React Native Brownfield provides first-class support for Swift.
It is possible to build react-native-brownfield with use_frameworks! directive in CocoaPods as long as React can be built this way.
| React Native version | use_frameworks! compatibility |
|---|---|
| <= 0.59.X | Compatible |
| 0.60.X | Not compatible |
| 0.61.0-rc.0 | Not compatible |
Please reffer to this issue to learn more about use_frameworks! state in React Native.
Until this behavior is fixed, you can access react-native-brownfield API in Swift via Bridging Header.
The library is meant to work with auto linking. In case you can't use this feature, please check out the following options:
react-native link
Run the following command in your terminal: react-native link @callstack/react-native-brownfieldCocoaPods
Add the following line to your `Podfile`: pod 'ReactNativeBrownfield', :path => '../node_modules/@callstack/react-native-brownfield/ios'Manually link the library on iOS
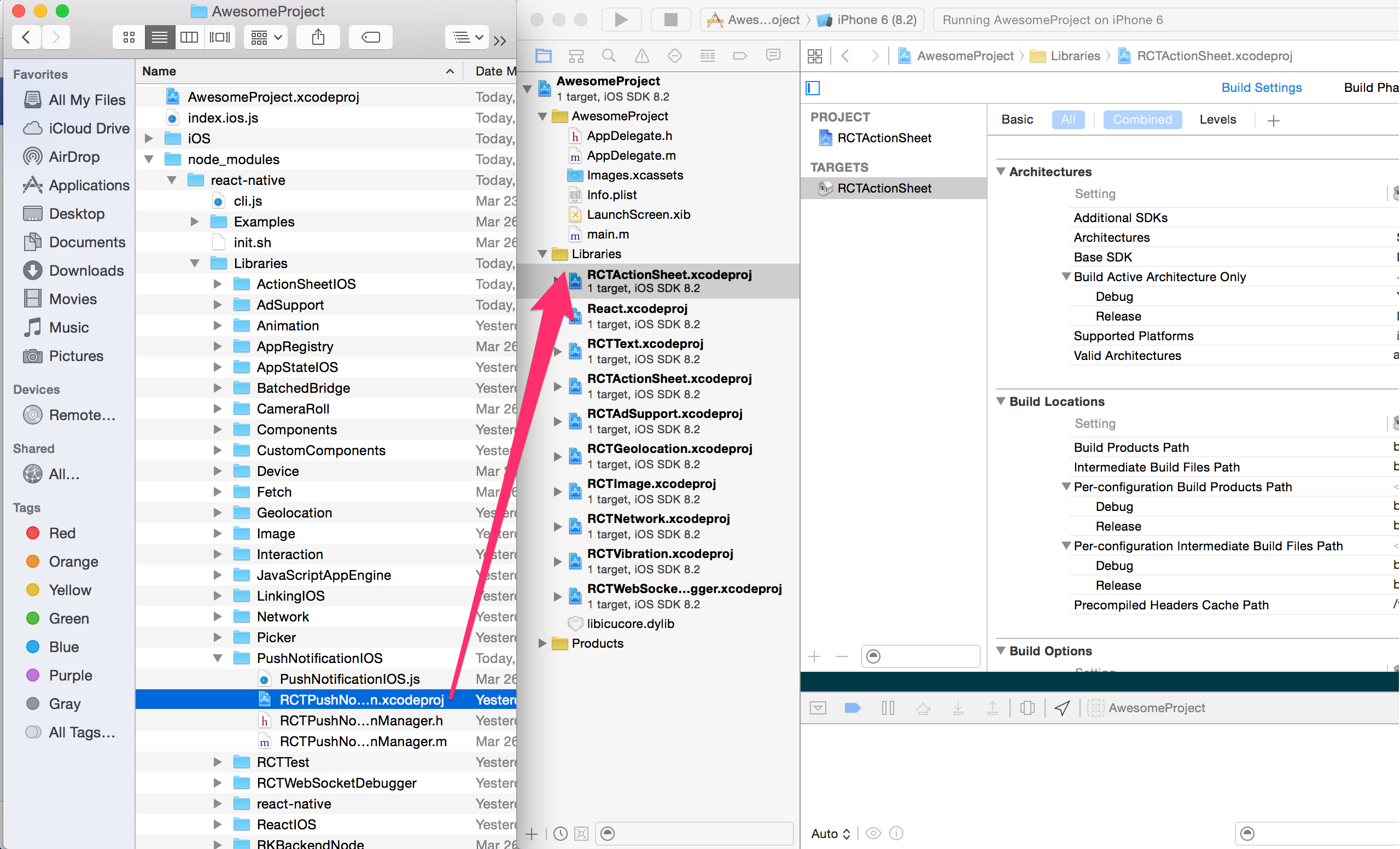
Drag ReactNativeBrownfield.xcodeproj to your project on Xcode (usually under the Libraries group on Xcode):
Click on your main project file (the one that represents the .xcodeproj) select Build Phases and drag the static library from the Products folder inside the Library you are importing to Link Binary With Libraries (or use the + sign and choose library from the list):
You can import the object from:
import ReactNativeBrownfieldStatics:
shared()
A singleton that keeps an instance of ReactNativeBrownfield object.
Examples:
ReactNativeBrownfield.shared()Properties:
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| bridge | RCTBridge | nil | Launch options, typically passed from AppDelegate. |
| entryFile | NSString | index | Path to JavaScript root. |
| fallbackResource | NSString | nil | Path to bundle fallback resource. |
| bundlePath | NSString | main.jsbundle | Path to bundle fallback resource. |
Methods:
startReactNative
Starts React Native, produces an instance of a bridge. You can use it to initialize React Native in your app.
Params:
| Param | Required | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| onBundleLoaded | No | () -> void | Callback invoked after JS bundle is fully loaded. |
| launchOptions | No | NSDictionary | Launch options, typically passed from AppDelegate. |
Examples:
ReactNativeBrownfield.shared().startReactNative() ReactNativeBrownfield.shared().startReactNative {
print("React Native started")
} ReactNativeBrownfield.shared().startReactNative({
print("React Native started")
}, launchOptions)A view controller that's rendering RCTRootView within its bounds. It automatically uses an instance of a bridge created in startReactNative method. It works well with exposed JavaScript module. It's the simplest way to embed React Native into your navigation stack.
You can import it from:
import ReactNativeBrownfieldConstructors:
ReactNativeViewController(moduleName: moduleName, initialProperites:initialProperties)
| Param | Required | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| moduleName | Yes | NSString | Name of React Native component registered to AppRegistry. |
| initialProperties | No | NSString | Initial properties to be passed to React Native component. |
Examples:
ReactNativeViewController(moduleName: "ReactNative") ReactNativeViewController(moduleName: "ReactNative", initialProperites:["score": 12])You can find an example app here.