| page_title |
|---|
Provisioning Databricks on AWS with PrivateLink |
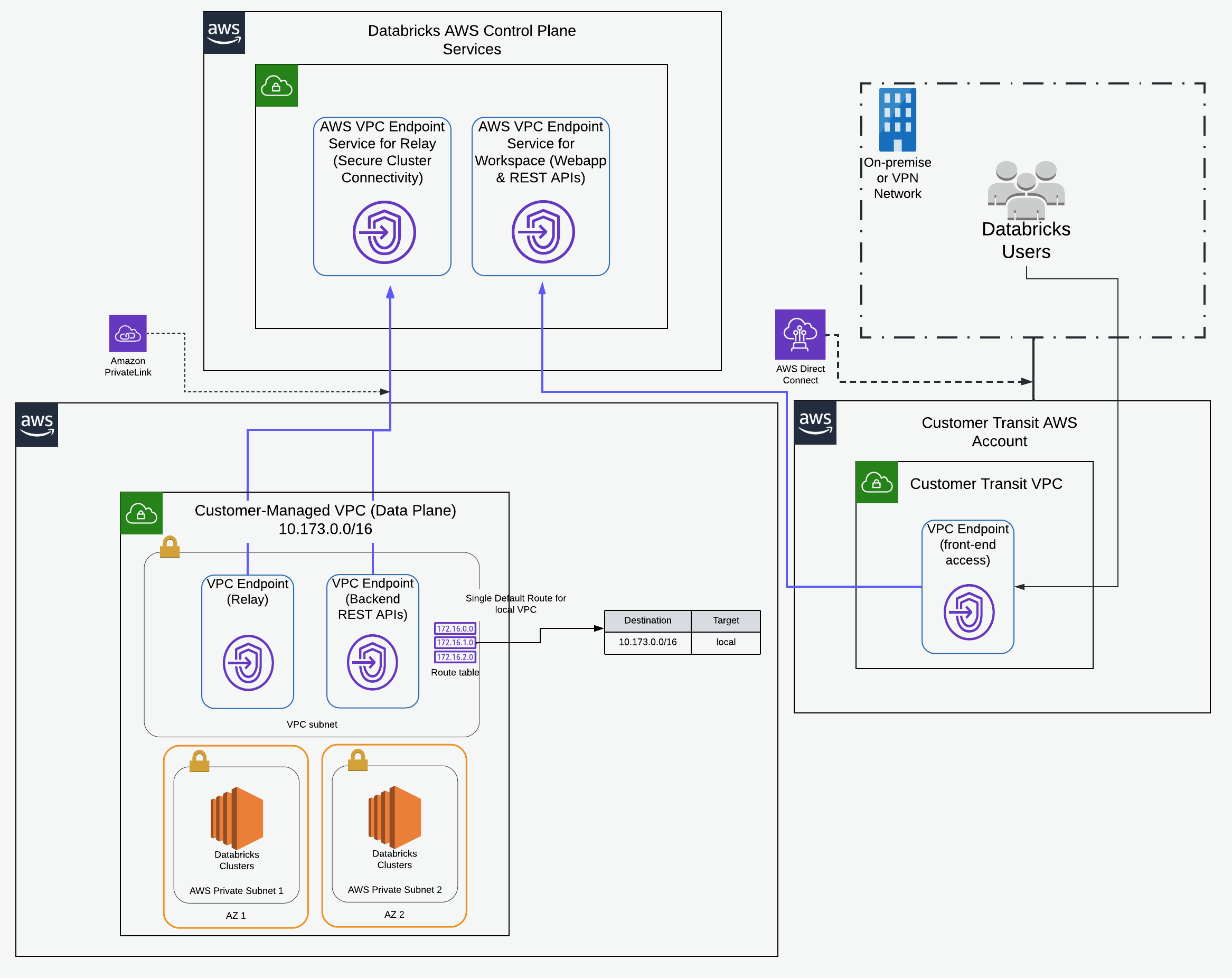
Databricks PrivateLink support enables private connectivity between users and their Databricks workspaces and between clusters on the data plane and core services on the control plane within the Databricks workspace infrastructure. You can use Terraform to deploy the underlying cloud resources and the private access settings resources automatically using a programmatic approach. This guide assumes you are deploying into an existing VPC and have set up credentials and storage configurations as per prior examples, notably here.
