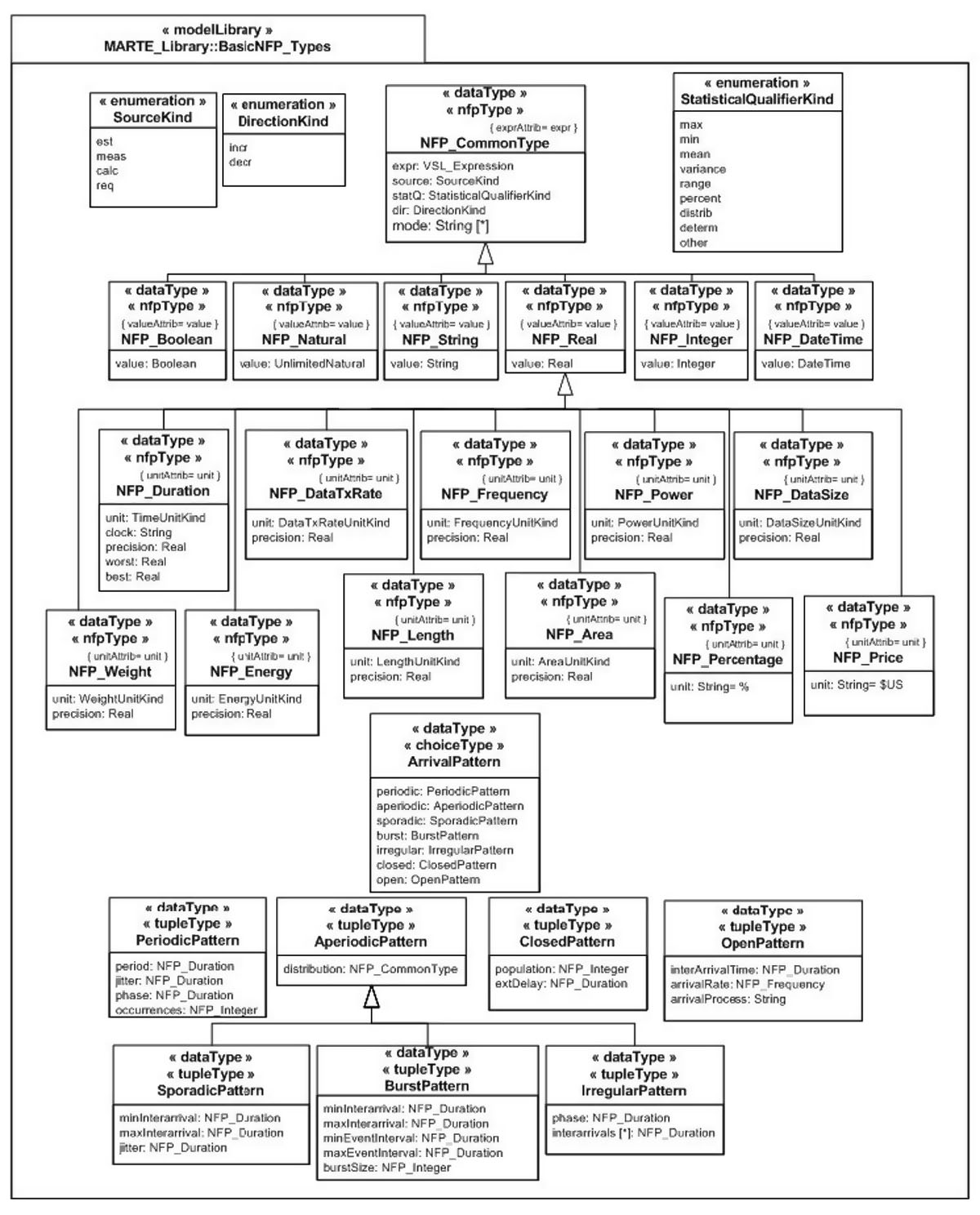
closed: ClosedPattern [0..1] It describes a workload characterized by a fixed number of active or potential users or jobs that cycle between executing the scenario. -
open: OpenPattern [0..1] It describes a workload that is modeled as a stream of requests that arrive at a given rate in some predetermined pattern (such as Poisson arrivals). periodic: PeriodicPattern [0..1]aperiodic: AperiodicPattern [0..1]sporadic: SporadicPattern [0..1]burst: BurstPattern [0..1]irregular: IrregularPattern [0..1]
-
population: NFP_Integer [0..1] The size of the workload (number of system users). -
extDelay: NFP_Duration [0..1] The delay between the end of one response and the start of the next for each member of the population of system users.
interArrivalTime: NFP_Duration [0..1]-
arrivalRate: NFP_Frequency [0..1] The average rate of arrivals. arrivalProcess: String [0..1]