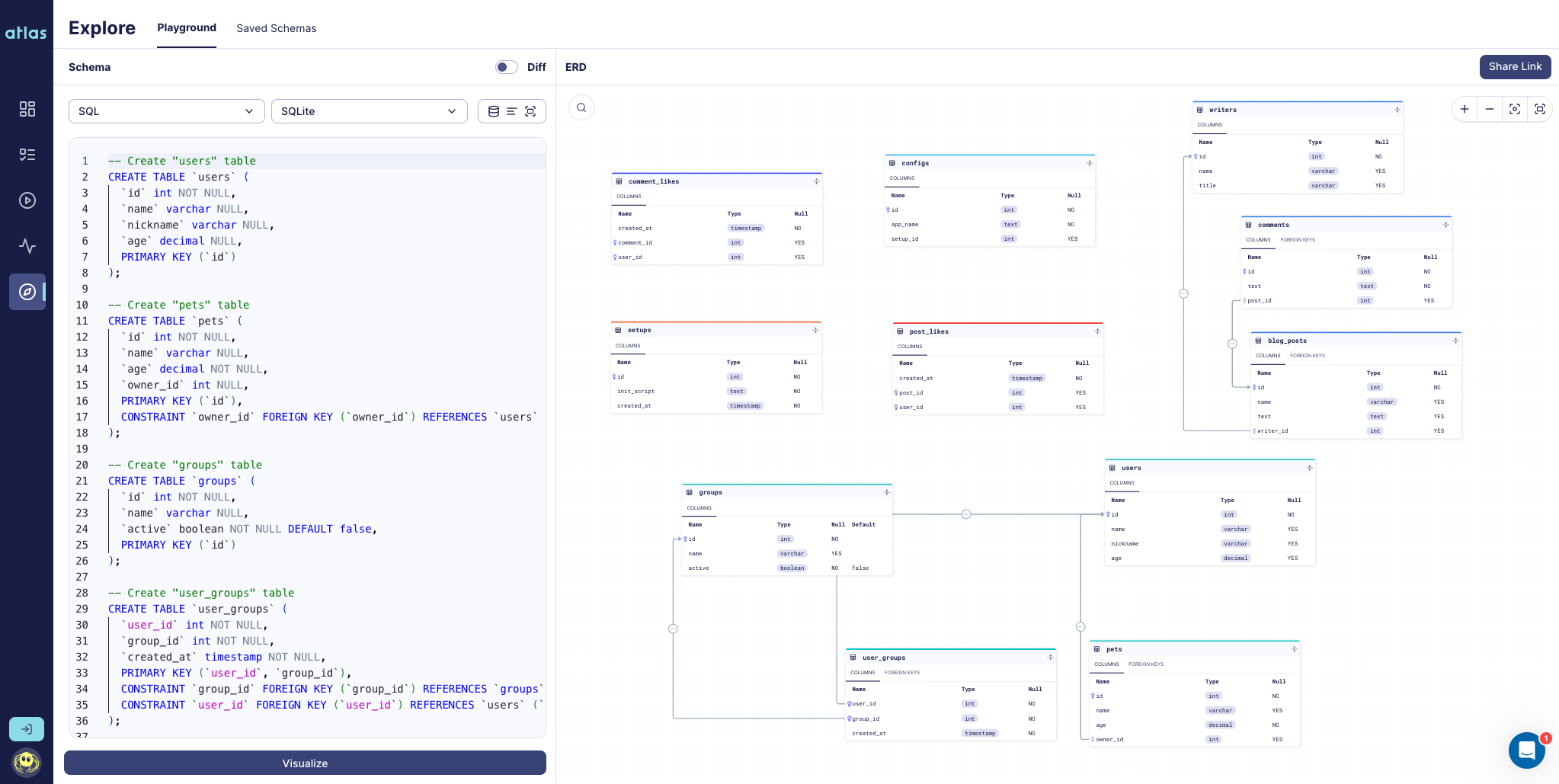
Load Django models into an Atlas project.
- Declarative migrations - use a Terraform-like
atlas schema apply --env djangoto apply your Django schema to the database. - Automatic migration planning - use
atlas migrate diff --env djangoto automatically plan a migration from the current database version to the Django schema.
Install Atlas for macOS or Linux by running:
curl -sSf https://atlasgo.sh | shSee atlasgo.io for more installation options.
Install the provider by running:
pip install atlas-provider-djangoAdd the provider to your Django project's INSTALLED_APPS in settings.py:
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...,
'atlas_provider_django',
...
]In your project directory, create a new file named atlas.hcl with the following contents:
data "external_schema" "django" {
program = [
"python",
"manage.py",
"atlas-provider-django",
"--dialect", "mysql" // mariadb | postgresql | sqlite | mssql
// if you want to only load a subset of your app models, you can specify the apps by adding
// "--apps", "app1", "app2", "app3"
]
}
env "django" {
src = data.external_schema.django.url
dev = "docker://mysql/8/dev"
migration {
dir = "file://migrations"
}
format {
migrate {
diff = "{{ sql . \" \" }}"
}
}
}You can use the atlas schema inspect command to visualize your Django schema in Atlas Cloud.
atlas schema inspect -w --env django --url env://srcYou can use the atlas schema apply command to plan and apply a migration of your database to your current Django schema.
This works by inspecting the target database and comparing it to the Django Apps models and creating a migration plan.
Atlas will prompt you to confirm the migration plan before applying it to the database.
atlas schema apply --env django -u "mysql://root:password@localhost:3306/mydb"Where the -u flag accepts the URL to the
target database.
Atlas supports a versioned migrations
workflow, where each change to the database is versioned and recorded in a migration file. You can use the
atlas migrate diff command to automatically generate a migration file that will migrate the database
from its latest revision to the current Django schema.
atlas migrate diff --env django The provider supports the following databases:
- MySQL
- MariaDB
- PostgreSQL
- SQLite
- Microsoft SQL Server
Please report any issues or feature requests in the ariga/atlas repository.
This project is licensed under the Apache License 2.0.