This guide uses the following variables in configurations:
client_id:application_idof the service principal, see instructionclient_secret: the secret of the service principal.databricks_account_id: The numeric ID for your Databricks account. When logged in, it appears in the top right corner of the page.vpc_id- The ID for the AWS VPC.region- AWS region.security_group_id- Security groups set up for the existing VPC.subnet_ids- Existing subnets used for the customer-managed VPC.workspace_vpce_service- Choose the region-specific service endpoint from this table.relay_vpce_service- Choose the region-specific service from this table.vpce_subnet_cidr- CIDR range for the subnet chosen for the VPC endpoint.tags- tags for the Private Link backend setup.root_bucket_name- AWS bucket name required for databricks_mws_storage_configurations.cross_account_arn- AWS EC2 role ARN required for databricks_mws_credentials.
This guide is provided as-is, and you can use this guide as the basis for your custom Terraform module.
This guide takes you through the following high-level steps to set up a workspace with AWS PrivateLink:
- Initialize the required providers
- Configure AWS objects
- A subnet dedicated to your VPC relay and workspace endpoints
- A security group dedicated to your VPC endpoints
- Two AWS VPC endpoints
- Workspace Creation
To set up account-level resources, initialize provider with mws alias. See provider authentication for more details.
terraform {
required_providers {
databricks = {
source = "databricks/databricks"
}
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
version = "~> 4.15.0"
}
}
}
provider "aws" {
region = var.region
}
provider "databricks" {
alias = "mws"
host = "https://accounts.cloud.databricks.com"
account_id = var.databricks_account_id
client_id = var.client_id
client_secret = var.client_secret
}Define the required variables:
variable "databricks_account_id" {}
variable "client_id" {}
variable "client_secret" {}
variable "root_bucket_name" {}
variable "cross_account_arn" {}
variable "vpc_id" {}
variable "region" {}
variable "security_group_id" {}
variable "subnet_ids" { type = list(string) }
variable "workspace_vpce_service" {}
variable "relay_vpce_service" {}
variable "vpce_subnet_cidr" {}
variable "private_dns_enabled" { default = true }
variable "tags" { default = {} }
locals {
prefix = "private-link-ws"
}Create new storage configuration with databricks_mws_storage_configurations:
resource "databricks_mws_storage_configurations" "this" {
provider = databricks.mws
account_id = var.databricks_account_id
bucket_name = var.root_bucket_name
storage_configuration_name = "${local.prefix}-storage"
}Create new cross-account credentials with databricks_mws_credentials:
resource "databricks_mws_credentials" "this" {
provider = databricks.mws
account_id = var.databricks_account_id
role_arn = var.cross_account_arn
credentials_name = "${local.prefix}-credentials"
}In this section, the goal is to create the two back-end VPC endpoints:
- Back-end VPC endpoint for SSC relay
- Back-end VPC endpoint for REST APIs
-> Note If you want to implement the front-end VPC endpoint as well for the connections from the user to the workspace front-end, use the transit (bastion) VPC that terminates your AWS Direct Connect or VPN gateway connection or one that is routable from such a transit (bastion) VPC. Once the front-end endpoint is created, it can be supplied to databricks_mws_networks resource using vpc_endpoints argument. Use the databricks_mws_private_access_settings resource to control which VPC endpoints can connect to the UI or API of any workspace that attaches this private access settings object.
The first step is to create the required AWS objects:
- A subnet dedicated to your VPC endpoints.
- A security group dedicated to your VPC endpoints and satisfying required inbound/outbound TCP/HTTPS traffic rules on ports 443 and 6666, respectively.
For workspace with compliance security profile, you need additionally allow bidirectional access to port 2443 for FIPS connections. The ports to allow bidirectional access are 443, 2443, and 6666.
data "aws_vpc" "prod" {
id = var.vpc_id
}
// this subnet houses the data plane VPC endpoints
resource "aws_subnet" "dataplane_vpce" {
vpc_id = var.vpc_id
cidr_block = var.vpce_subnet_cidr
tags = merge(data.aws_vpc.prod.tags, {
Name = "${local.prefix}-${data.aws_vpc.prod.id}-pl-vpce"
})
}
resource "aws_route_table" "this" {
vpc_id = var.vpc_id
tags = merge(data.aws_vpc.prod.tags, {
Name = "${local.prefix}-${data.aws_vpc.prod.id}-pl-local-route-tbl"
})
}
resource "aws_route_table_association" "dataplane_vpce_rtb" {
subnet_id = aws_subnet.dataplane_vpce.id
route_table_id = aws_route_table.this.id
}Define security group for data plane VPC endpoint backend/relay connections:
data "aws_subnet" "ws_vpc_subnets" {
for_each = toset(var.subnet_ids)
id = each.value
}
locals {
vpc_cidr_blocks = [
for subnet in data.aws_subnet.ws_vpc_subnets :
subnet.cidr_block
]
}
resource "aws_security_group" "dataplane_vpce" {
name = "Data Plane VPC endpoint security group"
description = "Security group shared with relay and workspace endpoints"
vpc_id = var.vpc_id
dynamic "ingress" {
for_each = toset([
443,
2443, # FIPS port for CSP
6666,
])
content {
description = "Inbound rules"
from_port = ingress.value
to_port = ingress.value
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = concat([var.vpce_subnet_cidr], local.vpc_cidr_blocks)
}
}
dynamic "egress" {
for_each = toset([
443,
2443, # FIPS port for CSP
6666,
])
content {
description = "Outbound rules"
from_port = egress.value
to_port = egress.value
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = concat([var.vpce_subnet_cidr], local.vpc_cidr_blocks)
}
}
tags = merge(data.aws_vpc.prod.tags, {
Name = "${local.prefix}-${data.aws_vpc.prod.id}-pl-vpce-sg-rules"
})
}resource "aws_vpc_endpoint" "backend_rest" {
vpc_id = var.vpc_id
service_name = var.workspace_vpce_service
vpc_endpoint_type = "Interface"
security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.dataplane_vpce.id]
subnet_ids = [aws_subnet.dataplane_vpce.id]
private_dns_enabled = var.private_dns_enabled
depends_on = [aws_subnet.dataplane_vpce]
}
resource "aws_vpc_endpoint" "relay" {
vpc_id = var.vpc_id
service_name = var.relay_vpce_service
vpc_endpoint_type = "Interface"
security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.dataplane_vpce.id]
subnet_ids = [aws_subnet.dataplane_vpce.id]
private_dns_enabled = var.private_dns_enabled
depends_on = [aws_subnet.dataplane_vpce]
}
resource "databricks_mws_vpc_endpoint" "backend_rest_vpce" {
provider = databricks.mws
account_id = var.databricks_account_id
aws_vpc_endpoint_id = aws_vpc_endpoint.backend_rest.id
vpc_endpoint_name = "${local.prefix}-vpc-backend-${var.vpc_id}"
region = var.region
depends_on = [aws_vpc_endpoint.backend_rest]
}
resource "databricks_mws_vpc_endpoint" "relay" {
provider = databricks.mws
account_id = var.databricks_account_id
aws_vpc_endpoint_id = aws_vpc_endpoint.relay.id
vpc_endpoint_name = "${local.prefix}-vpc-relay-${var.vpc_id}"
region = var.region
depends_on = [aws_vpc_endpoint.relay]
}resource "databricks_mws_networks" "this" {
provider = databricks.mws
account_id = var.databricks_account_id
network_name = "${local.prefix}-network"
security_group_ids = [var.security_group_id]
subnet_ids = var.subnet_ids
vpc_id = var.vpc_id
vpc_endpoints {
dataplane_relay = [databricks_mws_vpc_endpoint.relay.vpc_endpoint_id]
rest_api = [databricks_mws_vpc_endpoint.backend_rest_vpce.vpc_endpoint_id]
}
}For a workspace to support any of the PrivateLink connectivity scenarios, the workspace must be created with an attached databricks_mws_private_access_settings resource.
The credentials ID, referenced below, is one of the attributes created as a result of configuring the cross-account IAM role, which Databricks uses to orchestrate EC2 resources. The credentials are created via databricks_mws_credentials. Similarly, the storage configuration ID is obtained from the databricks_mws_storage_configurations resource.
resource "databricks_mws_private_access_settings" "pas" {
provider = databricks.mws
account_id = var.databricks_account_id
private_access_settings_name = "Private Access Settings for ${local.prefix}"
region = var.region
public_access_enabled = true
}
resource "databricks_mws_workspaces" "this" {
provider = databricks.mws
account_id = var.databricks_account_id
aws_region = var.region
workspace_name = local.prefix
credentials_id = databricks_mws_credentials.this.credentials_id
storage_configuration_id = databricks_mws_storage_configurations.this.storage_configuration_id
network_id = databricks_mws_networks.this.network_id
private_access_settings_id = databricks_mws_private_access_settings.pas.private_access_settings_id
pricing_tier = "ENTERPRISE"
depends_on = [databricks_mws_networks.this]
}